* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download EI1204-Sensors and Measuring - Dhanalakshmi Srinivasan Group
Time-to-digital converter wikipedia , lookup
Spectral density wikipedia , lookup
Mechanical filter wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Chirp spectrum wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
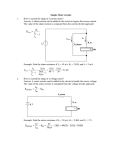
DHANALAKSHMI SRINIVASAN ENGINEERING COLLEGE PERAMBALUR-621212 DEPARTMENT OF BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERING EI1204-Sensors and Measuring Techniques QUESTION BANK UNIT-I Science of Measurements 2-Marks 1. What is the difference between accuracy and precision? 2. What is Recalibration? When it is done? 3. Mention any three types of errors in measuring instruments. 4. What are the applications of measuring systems? 5. Define drift and dead zone. 6. What is Gross Error? 7. Define periodically varying inputs and transient inputs. 8. Define sensitivity and Linearity of measurement system with example 9. Define Measurement. 10. What is Error? Mention the types of Error. 11. Draw the Block Diagram for the functional elements of an Instrumentation system. 12. How standards are classified by their functions and classification? 13. Define Accuracy. 14. Draw the static characteristics of measurement system, 15. Define static error and calibration. 16. State the dynamic characteristics of measurement system. 17. Define Instrumentation system. 16-Marks 1. Briefly describe the standards of Temperature and Luminous Intensity. 2. Explain the different categories of systematic errors and how it can be avoided. 3. Explain the static characteristics of measuring Frequency. 4. Write down the transfer function of a second order instrumentation and explain the terms damping factor, natural frequency. 5. Discuss about the probability of errors. 6. Determine the overall accuracy of a process measuring system which comprised of Thermometer accuracy +5% Pressure gauge accuracy +10% Flow meter accuracy 2% Viscosity accuracy 4% 7. Describe the static and dynamic characteristics of the measuring system. 8. What are the elements of generalized measurements system? Explain. 9. Define standard. Explain the types of standards. 10. Define calibration. Explain calibration types. UNIT-II Displacement, Pressure, Temperature Sensors 2-Marks 1. Compare the characteristics of Thermistor and RTD. 2. Define the primary and secondary transducers with typical application examples. 3. What are the various types of strain gauges? 4. Draw the circuit diagram for the measurement of temperature with thermocouple. 5. What are the advantages of LVDT transducers? 6. What are the advantages of thermocouple? 7. Define Transducer. 8. Define passive and active transducers. 9. State the working principle of thermister. 10. Define Gauge Factor. 11. State the principle of capacitive transducer. 12. Define seeback Effect. 13. Draw any one Biomedical application of unbounded strain gauge. 14. What are the Force summing devices available? 15. State the principle of Inductive transducer. 16-Marks 1. Describe the static characteristics of Transducers. 2. Explain how LVDT can be used for pressure measurement. 3. Explain with suitable diagram the measurement of gas flow using Hot wire Anemometer. 4. Describe the working and construction of resistance thermometer. 5. A capacitive transducer circuit used for measurement of linear displacement. T he transducer of parallel plate air capacitor wherein the capacitance can be changed by changing the distance between plates. This transducer is to be used for dynamic measurements. Suppose a flat frequency response with ab amplitude ratio within 5% is required down to a frequency range of 20 Hz. what is the minimum allowable value of time constant? Calculate the phase shift at this frequency .The area of plates is 300 mm2 and distance between plates is 0.125 mm. calculate the value of series resistance R. what is the amplitude ratio at 5Hz with the above time constant? 6. Explain Inductive transducer and strain gauge. 7. Describe the classification and characteristics of transducer. 8. Explain the characteristics of thermistor. 9. Describe the working and construction of the thermocouple. 10. Explain with neat sketches and suitable equations, the working of a capacitive transducer. What are the advantages and disadvantages of capacitive transducer? 11. Explain the construction and working of RTD. 12. Explain the different configuration of strain gauge with their sensing elements. 13. Explain the biomedical application of temperature sensor. 14. Explain the construction and working of unbounded strain gauge. 15. Explain the biomedical application of unbounded strain gauge. UNIT-III Photo Electric and Piezo Electic Sensors 2-Marks 1. List the advantages of optical sensor 2. Explain the characteristics of a vacuum photo tube. 3. Draw the circuit of a piezo electric crystal under conditions load. 4. What is the use of photosensitive device? 5. What are the types of photo sensitive device? 6. State the principle of photo multiplier. 7. What is the different between photo emissive and photo conductive dells? 8. State the principle of gas filled photo tube. 9. What are the advantages of photo transistor? 10. Draw the characteristic curve of photo voltaic cell. 11. Define dark resistance. 12. Explain Luminous Intensity and luminous Excitance. 13. State the principle of ultrasound transducer. 14. State the spectrometric application of photo electric transducers. 15. Define Piezo electric Effect. 16-Marks 1. Explain the working of various photo sensitive devices. 2. Describe the different modes of operation of piezo electric transducers. Explain the applications of piezo-electric transducers. 3. Explain the working principle of photovoltaic and photoconductive cell in detail. 