* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
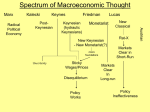
Download 1. Classical theory advocates ______ policy and Keynesian theory
Monetary policy wikipedia , lookup
Full employment wikipedia , lookup
Modern Monetary Theory wikipedia , lookup
Steady-state economy wikipedia , lookup
Edmund Phelps wikipedia , lookup
Money supply wikipedia , lookup
Ragnar Nurkse's balanced growth theory wikipedia , lookup
Phillips curve wikipedia , lookup
Non-monetary economy wikipedia , lookup
Fiscal multiplier wikipedia , lookup
Austrian business cycle theory wikipedia , lookup
Stagflation wikipedia , lookup
Post-war displacement of Keynesianism wikipedia , lookup
Chapter 26A Policy Disputes Using the Self-Correcting Aggregate Demand and Supply 1. Classical theory advocates __________ policy and Keynesian theory advocates __________ policy. a. nonintervention; intervention. b. active; nonstabilization. c. fixed wages; flexible wages. d. active; passive. ANS a. Correct. Classical theory argues that the economy self corrects and Keynesians argue that the government should influence aggregate demand. b. Incorrect. Classical theory advocates a passive role for government and Keynesian theory is based on active government stabilization. c. Incorrect. Classical theory is based on flexible wages and Keynesian theory is based on fixed wages. d. Incorrect. Classical theory is based on a passive role for the government and Keynesian theory is based on an active role. 2. If the economy is in short-run disequilibrium, an economist following classical theory would advocate that the Federal Reserve make appropriate changes in the a. money supply. b. reserve requirement. c. federal funds rate. d. none of the above. ANS a. Incorrect. Classical theory advocates a noninterventionist monetary policy. b. Incorrect. Classical theory advocates a noninterventionist monetary policy. c. Incorrect. Classical theory advocates a noninterventionist monetary policy. d. Correct. Classical theory advocates a noninterventionist monetary policy. 3. Assuming the economy is experiencing a recessionary gap, classical economists predict that a. wages will remain fixed. b. monetary policy should intervene. c. higher wages will shift the short-run aggregate supply curve leftward. d. lower wages will shift the short-run aggregate supply curve rightward. 1 ANS a. Correct. Classical economists predict that wages are flexible. b. Incorrect. Classical economists advocate that the Fed should take a passive role. c. Incorrect. Classical economists predict that lower wages will shift the short-run aggregate supply curve rightward. d. Correct. Classical economists predict that lower wages will shift the short-run aggregate supply curve rightward. 4. Assume the economy is operating at a real GDP above full-employment real GDP. Keynesian economists would prescribe which of the following policies? a. Nonintervention. b. Passive monetary policy. c. Contractionary. d. Expansionary. ANS a. Incorrect. Keynesians advocate interventionist government policy. b. Incorrect. Keynesian theory advocates active monetary policy. c. Correct. Keynesians advocate contractionary government policy, such as decrease in government spending, increase in taxes, and decrease in the money supply. d. Incorrect. Expansionary policy would be used for a recessionary gap and not an inflationary gap situation. 5. Assume the economy is experiencing an inflationary gap, Keynesian economists believe that a. flexible wages will restore full employment. b. the federal government should decrease spending to shift the aggregate demand curve leftward. c. the Federal Reserve should lower the interest rate. d. the federal government should increase spending to shift the aggregate demand curve rightward. ANS a. Incorrect. Classical theory is based on flexible wages. b. Correct. Keynesian economics advocates an active role for the federal government. c. Incorrect. A higher interest rate is required to slow economy and reduce inflation. d. Incorrect. To reduce inflation, the federal government should decrease spending. 6. Assume the economy is in short-run equilibrium at a real GDP below its potential real GDP. According to Keynesian theory, which of the following policies should be followed? a. The Federal Reserve should increase the money supply. b. The federal government should increase spending. c. The federal government should do nothing because the economy will self correct to potential real GDP. d. All of the answers are correct. 2 ANS a. Incorrect. An increase in the money supply shifts the aggregate demand curve (AD) leftward and move the economy further away from potential real GDP. b. Correct. An increase in federal government spending (G) shifts the aggregate demand curve (AD) rightward toward potential real GDP. c. Incorrect. Keynesian theory argues that the economy will not self correct without government intervention. 7. A policy to do nothing and allow the economy to self-correct or adjust without interference from the federal government is also called a(an) _______________ policy a. nonintervention b. active c. stabilization d. fixed rule a. Correct. This is a passive role in which the federal government does not use taxation and/or spending to control the economy. b. Incorrect. This is an active role in which the federal government uses taxation and/ or spending to control the economy. c. Incorrect. This is an active role in which the federal government uses taxation and/ or spending to control the economy. d. Incorrect.This is a passive role monetarist prescription for the Fed and not the federal government. 8. Assume the economy is experiencing a recessionary gap. Keynesian economists would support which of the following policies? a. Nonstabilization b. Expansionary c. Nonintervention d. Fixed wage a. Incorrect. Keynesian economists advocate an active role (stabilization) in which the federal government uses taxation and/ or spending to control the economy. b. Correct. Keynesian economists advocate an active role in which the federal government uses taxation and/ or spending to control the economy. c. Incorrect. Keynesian economists advocate an active role in which the federal government uses taxation and/ or spending to control the economy. d. Incorrect. Keynesian economists believe in fixed wages and prices, but this is not a spending and tax policy. 