* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download AHSGE Math Vocabulary
Analytic geometry wikipedia , lookup
Rotation formalisms in three dimensions wikipedia , lookup
Technical drawing wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Approximations of π wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Area of a circle wikipedia , lookup
AHSGE Math Vocabulary
Items marked with * are extremely important
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
21.
22.
23.
24.
25.
26.
27.
Variable- symbol, usually a letter, that represents one or more numbers
*Absolute Value- a number’s distance from zero. There are no negatives. [ l-9l = 9 and l9l = 9]
Integer- positive or negative whole number.
Polynomial- a monomial or the sum of monomials.
Distributive Property- property that states you can distribute a number to a mathematical
sentence. Such as 3(4+9) is the same as 12+27
Denominator- bottom number in a fraction
Exponent- number that an integer is taken up to. As in 4 to the 2nd power (2 is the exponent)
Binomial- a polynomial with two terms
Monomial- an algebraic expression consisting of only one term
Factor- one of two or more quantities that divide a given quantity without a remainder.
Greatest Common Factor- greatest number that is a factor of two or more quantities.
Inequality- algebraic relation showing that a quantity is greater than or less than another
quantity
Equation- statement asserting the equality of two expressions that is usually represented by
symbols and separated into left and right sides by an equal sign
Coefficient- number or symbol multiplied with a variable or unknown quantity in an equation
Quadratic Equation- equations equipped with quantities of the second degree (x2+3x-2)
Trinomial- consisting of three terms
Linear Equation- Equation involving slopes of a line. These can be written in slope-intercept form
(y = mx + b) or standard form (Ax + By=C) or point-slope form [y-y1 = m (x-x1)] {these are located
on the reference page]
Intersection- the point of points where one line crosses another. A single point is listed as an
(x,y) coordinate pair
Ordered Pair- a set of numbers that represent a point in a plane or on a line (x,y)
*Function- each value assumed by one there is a value determined for the other. [Where x does
NOT repeat]. You can use the vertical-line test to see if a graph is a function.
*Domain- set of all possible values of an independent variable of a function [the set of x-values]
*Range- set of all values a given function may take on [the set of y-values]
Perimeter- the length around a given object or shape [add up the sides]
Circumference- the length around the edge of a circle (like the perimeter of a circle). Note: [The
formula is on the reference page]
Area- extent of a planar region or of the surface: measurement [the formulas are on the
reference page]
Volume- amount inside an object [the formulas are on the reference page]
*Diameter- a straight line segment passing through the center of a circle or sphere. A chord
through the middle of a circle. It runs from one edge to the other. Its twice the length of the
radius.
28. *Radius- line segment that joins the center of a circle with any point on its circumference. A
segment that connects the center of a circle to the edge. It’s half the diameter.
29. Rectangular Prism- a prism in the shape of a rectangle; like a shoebox [formulas for area and
volume can be found on the reference page]
30. Pi- approximately 3.14159, represented by the symbol
31. Slope- Vertical change over Horizontal change. Rise over run. [formula on reference page]
32. Midpoint- point in the middle of a line segment. It divides the segment into two parts of the
same length [the formula is on the reference page]
33. Coordinate- any set of two numbers (x,Y) used to determine the position of a point
34. Coordinate Plane- graph where lines and points are plotted
35. *Y-Intercept- the point where a line crosses the Y-axis. [Plug 0 in for x to find the y-intercept]
36. *X-Intercept- the point that a line crosses the X-axis. [Plug 0 in for y to find the x-intercept]
37. *Complementary Angles- two angles whose sum totals 90 degrees [The complement of a 40
degree angle is a 50 degree angle]
38. *Supplementary Angles- two angles whose sum totals 180 degrees [The supplement of a 120
degree angle is a 60 degree angle]
39. Transversal- a line that intersects a system of other lines
40. Parallel- two or more lines that do not intersect
41. Perpendicular- intersecting at or forming right angles
42. Adjacent Angles- angles that are beside each other that share a common ray and a common
vertex
43. Vertical Angles- angles that are straight up and down across from each other. Vertical angles are
congruent.
44. Linear Pair- when 2 adjacent angles together make a straight line with their non-common sides.
45. Pythagorean Theorem- a squared plus b squared equals c squared. Used in right triangles.
46. Radical- root of a quantity as indicated by the radical sign
47. Similar- having corresponding angles and line segments proportional. Same shape but not
necessarily the same size.
48. Scale Factor- ratio of 2 corresponding sides in figures that are similar.
49. Ratio- relationship between two quantities
50. Proportion- statement of equality between two ratios. You can cross multiply to solve
proportional problems.
51. Probability- the study of the chances of something happening. If you have a compound
probability using the word “and,” you add the two probabilities. If you have a compound
probability using the word “or,” you multiply the two probabilities.
52. *Mode- value that occurs most frequently. Most often distributed entry.
53. *Mean- average [the “Mean” teacher gave me my “average.]
54. *Median- number in middle after putting them in order from least to greatest [like the middle
of a road]
55. Direct Variation- numbers that vary directly with each other. These can be set up in a
proportion. [2 is to 6 as 8 is to 24].
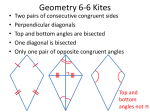
56. Quadrilateral – Polygon with 4 sides. Special quads include parallelograms, rectangles, squares,
trapezoids, rhombuses, and a kites.
57. Pentagon – a polygon with 5 sides
58. Hexagon– a polygon with 6 sides
59. Heptagon– a polygon with 7 sides
60. Octagon– a polygon with 8 sides
61. Nonagon-– a polygon with 9 sides
62. Decagon– a polygon with 10 sides
63. Regular Polygon – a polygon where all sides are congruent and all angles are congruent
64. Hints:
a. A square suggests there are 4 right angles and 4 equal sides
b. A cube suggests that all edges are equal
c. A parallelogram suggests that opposite sides are parallel and congruent
d. Twice means to multiply by 2
e. Half means to divide by 2 or multiply by one-half
f. Square (x2) means to multiply the number by itself
g. (a+b)2 must be re-written as (a+b)(a+b) and multiplied using F.O.I.L.
h. A shoebox suggests that you must use the formulas for rectangular prism
i. The hypotenuse is always opposite the right angle. It is the longest side of a right
triangle.
j. An isosceles triangle has two congruent sides and two congruent angles that are
opposite those sides.
k. Equilateral triangle’s angles are equal to 60 degrees each and all the sides are the same
size.
l. The Exterior angles of any polygon totals 360 degrees regardless of the number of sides.
m. When parallel lines are cut by a transversal, the following happens:
i. Alternate interior angles are congruent
ii. Alternate exterior angles are congruent
iii. Corresponding angles are congruent
iv. Same side interior (or consecutive interior angles) are supplementary
Test-taking strategies:
1) Plug in and test the answer choices to see if they make sense (plug and chug)
2) Convert radicals and fractions to decimals as needed
3) Process of elimination…..eliminate those that are obviously not the right answer
4) Look at the formula sheet for clues
5) Guesstimate the answer using logical reasoning and compare it to the answer choices