* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Storage effect wikipedia , lookup
Source–sink dynamics wikipedia , lookup
The Population Bomb wikipedia , lookup
Human overpopulation wikipedia , lookup
World population wikipedia , lookup
Molecular ecology wikipedia , lookup
Two-child policy wikipedia , lookup
Maximum sustainable yield wikipedia , lookup
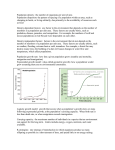
APES STUDY GUIDE Chapter 9: Population Dynamics You will be quizzed on information provided on this handout. VOCABULARY: see next page Study Objectives: THIS IS NOT A HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT!! 1. Be familiar with all material from previous chapters. 2. What does it mean to say populations are dynamic? Name at least three major ways in which populations demonstrate they are dynamic. 3. In general, what are the four factors that determine the size of a population? 4. Be able to name at least three common characteristics of populations that have a high intrinsic rate of increase. 5. Explain how exponential growth and intrinsic growth are different and be able to draw a simple graph of each. 6. Explain the difference between density-dependent and density-independent factors on a population’s size. Be able to give at least two examples of each. 7. Be able to describe and draw each of the four common patterns of population fluctuation. 8. Explain how bottom-up and top-down methods of population control are related to predator-prey relationships. 9. Name at least four characteristics of r-selected populations and K-selected populations. 10. What factors is the most important in determining the size of a population? 11. Be able to interpret the various types of survivorship curves. 12. What fundamental questions are associated with the field of Conservation Biology? What are the three fundamental principles of conservation biology? 13. Be able to name at least 5 ways technology has been used to extensively modify ecosystems. 14. Describe at least four lessons we can learn from nature in order to preserve ecosystems. Ch12 Human Population: Objectives: 1- Be familiar with material from all previous chapters. 2- Be able to calculate the rate of change for a population. What does it mean to say populations are dynamic? 3- Be familiar with recent trends in global total fertility rates, infant mortality rates, and life expectancy. 4- Know which type of country (developed or developing) has the highest rates of growth, fertility, life expectancy, and infant mortality. 5- Know when demographic transition occurred in the United States. 6- Name and be able to explain the impact of the key factors affecting a country’s birth and fertility rates. 7- Be able to list the major factors that influence death rates. 8- Be able to explain why infant mortality remains relatively high in the United States. 9- Be able to interpret age structure diagrams (see page 263). 10- Be familiar with some of the major impacts HIV/AIDS has had in Africa and what has been suggested as possible solutions to the problem. 11- Be able to explain the demographic transition model in detail (page 269). 12- Explain how empowering women can help reduce birth rates. 13- Discuss how economic rewards and penalties can be used to reduce birth rates. 14- What were some of the major suggestions proposed by the United Nations Conference on Population and Development concern how to slow global population growth? 15- Explain what is meant by the Cultural Carrying Capacity. 16- In addition, be able to interpret all figures and diagrams in Chapter 12. LAWS, FORMULAS, AND CHEMISTRY REVIEW: Sulfur Air Pollution Equations 4FeS2 + 11O2 -- 2Fe2O3 + 8SO2 Impurities such as pyrite or iron pyrite are found in coal, when we burn coal it interacts with atmospheric oxygen to form iron oxide and sulfur dioxide (a primary air pollutant). 2SO2 + O2 ---- 2SO3 SO3 +H2O --- H2SO4 SOX The generalized representation of sulfur oxides, whether it be sulfur dioxide or sulfur trioxide. The Sulfur oxides are considered primary air pollutants. Vocabulary: You will have a vocabulary quiz on these terms. You may be required to provided examples for some terms. A Word Wall can be made from one of these words (vocabulary list) for this Chapter's Quiz. Due on the date of the quiz. 1. Population dynamics 2. biotic potential 3. environmental resistance 4. intrinsic rate of increase (growth) 5. minimum viable population 6. asexual reproduction 7. sexual reproduction 8. carrying capacity 9. r-selected 10. K-selected 11. Bioinformatics 12. fragmentation. 13. Survivorship curve Ch 12 Vocabulary: 1. Demography 2. crude birth rate 3. crude death rate 4. replacement level fertility 5. total fertility rate 6. demographic transition 7. life expectancy 8. infant mortality rate 9. Age Structure Diagrams 10. Baby boom 11. Echo boom APES: Chapter 9 Population Dynamics, Carrying Capacity, Conservation Biology EQ: What are the characteristics of dynamic populations. INTRODUCTION: 9-1 Population Dynamics and Carrying Capacity Populations are________________, constantly undergoing changes in_____________, __________________, and age distribution due to ____________________stress and changing environmental conditions. In general there are four factors that influence the size of a population: 1. 