* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
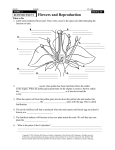
Sample exam. None of these questions will be on the exam, but these questions almost made it to the exam. I pulled them from the exam to shorten it, so if you can answer them, you should do pretty well on the exam. Some of these questions are easier than the exam questions, so if you struggle here, you may need to study more. Answers to multiple choice at the bottom. 1. The correct order of Embryogenesis is: a. Cleavage, Gastrulation, Fetus b. Fertilization, Gastrulation, Neurulation c. Cleavage, Neurulation, Gastrulation d. Cleavage, Gastrulation, Neurulation 2. Which statement is true? In a fertilized egg, a. the animal pole will become the future embryo, the vegetal pole will become yolk or yolk cells b. the vegetal pole will become the future embryo, the animal pole will become yolk or yolk cells c. both the animal and vegetal poles will become the future embryo and yolk or yolk cells 3. The egg contributes a haploid nucleus and what to the zygote? a. cytoplasm including nutrients, b. ribosomes, c. mitochondria d. all of the above e. none of the above 4. Which two systems are still developing in childhood (exclude growth)? a. The nervous system (brain) and immune system b. The reproductive system and lymphatic system c. The nervous system (brain) and reproductive system d. none of the above 5. Why do adaptations never reach perfection? a. Environments change b. New genetic variation arises by mutation c. Adaptations sometimes go in the wrong direction d. a and b 6. Why was the initial hybrid between the radish and cabbage cross sterile? a. Because hybrids between two different species are sterile b. Because the hybrid produced pollen of the radish and eggs of the cabbage c. Because they hybrid had mismatched chromosomes that did not pair properly in meiosis d. Because they hybrid had mismatched chromosomes that did not pair properly in mitosis 7. How was he able to keep the sterile hybrid of the radish/cabbage cross alive? a. he bred offspring b. he continually crossed radishes and cabbage c. he made clones by grafting the plant 8. What can evolve? a. populations b. people or individual organisms c. genes d. a and c e. all of the above 9. Which of the following is the correct order for life in the fossil record? (Yes, we did not talk about the first cat, but I think it is pretty obvious.) a. First cat, first prokaryotic cells, photosynthesizing bacteria, eukaryotic cells, animals, life on land, b. First prokaryotic cells, photosynthesizing bacteria, animals, eukaryotic cells, life on land, first cat c. First prokaryotic cells, photosynthesizing bacteria, animals, eukaryotic cells, first cat, life on land d. First prokaryotic cells, photosynthesizing bacteria, eukaryotic cells, animals, life on land, first cat 10. Why was the evolution of pollen important for land plants? a. With the evolution of pollen, plants could freely engage in promiscuous sex b. With the evolution of pollen, bees and insects accomplished a plant’s reproduction c. With the evolution of pollen, the wind accomplished a plant’s reproduction d. With the evolution of pollen, plants stopped relying on water for reproduction 11. From your reading, did all the dinosaurs go extinct? a. Yes b. Yes, most died out 65 million years ago but a few survived till primitive humans eliminated them c. No, some are hiding among us and occasionally eat us d. No, some are still living with us but other than occasionally pooping on us are relatively harmless 12. The yolk sac is normally a source for food, but it is not in most mammals. Why is this? a. Because most baby mammals do not need to eat much food b. Because most baby mammals have a parent to bring them food c. Because most baby mammals have a placenta d. Because most baby mammals have an amnion 13. Populations change in genetic characteristics over time. This change can be measured by? a. Allele frequency changes b. Genotype frequency changes c. Individual frequency changes d. all of the above e. a and b 14. During the winter, the black kitty matures and it begins mating with the other cats. Female cats in the area seem to prefer the black kitty, increasing the frequency of the black coat color allele in the population. Its increase in frequency is largely because of? a. Artificial selection b. c. d. e. Gene flow Genetic drift Natural selection Sexual selection 15. What does the Fossil Record do? a. Documents the history of life on Earth. b. Shows that a succession of organisms has populated the Earth throughout time. c. Provides some support for evolution d. all of the above 16. This question is worth double the points. In a population of 1000 diploid plants, 360 are white, 640 are red. White flowers are recessive to red. What is the frequency of the white allele? What is the frequency of the red allele? p+q=1 p2 + 2pq + q2 = 1 17. Essay and extra credit. Name and describe a human adaptation that has an ecological trade-off in the adaptation. 18. Essay: define evolution 19. Essay. What is speciation? 20. Essay. From the chart below, what is special about Devonian and Silurian periods to the evolution of life? Paleozoic Era PLANT EVOLUTION ANIMAL EVOLUTION 286 Seedless vascular forests decline as gymnosperms appear. Nearly all the tree Amphibians decline as reptiles dominate; is sporophyte, gametophyte is a few cells arthropods abundant in the cones. Sex can be done without water 360 AGE OF GREAT COAL FORMING FORESTS. Seedless vascular plants dominate land; phytoplankton continue to dominate water AGE OF AMPHIBIANS. Arthropods share dominance with amphibians on land; 1st reptiles; bony fishes & zooplankton continue to dominate water Devonian 410 Seedless vascular plants appear (whisk ferns, lycophytes, ferns, horsetail produce spores). Sporophytes are the dominant generation. First land animals; arthropods (insects, crabs, spiders) followed by amphibians late in the period Silurian 440 Bryophytes appear on land (liverworts, moss, gametophytes are the dominant generation). 1st land plants ~435 mya AGE OF FISHES. Fishes explode in diversity; share dominance of water with zooplankton, 1st bony fish late in period Ordovician 505 no life on land AGE OF INVERTEBRATES. First fishes appear; mollusks & protozoans dominate the seas Cambrian 544 Algae explodes in diversity (no plants). AGE OF INVERTEBRATES. Trilobites Permian Carboniferous Phytoplankton dominate the water. No life on land abundant, invertebrates & protozoans dominate the water; no life on land Answers: 1 b, 2 a, 3 d, 4 a, 5 d, 6 c, 7 c, 8 d, 9 d, 10 d, 11 d, 12 c, 13 e, 14 e, 15 d, 16 white is q=.6, red is p = .4.