* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download G1.4 notes
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
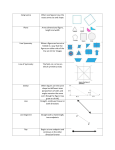
1.4 – Angle Measure A ray is a part of a line. It has one endpoint and extends indefinitely in one direction. Rays are named stating the endpoint first and then any other point on the ray. The figure shows ray EF, which can be symbolized as EF . If you choose a point on a line, that point determines exactly two rays called opposite rays. Line m is separated into two opposite rays, PQ and PR . Point P is the common endpoint of those rays. PQ and PR are collinear rays. An angle is formed by two noncollinear rays that have a common endpoint. The rays are called sides of the angle. The common endpoint is the vertex. KEY CONCEPT – Angle Words An angle is formed by two noncollinear rays that have a common endpoint. Symbols A BAC CAB 4 Model An angle divides a plane into three distinct parts. o Points A, D and E lie on the angle. o Points C and B lie in the interior of the angle. o Points F and G lie in the exterior of the angle. Example 1 – a. Name all angles that have B as a vertex. b. Name the sides of 5 . c. Write another name for 6 . KEY CONCEPT – Classify Angles Name Measure Model right angle acute angle obtuse angle mA 90 mB 90 90 mC 180 Example 2 – Classify each angle as right, acute or obtuse. a. TYV b. WYT c. TYU KEY CONCEPT – Congruent Angles Words Angles that have the same Model measure are congruent angles. Arcs on the figure indicate which angles are congruent. Symbols NMP QMR Example 3 – Find mGBH and mHCI if GBH HCI , mGBH 2 x 5 , and mHCI 3x 10 . A ray that divides an angle into two congruent angles is called an angle bisector. If PQ is the angle bisector of RPS , then point Q lies in the interior of RPS , and RPQ QPS . In the figure, mRPS mRPQ mQPS . L5 – pg 36 (9-12, 17-20 & 25-30)