2. 3. 4. Different populations vary in their ability to grow (________ ____________). The Define intrinsic rate of increase: Organisms with high intrinsic rates of increase typically have the following characteristics: 1. _______________________________________________ 2. _______________________________________________ 3. _______________________________________________ 4. _______________________________________________ The intrinsic rate of increase of many species depends upon having a certain _____________________________________________________(minimum viable population). Define Environmental resistance: _______________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ Define carrying capacity:__________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ Populations with unlimited access to resources grow slowly at first and at a faster rate with time (exponential growth). When graphed this yields a_______________________ _________________. As populations experience environmental resistance the rate of growth begins to slow as the carrying capacity is reached (______________________________growth). When graphed this yields an ____________________ curve (see Fig. 9-4). At times a population may overshoot the carrying capacity and eventually suffer a population crash or ________________(See Fig. 9-6). Human populations are not exempt from dieback although __________________and _______________ changes have increased the carry capacity of the earth for our species. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9_9SutNmfFk Mini HW #1: page 201: #’s 2, 5, 6 (all parts), 7, 8. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BSVbdaubxxg section summary EQ: What are the major patterns associated with population change and what reasons have been proposed to explain them? DENSITY FACTORS Some controls on populations have an impact independent of the population’s density (density independent controls): 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Other controls have a greater impact if the density of the population is large (density dependent controls): 1. 2. 3. Overall there are four common patterns of population fluctuations: 1. stable: the population stays pretty close to the carrying capacity. 2. Irruptive: populations explode to high levels then return to a stable level or crash. 3. Chaotic: irregular fluctuations that are not predictable 4. Cyclic: population’s size varies on a fairly regular basis. Draw examples of each below: Predation and Population Size The role of predators in ecosystems has been studied extensively. At one time most biologists accepted the top-down control hypothesis. Explain: ______________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ This idea was used to explain the cycling of hare and lynx populations studied since the 1800’s (see Fig 9-8). It is now believed the size of some populations might be better explained using the bottom-up control hypothesis. Explain: ______________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ Although some bottom-down controls are still believed to exist, the size of predator-prey populations are probably a combination of both factors. Mini HW #2: page 201 #’s: 9, 10, 11, 12. EQ: How are different patterns of reproduction utilized by organisms to maximize their Darwinian Fitness? 9-3 Reproductive Patterns All organisms are constantly struggling for____________________________ __________________________. Remember, Darwinian Fitness is a measure of the ________________________success of an organism or population. There is not however one reproductive strategy that is always better than another Asexual reproduction involves no exchange of ______________________information and the offspring are genetic _____________________of the original cell. Binary Fission Budding Sexual reproduction involves an exchange of _____________information between organisms and is estimated to occur in _______% of all life. There many costs associated with sexual reproduction (research at least two of them in your textbooks) but these are outweighed by the advantage of generating genetic diversity. Scientists have identified two fundamental reproductive patterns: r- selected (opportunists): put most of their energy and resources into reproduction. _______________________________________________ _______________________________________________ _______________________________________________ early successional species generalist niche K- selected: tend to do well in competitive situations when their population is near the carrying capacity. 