* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Course - Wsfcs
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
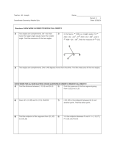
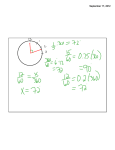
Main Street Academy 2011-20012 Weekly Lesson Plan Format C.CLARK Course: Geometry/ Tech Math II Unit of Study: Basics of Geometry Unit Essential Question: How do you apply the basic terms and properties of lines and angles to solve problems? Beginning Date: 1/30/12 Ending Date: 2/3/12 State competency goal and objective: 2.02-Apply properties, definitions, and theorems of angles and lines to solve problems and write proofs. 2.01 Use logic and deductive reasoning to draw conclusions and solve problems. Teacher Input (2. Presentation) Essential Question (s): Activating Strategy/ Emotional Hook (1. Start the lesson) Date 01/30/12 01/31/12 How and when do you use the Distance Formula, the Midpoint Fomula and/or the Segment Addition Postulate? 2.01 How and when do you use Angle Addition Postulate and the definition of angle bisector to set up an equation? 2.02 Warm- ups: 11-2 skills practice: Points, lines, and planes Warm- ups: Review problems from previous lessons Student Active Participation (3. Guided practice) __________________________ Additional Student Activities (4. Independent practice) Instruction: Meaning of Congruent segments… cont’d. Using segment addition Guided Practice: Geometry handout 1B (Students work at board) Independent Practice: Mixed Practice with Lines Instruction: 1.3: Segments and Their measures 1.4: Angles and their measures 1.5: Segments and Angle Bisectors cont’d. Guided Practice: 1.5 Concept Activity: Bisectors Independent Practice: Section 1.5: pp. 38-39 #18-52 even Summarizing Activity (5. Evaluation) Closure ________________________ Homework Q&A None Ticket out the Door Answer the Essential Question. 1. Find n if W is the midpoint of VX 2. If two segments have the same length, they are ______________. 3. Points R, S, and T are collinear. If RS = 48, ST = 21, and RT = 27, determine which point is between the other two. A) S is between R and T. B) T is between R and S. C) R and T describe the same point. D) R is between S and T. Sections 1.2, 1.3, 1.4, and 1.5 in student workbook with examples (blue book) Main Street Academy 2011-20012 Weekly Lesson Plan Format C.CLARK 02/01/12 How do you use "special pairs" in a diagram to set up and solve an equation? Warm- ups: Review problems from previous lessons Instruction: 1.6: Angle Pair Relationships- notes on linear pairs and vertical angles Answer the Essential Question. Guided Practice: Angle Pair Relationships.pdf Quiz 1 ( 1.2 to 1.4) Chapter Test: p. 63 #1-22 all Independent Practice: Quiz 1 ( 1.2 to 1.4) 2.02 Instruction: n/a 02/02/12 How do you use the properties of lines and angles to solve problem? Warm- ups: Sample test questions How do you rewirte a conditional into four other forms? Which of those are logically equivalent? Chapter Review: pp. 60-62 # 1-4 all, 6-33 all Independent Practice: Chapter 1 Test 2.02 02/03/12 Chapter 1 Test Guided Practice: Review- Basketball: students on teams answering sample test questions. Warm- ups: Review problems from previous lessons 2.01 Instruction: Logic statements- introduce previously visited symbols with forms Chapter 2-1 Notes & PowerPointCONDITIONALS.ppt Guided Practice: Think, Pair, Share- students creates statements and partners must create the other 3 forms. Independent Practice: Section 2.1: pp. 75-78 #10-50 even, 51 Answer the Essential Question. Create your own graphic organizer showing the different forms.- Must include facts to support (i.e. definition, examples) Share organizers with class/ partners none See attached: organizer Literacy enhancements /Key Vocabulary: midpoint segment bisector perpendicular bisector length congruent segments postulate Midpoint Formula Distance Formula Addition Postulate Segment Ruler Postulate angle bisector congurent angles acute obtuse right straight interior points Angle Addition Postulate Protractor Postulate exterior point theorem adjacent angles vertical angles linear pair complementary angles supplementary anges Adaptations/ Differentiation: 3-D midpoint and distance Use manipulatives for lines, segments, and rays (i.e. toothpick, floor) Use paper as examples of planes Use students’ names in logic statements. Refer to science when making hypothesis and conclusions.