* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 1 - West Ada
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
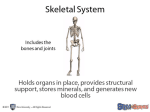
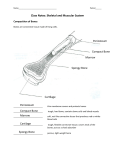
Names of bones on skeleton… *Human Body System Review Sheet* (save this page to study for the final exam at the end of May) Name___________________________ 1. Five Functions of skeletal system A. Give Shape and structure to the body B. Protects internal organs C. Makes blood in bone marrow D. Helps with movement – muscles attach to bone E. Stores minerals like calcium and phosphorus 2. Five joint types Describe A. HINGE Elbow, moves in one direction B. BALL –IN – SOCKET C. IMMOVABLE Shoulder, moves in all directions D. GLIDING Between vertebra in back, Slides a little in all directions E. PIVOT Forearm, twists 3. Bone structure Describe A. Compact bone Strong layer on the surface of bones B. Spongy bone Lightweight bone on the ends of long bones C. Bone Marrow (Marrow Cavity) D. Cartilage Make blood cells A. Muscular System B. Circulatory system C. Nervous system Bones give muscles a place to attach to help with movement 5. Connective tissue 6. Three functions of the digestive system? 7. Know the parts of the digestive system, their jobs, and how food passes through the digestive system. a. Ligament - Attaches bone to bone b. Tendon - Attaches muscle to bone 1. Digestion - Break down food 2. Absorption - get nutrients into the blood 3. Elimination – get rid of waste Mouth – starts digestion Esophagus – connects mouth to stomach Stomach – digests food using acids Small intestine – absorbs nutrients Large intestine – reabsorbs water And others Does not move, skull Smooth covering over ends of bone that help cushion and reduce friction. 4. Interactions of skeletal with other systems. Tell system and then how it interacts. Bone Marrow makes blood cells to help the circulatory system The skull of the skeletal system helps protect the brain of the nervous system 8. Villi Microscopic finger like things in the small intestine that help increase the surface area. Breaking down food pieces into smaller food pieces. 9. mechanical digestion 10. chemical Breaking down food particles into the molecules to be absorbed into digestion the blood. RESPIRATORY SYSTEM 12. Alveoli 13. Two main functions of the respiratory system. 14. What is the difference between breathing and respiration? 15. How are breathing and respiration related? 16. Three main functions of Circulatory system 17. Vein AIR SACS TO INCREASE SURFACE AREA, WHERE OXYGEN AND CARBON DIOXIDE ARE EXCHANGED - Get oxygen into blood - Get carbon dioxide out of blood - Breathing is getting air in and out Respiration is cells using oxygen and glucose to make energy for the cell Breathing gets the oxygen needed for respiration (oxygen + glucose = carbon dioxide + water + energy) so cells can have energy. - get nutrients and oxygen to cells - get waste and carbon dioxide away from cells - fights infection (white blood cells) Carries blood toward the heart 18. Artery Carries blood away from the heart 19. Capillaries 20.a) Aorta Smallest blood vessels where exchange of nutrients and gasses takes place. Main artery from heart to carry blood out to body 20.b) Vena Cava Main vein carrying blood back into the heart. 21. Ventricles Lower chambers of the heart 22. Atria Upper chambers of the heart 23. Functions of Transport things through the circulatory system Blood 24. Red blood cells carry oxygen 25. White blood cells. 26. Platelets fight infection 27. Plasma carry nutrients 28. Three Main functions of Muscular System (these correspond to the three types of muscle.) clot blood - - move the body move blood (heart) move food through digestive system 29. Cardiac muscle heart 30. Smooth muscle digestive system 31. Skeletal attached to bones muscle 32. How do pull only (contract) so they must work in pairs muscles work to move the body? 33. Voluntary control by thinking about it muscle 34. Involuntary work without thinking about it muscle 36. Study the names of the muscles on the muscle man coloring page. Bicep, tricep, quadriceps, and hamstring. 37. three main 1. receive information functions of the 2. respond to information nervous system 4. maintain homeostasis 38. Three parts of the brain A. Cerebrum B. Cerebellum C. Brain stem 39. Neuron 40. Sensory Neuron 41. Interneuron higher level thinking balance main body functions like heart rate and breathing nerve cell carries message from senses to brain 42. Motor Neuron carries message from brain to muscles to move 43. Function of the urinary system 44. Kidney Filter blood 45. Nephron Basic functioning unit of the kidney, to make urine. 46. Excretory system 47. xylem Removes wastes from the body, includes respiratory, digestive, skin, and urinary systems Vascular tissue in plants to - Carries water up in plants 48.phloem Vascular tissue in plants to – carry food down Processes information in brain Main organ of urinary system 49. Root functions 1. Anchor plant to ground 2. Absorb water from soil for plant 3. Store food for the plant 50. Stem Function Hold plant upright to reach for sun 51. Leaves function 52. Photosynthesis equation (reaction) Absorb sunlight and make food for the plant Water + carbon dioxide + sunlight = sugar (glucose) + oxygen It is important to study the nervous system (a lot) because we did not spend much time on this system.