1. Few, large ___________________ 2. ______________reproductive age 3. extensive parental care 4. typically follow a ______________________growth pattern 5. because the intrinsic rate of growth is low they are prone to ____________ No matter what pattern organisms used their ultimate population size is determined by available ___________________________ _______________________________. Survivorship Curves Survivorship curves indicate the number of individuals alive in a population during a given time. There are three generalized patterns: Late loss curves: ____________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________(most die late) Early loss curves: __________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________(most die early) Constant loss curves: _______________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ Mini HW #3: page 201 #’s: 13, 14, 15, 16. EQ: How have humans utilized technology to impact the natural world and what solutions have been proposed to minimize future damage. 9-4 Conservation Biology Conservation biology began in the 1970’s in attempt to use science to preserve species and ecosystems. There are several fundamental questions that ask: - __________________________________________________ what is the status of functioning _________________and the services they provide what actions can be taken to ________________________________ecosystems, their services, and their populations? Conservation biology is heavily dependent upon ____________________________research and focuses upon three essential principles: 1. ______________________________is essential to all life and should be preserved 2. humans should not ____________________the extinction of species or ____________________ ecological processes 3. the best way to preserve biodiversity and ecological functions is to _____________ ____________________________________________. The new discipline of bioinformatics has contributed enormously to the field of Conservation Biology by providing access to key biological information through databases. Human Impacts on Nature Humans have used technology to modify nature extensively in numerous ways: 1. fragmentation and degradation of habitats http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KEINq3-9Tu0 2. 3. _________________________________________ use and/or waste an increasing percentage of the planet’s net primary productivity 4. strengthen some __________________________species 5. 6. eliminate ________________________ introduce ______________________________species http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2iKYcqKyXic Answer the following questions as you watch the video. 1. How did Burmese Pythons arrive in the Everglades? 2. What is the economic cost? 3. What is the ecological cost? 4. How has ballast water contributed to the invasive species problem? 5. Describe one impact (ecological/economic) zebra mussels have had on the great lakes. 7. 8. over-harvest natural resources interfere with the normal __________________________of chemicals and the flow of energy in ecosystems Solutions Many biologists now believe the best way for us to live more sustainably is to learn how nature ________________________________________________________________. These lessons include: 1. we are totally ______________________upon the earth and sun 2. everything is _______________________ 3. we can never merely do one thing 4. we should _______________________the damage we are doing to nature and heal some of the ecological wounds we have caused 5. we should use care, restraint, humility, and cooperation with nature as we alter it to meet our needs. APES: Chapter 12 Human Population: Growth, Demography, and Carrying Capacity http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=d1dIAtvSFLM 12-1 Factors Affecting Human Population Define Demography: ___________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________ The rate at which the human population changes is frequently measured by subtracting the _______________________(the number of deaths per 1,000) from the ________________________________________(number of births per 1,000). This is usually expressed as a percentage using the following equation: % change = which equals: birth rate- death rate X 100 1,000 _________________________ 10 Even though the birth rate has _________________around the world the death rate has fallen__________ ____________. Exponential growth has slowed in the last 40 years but the base population has still almost____________________. Problem: Calculate the number of people that would be added to a population of 3 billion people at a fertility rate of 5%: Problem: Calculate the number of people that would be added to a population of 6 billion people at a fertility rate of 2.6 %: Two types of fertility rates affect a country’s population size and growth rate. 1- replacement fertility level: __________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________(approximately 2.1 children). Even when (if?) this number was to be achieved the global population would continue to grow for another 50 years (assuming death rates stay the same). 