* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Mgmt 500 Module 3 summary
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
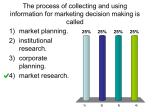
Module summary: Planning is the process of determining how the organization can get where it wants to go. The fundamental purpose of planning is to help the organization reach its objectives. Advantages of planning include: (1) an emphasis on the future, (2) coordination of decisions, and (3) a clear focus on the objectives. If done incorrectly or excessively, planning can be disadvantageous, but its benefits outweigh its disadvantages. The six steps of the planning process are: (1) stating objectives, (2) listing alternatives, (3) developing premises, (4) choosing alternatives, (5) developing plans to pursue the chosen objective, and (6) putting the plan into action. A decision is a choice made between two or more available alternatives. There are two basic types of decisions which are at the opposite ends of a continuum: (1) programmed decisions are routine and repetitive, and (2) nonprogrammed decisions are one-shot occurrences and are usually less structured than programmed ones. The scope of the decision is the proportion of the total management system that a particular decision will affect. The broader the scope of a decision, the higher the level of the manager responsible for making that decision. With decisions through consensus, everyone agrees. Strategic planning is long-term planning that focuses on the organization as a whole. To determine how far into the future they should plan, managers should use the commitment principle. Strategy is the end result of strategic planning. Strategic management is the process of ensuring that an organization possesses and benefits from the use of an appropriate organizational strategy. It consists of five sequential and continuing steps: (1) environmental analysis, (2) the establishment of organizational direction, (3) strategy formulation, (4) strategy implementation, and (5) strategic control. The successful implementation of strategy requires four skills: (1) interacting skills, (2) allocating skills, (3) monitoring skills, and (4) organizing skills. The last step, strategic control, focuses on ensuring that all steps of the strategic management process are appropriate, compatible, and functioning properly. Tactical planning should reflect strategic planning. Tactical planning focuses on what to do in the short-term to help the organization achieve the long-term objectives determined by strategic planning. As managers move from lower to upper management, they spend more time on strategic planning and less time on tactical planning. A plan is a specific action proposed to help the organization achieve its objectives. A plan has four dimensions: (1) repetitiveness, (2) time, (3) scope, and (4) level. Using the repetitiveness dimension as a guide, organizational plans are usually either standing plans or single-use plans. Three specific types of standing plans are policies, procedures, and rules. Single-use plans, on the other hand, are exemplified by programs designed to carry out a special project and budgets. Managers should know what causes plans to fail and should take appropriate steps to prevent plan failure. A comprehensive organizational plan includes plant facilities planning and human resource planning. Both are types of input planning. Planning tools are techniques that managers can use to help develop plans. Forecasting involves predicting the future organizational environment. Sales forecasting is the most important form of organizational forecasting. Methods of sales forecasting include: (1) the jury of executive opinion method, (2) the sales force estimation method, and (3) the time series analysis method. Scheduling is another commonly used planning tool. It involves the listing of activities for reaching an objective. Two frequently used scheduling methods are Gantt charts and the program evaluation review technique (PERT).