* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Test 2 review
Motive (algebraic geometry) wikipedia , lookup
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
Duality (projective geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Riemann–Roch theorem wikipedia , lookup
System of polynomial equations wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Algebraic variety wikipedia , lookup
Algebraic geometry wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Compass-and-straightedge construction wikipedia , lookup
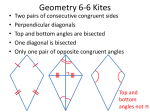
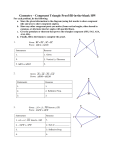
Name: _______________________________________________ Date: ____________ Period: _____ Geometry GT/Pre-AP Test # 2 Review (and POW #3, so this is worth +5 on the test!) Use this review to check your knowledge and skills in each section that will be covered by the test. Most of the examples below are odd-numbered exercises in the Geometry textbook, so you can check the answers for them in the back of the book. (Selected Answers start at page 831.) Work the examples on a separate sheet of paper. Students should be able to: Examples: 1-3 Points, Lines, and Planes Pages 19-21 Exercises: Apply the following postulates: 1-1. Through any _____ points there is exactly one _____. 1-2. If two lines intersect, then they intersect in exactly one _____. 1-3. If two planes intersect, then they intersect in exactly one _____. 1-4. Through _____ three points there is exactly one _____. # 55-60 (Use always, sometimes, or never to make a true statement) Identify and name the following in a diagram: a. Point b. Line c. Plane d. Collinear e. Noncollinear f. Coplanar g. Noncoplanar # 1, 3, 35 Matching (use the list on the left): AC is a EAD is a C is a E, B, C, and F are E, B, and C are E, B, and D are 1-4 Segments, Rays, Parallel Lines and Planes Identify and name the following in a diagram: a. Segment b. Ray c. Opposite rays d. Parallel lines e. Skew lines f. Intersecting lines g. Parallel planes h. Intersecting planes _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ & _____ _____ Page 25 Exercises: # 3, 5, 7, 10 Matching (use the list on the left): BA is a AB is a BA and BC are Use both this diagram and the above diagram. KJ and LP are KJ and KP are KJ and PN are GLPK and LMNP are GLPK and HMNJ are 1-5 Measuring Segments Page 33 Exercises: Use the Ruler Postulate to find the length of a segment given its coordinates. # 1, 3 Use the Segment Addition Postulate to set up algebraic equations and find the lengths of segments. # 9, 11 Use the definition of midpoint to set up algebraic equations and find the lengths of segments. # 12, 13 _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ 1-6 Measuring Angles Pages 40-41 Exercises: Use the Angle Addition Postulate to find the degree measure of angles. # 13, 14 Identify, name, and find the degree measure of the following types of angles in a diagram: a. Acute b. Right c. Obtuse d. Straight e. Congruent f. Vertical g. Complementary h. Supplementary i. Adjacent # 15, 21, 33 Set up and solve algebraic equations to find the degree measures of congruent angles, complementary angles, supplementary angles, etc. Matching (use the list on the left): EOA is _____ EOA and DOB are _____ COB is _____ EOA and AOB are _____ EOD and AOB are _____ DOC is _____ DOA is _____ DOC and COB are _____ COB and BOA are _____ # 43, 45, 47 1-7 Basic Constructions Pages 47-78 Exercises: Use a compass and straightedge to construct a: o Congruent segment o Congruent angle o Perpendicular bisector o Angle bisector # 3, 5, 7, 13 Show all construction marks; don't erase them after you're done. Use the definition of angle bisector to set up algebraic equations and find the degree measures of angles. # 11 2-5 Proving Angles Congruent Pages 112-113 Exercises: # 1, 3, 23, 25 Use the following theorems to find the degree measures of angles by setting up and solving algebraic equations: o Vertical Angles Theorem o Congruent Supplements Theorem o Congruent Complements Theorem Review of previous units Make conjectures based on a pattern. (1-1) Find counterexamples to prove a conditional false. (2-1) Write sentences in if-then form. (2-1) Given a Venn diagram, write a conditional statement. (2-1) Given a conditional statement, write its converse, inverse, contrapositive, and biconditional. (2-1, 2-2, 5-4) Apply the Law of Detachment and Law of Syllogism (2-3) Use the Properties of Equality to justify each step. (2-4) Use the distributive property and solve one-variable equations. Simplify square roots and fractions. Page 71 # 10 Page 118 # 21 Page 119 # 24 Page 753 # 15