2- total fertility rate (TFR): _______________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=uOuzC0UMBHQ fertility rates TFR has dropped significantly since 1950 from about 5.0 to 2.6. Notice however it is still far above the replacement level of 2.1. More than _________% of the human population growth by the year 2050 is expected to take place in developing countries where living in _____________________ ___________________(less than $1.00 a day) is a way of life. There are many factors that affect fertility rates: importance of children in the ________________force ____________________________ cost of raising and educating ____________________________ educational and employment opportunities for _______________(empowerment) infant _____________________________rates average _________at marriage availability of abortions availability of reliable birth control methods _________________beliefs, traditions, cultural norms. Death Rates are influenced by access to: - ________________supply - medical care - medical and health technology - improved _____________________ - safe _____________________ (#1) Two common ways of measuring the overall health of people in a country are: 1- life expectancy_________________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=p6qhwUd9uw0 life expectancy 2- infant mortality rates (commonly defined as _________________________before the age of______________________________) Although infant mortality rates are falling, almost _________________________ infants die each day due to __________________________causes. There are 37 countries that have lower infant mortality rates than the United States due mainly to: inadequate ________________care for the _____________________ drug addiction during _____________________________ high birth rates among __________________________________girls (the highest of any industrialized country). ** Infant Mortality Rate is a determining factor in figuring out if a country is ____________ or _____________ 12-2 Population Age Structure Diagrams Age structure diagrams show the proportion of a population (or gender) at a particular age. They are typically divided into three broad categories: 1- __________________________________________(ages 0-14) 2- __________________________________________(14- 44) 3- __________________________________________(45 and up). Age structure diagrams that have a _______________shape have the potential to grow_______________. About 30% of the world’s population is in the pre-reproductive group. The more ____________the diagram becomes the ___________the birth rate. Rapid changes in population growth rates can have severe cultural impacts (__________________________ _______________________in this country). If population decline is gradual the harmful effects can usually be managed. HW #4 p 275- 2, 15, 17 HIV/AIDS is having a major impact of the age structure of many African countries. Life expectancy may drop _____________________years with the greatest impact on the most productive adults. Increases in the number of orphans and reduction in ____________production are expected to follow. The international community, especially developed countries, are being called upon to spearhead the effort to slow the spread of AIDS through improved_____________, health care, family planning, and contributing __________________aid. 12-3 Solutions There are several proposed solutions to the problem of human population growth: limiting ______________(the United States allows large numbers to immigrate compared to many of the other countries of the world.) reducing _____________rates through economic incentives, family planning, and empowering women. Many question the need to limit birth rates arguing: a- we do not know the __________________________of the earth b- humans are the world’s most valuable resource when it comes to solving global problems c- it violates their private or religious beliefs. 3- Economic development typically reduces birth rates in a fairly recognizable pattern known as _________________________transition. You should be familiar with this model in detail. 4- A small number of countries use ____________________rewards or penalties to help reduce birth rates. ________________has instituted the most extensive and intrusive controls and arguably the most effective. Mini HW #2: Review Questions page 275 #’s: 8, 9, 12, 14. End of Chapter Reading Assignment Due: _________________________________ ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- APES: Homework Assignment Name:_________________________________ Due Date: ___________ Directions: complete each of the following questions by the due date. Your answer must be hand written. You will be held responsible for them in class on the due date and on future tests and quizzes. Any questions left unanswered may also cost you points. READ THE ENTIRE CHAPTER!!!! Section 9-1 (page 191) 1. Name AND briefly describe four ways populations demonstrate they are dynamic. 1. 2. 3. 4. 2. Write the equation that includes the four variables that determine population change: 3. List four characteristics of populations with high intrinsic rates of growth (r): 1. 2. 3. 4. 