4. Describe the working principle of piezoelectric active transducer and any one of its application. 5. Describe the construction and working of Gas filled Photo emissive tubes. Draw their characteristics and explain their advantages. 6. Explain the working principle of photodiode in detail. Draw its characteristics and explain their advantages. 7. Explain the working of ultrasound transducers. UNIT-IV Signal Conditioning and Signal Analyzer 2-Marks 1. Give the application of wave analyzer. 2. What is the minimum detectable signal of a spectrum analyzer with a noise figure of 20dB and using a 1 KHz, 3-dB filter. 3. Give the name of the bridges which are commonly used for the measurement of inductance. 4. What is difference between a logic analyzer and a distortion analyzer? 5. State where a Guard is used a low level signal amplifier. Distinguish Shield from Guard. 6. Draw the circuit and phasor diagram of Maxwell’s inductance bridge. 7. What are the advantages of Kelvin Bridge? 8. Draw the circuit and phasor diagram of Hay’s bridge. 9. What is spectrum analyzer?state its applications. 10. Name any two A.C bridges for measuring inductance. 11. State the advantages of Hay’s bridge. 12. State the source and Null detector that are used for A.C bridges. 13. What is sliding balance? 14. What are incremental inductance and permeability? 15. Discuss the advantage sand disadvantages of Maxwell’s bridges. 16. Define spectrum analysis. 17. Define standing wave ratio. 18. Define the term “Total harmonic distortion”. 19. What is intermodulation distortion? 20. What is the different between A.C and D.C bridges? 16-Marks 1. Explain the working of a Hay Bridge and how it is different from Maxwell Bridge and also write its advantages and disadvantages. 2. Explain the Kelvin Double Bridge circuit and how it is used for low resistance measurement. 3. Draw and discuss the functional block diagram of the heterodyning wave analyzer. 4. Explain in details the applications of the spectrum analyzer. 5. What a.c bridge is sensitive to frequency? Draw its circuit and derive the relation for balance with respect to frequency. 6. Draw the fuctional block diagram of a function generator and explain its working. 7. Explain the use of a swept frequency function generator for filter testing. 8. Explain the working of low voltage Schering Bridge and derive the equations for capacitance and dissipation factor. Draw the phasor diagram of the bridge under condition of balance. 9. Describe the basic circuit of a spectrum analyzer explain how the spectra of the following is displayed. a) Continuous wave signal b) Amplitude modulated signal c) Frequency modulated signal d) Pulse modulated signal 10.In a low voltage Schering bridge designed for the measurement of permittivity, the branch ab consists of two electrode between which the specimen under test may be inserted :arm bc is a non reactive resistor R3 in parallel with a standard capacitor C3 arm and cd is a non reactive resistor R4 in parallel with a standard capacitor C4:arm da is standard air capacitor of capacitance C2.without the specimen between the electrodes ,balance is obtained with the following values:C3=C4=120 PF,C2=150PF, R3=5000 ohm. With specimen inverted these values become C3=200PF, C4=1000PF,C2=900PF,and R3=R4=5000 ohm. In each test w=5000 rad/sec. Find the relative permittivity of the specimen. 11. Draw and explain isolation amplifier. 12. Explain why Maxwell inductance –Capacitance Bridge is useful for measurement of inductance of coils having storage factor between1 and 10. 13. Explain the working of Schering Bridge. 14. Explain Wheatatone Bridge. 15. Describe the working of impedance matching circuits. UNIT-V Display and Recording Devices 2-Marks 1. What are the types of Digital voltmeter? 2. How can a prescalar be used to extend the range of a frequency counter? 3. What is Aquadog? What is the purpose of Aquadog in the CRT screen? 4. What are the advantages of dual trace over dual beam for multiple trace oscilloscope? 5. State any four types of recorders used in medical diagnostics instrumentation. 6. What is sampling oscilloscope and state for what frequencies it is useful? 7. What is the function of horizontal and vertical positioning? 8. What are the different types of amplifiers used in CRO? 9. What is the function of time base generator on a CRO? 10. What are the uses of x-y recorders in laboratories? 11. Mention some application of CRO. 12. What is a magnetic recorder? 13. Define deflection sensitivity and deflection factor of a CRT. 14. What are the applications of storage oscilloscope 15. Explain the principle of thermal recorders. 16-Marks 1. What is sweep frequency generator? What are its basic elements and explain its working with a block diagram. 2. Draw and explain the circuit arrangement for Time period measurement. 3. Describe working of a digital storage oscilloscope using an analog delay line. Use a block diagram. 4. Discuss in detail with necessary diagrams the construction and working of magnetic recorders. 5. What is a digital storage oscilloscope and explain its sue in observing biological signals. 6. Describe a suitable paper chart recorder with a neat sketch explaining the principle. 7. What is a multi channel analyzer and explain its use in radiation monitoring? 8. An electrically deflected CRT has a final anode voltage of 2000 V and parallel deflecting plates 1.5 cm long and 5 mm apart. If the screen is 50 cm from the center of the deflecting plates, find i) beam speed ii)the deflecting sensitivity of the tube iii)the deflecting factor of the tube. 9. Draw the block diagram of a general purpose CRO and explain the functions of the following controls i)intensity ii)focus iii)synchronization 10. Derive the expression for the vertical deflection of an electron beam in a CRT. 11. Explain with suitable circuit diagram, the working of X-Y recorder. Describe its applications.