* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download A battery
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
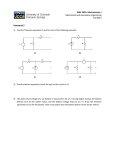
Honors Voltage Introduction Electric Potential Energy Charges obtain electric potential energy just like objects gain gravitational potential energy. What do you have to do to give an object gravitational potential energy? Recall: = Fd and W= In the same way, charge can gain electric potential energy. When a charge is placed in an electric field it experiences an electric ____________ (similar to how an object experiences a gravitational force). If an outside force displaces the charge in the opposite direction from that of the electric force then the charge ___________ electric potential energy. Therefore, ____________ causes a change in ________________________________. Electric Potential (V) – – A test charge has a value of 0 at the negative terminal of a battery – the positive terminal on a 6V battery is 6V higher in electric potential than the negative terminal - relates the distance a test charge is from a source charge o same distance, same potential Voltage Voltage (V) (electric potential difference) is _____________________________________________. - measured in ________________. - Equation: Ex: When 1 Coulomb of charge moves from the negative to the positive terminal in a 6V battery the potential energy of the charge increases by __________. Ex: When 3 Coulombs of charge moves from the negative to the positive terminal in a 6V battery the potential energy of the charge increases by __________. - After the charge gets energy, what does it do with it? Voltage Outside the Battery The energy that the charge gets from the battery has to go somewhere. It gets used by a _________. So inside the battery the voltage ______________ but in the ____________ the voltage ___________. Picture of circuit: Questions: ____1. A battery a. causes charge to move. b. does work on charges. e. all of the above. c. gives the charges potential energy. d. converts chemical energy into electric potential energy. 2. When work is done on a positive charge to move it from a negative position to a positive position, potential energy _________ (increases, decreases) and electric potential _________ (increases, decreases). ____3. In the presence of an electric field a. work is done on charge. b. the charge moves. c. the charge gains or loses electric potential energy. d. all of the above. 4. The quantity electric potential difference (voltage) is defined as the amount of _____. a. change in electric potential energy c. change in potential energy per charge b. change in force acting upon a charge d. change in force per charge 5. You know work is done on the charge to cause a gain in potential energy while it is inside the battery. Where does the energy to do that work come from? 6. While outside the battery (the external part of the circuit) the energy the charge has could be converted into what types of energy? 7. A 9-volt battery will increase the potential energy of 0.5 coulombs of charge by ____ joules. 8. A ___-volt battery will increase the potential energy of 3 coulombs of charge by 18 joules. 9. An electron (-1.6x10-19 C) is in a AAA, 1.5 V battery. How much work is done on the electron while it is in the battery? 10. Use the diagram to the right in answering the next 3 questions. Compared to point D, point A is _____ electric potential. a. 12 V higher in b. 12 V lower in c. exactly the same d. ... impossible to tell 11. The electric potential energy of a charge is zero at point _____. 12. Energy is required to force a positive test charge to move ___. a. through the wire from point A to point B b. through the light bulb from point B to point C c. through the wire from point C to point D d. through the battery from point D to point A Need Extra Practice?: Go to http://www.physicsclassroom.com/Class/circuits/u9l1c.cfm Find the check understanding questions on the website and click “See Answer” to check your answers and get an explanation.