4. Name two things that can happen to a population that falls below its MVP. a. b. 5. Draw a graph showing exponential growth, overshoot, and dieback. 6. Draw a graph showing logistic growth, overshoot, and carrying capacity. 7. Make a list of three density-independent population controls: 1. 2. 3. 8. Make a list of three density-dependent population controls: 1. 2. 3. 9.2 The Role of Predation 9. Explain what is meant by top-down control. Give an example. 10. Explain what is meant by bottom-up control. Give an example. 9.3 Reproduction Patterns 11. What types of organisms typically go through asexual reproduction? 12. Describe three costs associated with sexual reproduction? 1. 2. 3. 13. Make a list of 5 characteristics associated with r-selected species. a. b. c. d. e. What type of growth curve is associated with these organisms? 14. Make a list of 5 characteristics associated with K-selected species. a. b. c. d. e. What type of growth curve is associated with these organisms? 9.4 Conservation Biology 15. What are the three questions asked by conservation biologists when attempting to preserve species and ecosystems? a. b. c. 16. What are the three underlying principles of conservation biology? a. b. c. 9.5 Human Impacts on Ecosystems 17. Make a list of 5 ways humans have altered nature using technology. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 21. Describe all three principles that scientists have learned by studying the natural world that should help humans achieve a more sustainable lifestyle. 1. 2. 3. Connections (page 200). 22. Outline the important steps that occurred in the “Ecological Surprise” that occurred as a result of humans attempting to address the issue of malaria in Borneo. I have done the first and last one for you. a. W.H.O. sprays dieldrin to control mosquito populations. b. c. d. e. f. roofs begin to collapse because of an exploding caterpillar population Which of the 5 principles you listed in question 21 is illustrated by this example? http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fwXNsZf2Y0Q APES: Homework Assignment Chapter ___12___ Name:_________________________________ Due Date: ___________ Directions: complete each of the following questions by the due date. Your answer must be hand written. You will be held responsible for them in class on the due date and on future tests and quizzes. Any questions left unanswered may also cost you extra credit points. READ THE ENTIRE CHAPTER!!!! 12-1 (page 255) 1. What equation is used to calculate the crude birth rate? How is this modified to express the answer as a percentage? So if the crude birth rate is 17 and the crude death rate is 7 how long would it take a population to double in size? Show work! 2. Figure 12-3 a. Which continent has the highest crude birth rate? b. The highest crude death rate? c. A negative growth rate? 3. What is the “take home message” from figure 12-5 (page 256)? 4. Figure 12-9: What part of the world has had the largest decline in total fertility rates (not the lowest TFR but the largest drop). 5. Figure 12-12: When did the United States achieve the replacement level fertility rate? 6. Figure 12-13: During what years did the “baby boom” occur? 7. Rank from 1-5 the five factors that you think have the greatest effect on a country’s fertility rate. Be prepared to defend your top choice. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 8. What are the two most useful indicators of the overall health of the human population in a given country? 1. 2. 9. Figure 12-16. What is the only 100% effective birth control method? 10. What factors contribute to the relatively high infant mortality rates in the United States? a. b. 12-2 Population Age Diagrams 11. Look at Figure 12-21: In your opinion, what are the 3 most important differences in the demographic indicators (shown in the graph) between the United States (highly developed) and Nigeria (less developed)? 1. 2. 3. 12. Briefly define and indicate when each occurred of each of the following groups. a. baby boom: when: b. baby bust (generation x): when: c. echo-boom: when: 13. Briefly describe two harmful effects if population decline occurs too rapidly. 1. 2. 12-3 Solutions 14. Name two countries that allow large increases in population due to immigration. a. b. 15. According to many ecologists: If we cannot lower population growth by lowering birth rates we are deciding by default to (name two things). 1. 2. 16. Answer each of the following questions based upon the demographic transition model: a. What contributes to a low rate of population growth during the preindustrial stage? b. What factors contribute to an increased growth rate of a population during the transitional stage: c. Compare the birth rate to the death rate during the industrial stage: d. What percentage of the world’s population lives in a country with negative population growth? 17. Explain how each of the following may help to reduce birth rates: a. Empowering women: b. Economic Rewards: 12-4 (page 271) 18. Briefly describe three ways China has encouraged its population to lowers the country’s birth rate. 1. 2. 3.