9. Assuming the economy is in a recession, Keynesian economists predict that a. wages will remain fixed. b. monetary policy will sell government securities. c. higher wages will shift the short-run aggregate supply curve leftward. d. lower wages will shift the short-run aggregate supply curve rightward. 3 ANS a. Correct. Keynesian economists believe in fixed wages and prices during a recession. b. Incorrect. During a recession, Keynesians advocate that the Fed increase the money supply by buying government securities. c. Incorrect. Keynesians believe that the short-run aggregate supply curve does not shift during a recession. d. Incorrect. Keynesians believe that the short-run aggregate supply curve does not shift during a recession. 10. Assume the economy is in short-run equilibrium at a real GDP above its potential real GDP. According to classical theory, which of the following policies should be followed? a. The Federal Reserve should use open market operations and buy U.S. government securities. b. The Federal Reserve should not follow a fixed rule. c. The federal government should cut taxes. d. Fiscal policy and monetary policy should not be activist. ANS a. Incorrect. Monetarists (classical theory) advocate that the Fed follow a fixed rule and increase the money supply by a constant amount. b. Incorrect. Monetarists (classical theoy) advocate that the Fed follow a fixed rule and increase the money supply by a constant amount. c. Incorrect. Classical economist do not advocate cutting taxes to restore the economy to full employment. d. Correct. Classical economists do not advocate managing by changing the levels of taxation federal government spending. 11. Assume the economy is experiencing an inflationary gap, classical economists believe that a. flexible wages will restore full employment. b. the federal government should decrease spending to shift the aggregate demand curve leftward. c. the Federal Reserve should lower the interest rate. d. the federal government should increase spending to shift the aggregate demand curve rightward. ANS a. Correct. Classical economists believe that flexible wages and prices will restore an economy to full employment. b. Incorrect. Classical economists do not advocate managing by changing the levels of taxation or federal government spending. c. Incorrect. Monetarists (classical economists) do not believe the Fed should attempt to manage the economy by lowering the interest rate. d. Incorrect. Classical economists do not advocate managing by changing the levels of taxation or federal government spending. 4 Exhibit A.3 Policy Alternatives 12. In part (a) of Exhibit A.3, the economy is initially in short-run equilibrium at real GDP level Y1 and price level P2. Classical theory argues a. the federal government must shift AD1 to AD2 as shown in panel (b). b. the federal government must shift SRAS1 to SRAS2. c. that SRAS1 will shift to SRAS2 without government intervention. d. that AD1 will shift to AD2 without government intervention. ANS a. Incorrect. Classical theory argues that government actions to increase aggregate demand are unnecessary and only increases the price level. b. Incorrect. This result occurs over time because competition among unemployed workers reduces the wage rate, and not because of government actions. c. Correct. This result occurs over time because competition among unemployed workers reduces the wage rate without government intervention. d. Incorrect. Classical theory does not argue that the aggregate demand curve will automatically shift to restore full employment. 13. Assume that the economy depicted in partl (a) of Exhibit A.3 is in short-run equilibrium with AD1 and SRAS1. If the economy is left to correct itself according to classical theory a. wages will fall as long as real GDP is above Yp. b. lower wages will result in a shift from SRAS1 to SRAS2. c. long-run equilibrium will be established at Yp and P3. d. all of the above will take place. 5 ANS a. Incorrect. If real GDP exceeds Yp , then wages will rise and shift SRAS2 to SRAS1. b. Correct. Competition from unemployed workers results in lower wages. c. Incorrect. A recessionary gap after adjustment results in long-run equilibrium at P1, Yp. d. Incorrect. Answers a. and c. do not take place, but answer b is true. 14. In part (b) of Exhibit A.3, the economy is initially in short-run equilibrium at real GDP level Y1 and price level P2. If the government decides to intervene, it would a. increase taxes. b. decrease the money supply. c. increase the level of government spending for goods and services. d. decrease the level of government spending for goods and services. ANS a. Incorrect. A tax increase decreases the aggregate demand curve (AD1) rather than shifts the aggregate demand curve from AD1 to AD2. b. Incorrect. c. Correct. Increasing government spending (G) shifts the aggregate demand curve from AD1 to AD2 and full-employment is achieved at P3, Yp (potential GDP). d. Incorrect. Decreasing government spending (G) decreases the aggregate demand curve (AD) rather than shifting it from AD1 to AD2. 15. Assume that the economy depicted in part (b) of Exhibit A.3 is in short-run equilibrium with AD1 and SRAS1. Keynesian theory argues a. nominal wages will fall as long as employment remains above the natural level of unemployment. b. lower wages will result in a shift from SRAS1 to SRAS2. c. long-run equilibrium will be established at Yp and P1. d. government intervention must shift AD1 to AD2. ANS a. Incorrect. Nominal wages fall below the natural level of unemployment. b. Incorrect. This is classical theory, and not Keynesian theory. c. Incorrect. This is classical theory, and not Keynesian theory. d. Correct. The Keynesian theory is to use activist government policies to increase aggregate demand from AD1 to AD2. 6