* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 2 Polyphase induction motor File
Utility frequency wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Induction cooking wikipedia , lookup
Commutator (electric) wikipedia , lookup
Brushless DC electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Brushed DC electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Stepper motor wikipedia , lookup
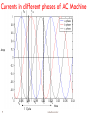
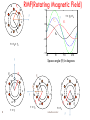
Chapter 2 Poly phase Induction Motor Prepared by:- Jaydeepsingh Chauhan Electrical Department SVBIT Gandhinagar Induction Motor •Most popular motor today in the low and medium horsepower range •Very robust in construction •Speed easily controllable using V/f or Field Oriented Controllers •Have replaced DC Motors in areas where traditional DC Motors cannot be used such as mining or explosive environments •Of two types depending on motor construction: Squirrel Cage or Slip Ring •Only Disadvantage: Most of them run with a lagging power factor 2 induction motor Construction of Induction Motor Stator Squirrel Cage Rotor Cut section Of Induction Motor Slip ring Rotor 3 induction motor AC Machine Stator ‘b’ phase axis 1200 1200 ‘a’ phase axis 1200 ‘c’ phase axis 4 induction motor Squirrel Cage Rotor 5 induction motor Slip Ring Rotor •The rotor contains windings similar to stator. •The connections from rotor are brought out using slip rings that are rotating with the rotor and carbon brushes that are static. 6 induction motor Currents in different phases of AC Machine t t 01 12 Amp t0 t1 1 Cycle 7 t2 t3 t4 time induction motor a Fc RMF(Rotating Magnetic Field) b’ c’ 1.5 Fa F 1 Fa c b t = t0= t4 F Fc 0.5 Fb a’ 0 Fb -0.5 t = t0= t4 -1 -1.5 -93 F Fb a c’ 8 Fc Fb b’ c a’ t = t1 113 216 Space angle () in degrees a c’ b 10 a b’ Fa F c b Fc t = t2 a’ b’ c’ c b t = t3 induction motor Fc a’ F Fb Torque Production in an Induction Motor •In a conventional DC machine field is stationary and the current carrying conductors rotate. •We can obtain similar results if we make field structure rotating and current carrying conductor stationary. •In an induction motor the conventional 3-phase winding sets up the rotating magnetic field(RMF) and the rotor carries the current carrying conductors. •An EMF and hence current is induced in the rotor due to the speed difference between the RMF and the rotor, similar to that in a DC motor. •This current produces a torque such that the speed difference between the RMF and rotor is reduced. 9 induction motor Slip in Induction Motor •However, this speed difference cannot become zero because that would stop generation of the torque producing current itself. •The parameter slip ‘s’ is a measure of this relative speed difference ns n s s ns s ns 120 f1 ; p # of poles p where ns,s,f1 are the speeds of the RMF in RPM ,rad./sec and supply frequency respectively n, are the speeds of the motor in RPM and rad./sec respectively •The angular slip frequency and the slip frequency at which voltage is induced in the rotor is given by 2 s , f 2 sf1 , E2 s 10 N2 s E1 N1 N1 Stator turns N2 Rotor turns induction motor