* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Confederate States of America wikipedia , lookup
Capture of New Orleans wikipedia , lookup
Hampton Roads Conference wikipedia , lookup
Opposition to the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Texas in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Lost Cause of the Confederacy wikipedia , lookup
Economy of the Confederate States of America wikipedia , lookup
Conclusion of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Secession in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Commemoration of the American Civil War on postage stamps wikipedia , lookup
Origins of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Virginia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Union (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Tennessee in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Alabama in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Border states (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Mississippi in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
United States presidential election, 1860 wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
South Carolina in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
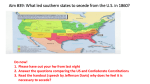
25 Topic: States' Rights Slavery Standard: Describes views about states' rights and slavery and analyzes reasons for secession. 26 Topic: Civil War Standard: Analyzes Georgia's role in the Civil War and outlines the impact of the war on the state and nation. Study Buddy A 1. The __________ (North or South) thought that states that voluntarily joined the Union/United States could voluntarily leave it (secede). 2. While ________________ tended to favor the doctrine of States’ Rights, this view was less popular in the ___________ regions of Georgia, Tennessee and the Carolinas. 3. Senator ____________ from South Carolina led those that believed in nullification. 4. Why did Georgia back away from the idea of nullification? 5. Economically, why did the North have less to gain from slavery than the South? 6. In the Compromise of 1820, ___________ was admitted as a free state while _________ was admitted as a slave state. Also, in the future, slavery would be prohibited north of latitude _______. 7. In which state was gold discovered in 1849? _____________ This led, in part, to the Compromise of __________. 8. Define popular sovereignty. 9. As cotton production increased, the price of slaves ________. 10. Abolitionist William Lloyd Garrison published a newspaper, the _________, that was illegal to be found in Georgia. 11. In Virginia, a slave revolt led by _____ ________, caused fear among southern whites that caused the restriction of slaves communicating with each other in any form. 12. How many slave revolts were there in the state of Georgia? 13. What were the years of the Civil War in America? 14. The 3 immediate causes of the American Civil War included: 1)_________________, 2)_________________________, and 3)____________________________. 15. GA’s Ordinance of Secession proclaimed 3 things for the state of Georgia. They were: 1)__________________________, 2)______________ and 3)_________________. 16. Pres. Abraham Lincoln thought secession by a state was _______________. 17. The Confederacy’s President was ________________ ___________ and Vice-President was ________________ _____________ of the state of __________. 18. The Confederate government prepared to take control of all US __________ bases in the South, but the US officials refused to turn them over to the Confederacy. A base near Charleston, at __________ ______________, South Carolina twice rejected Confederate demands for them to withdraw. On April 12, 1861, the war began with shots fired by _____________ forces. An hour later, the _______________ flag came down and the __________ flag was raised. 19. Pres. Lincoln declared a _________ blockade of the South 20. The Confederate government moved its capital to _________, ___. 21. The western part of Virginia seceded and joined the Union as the new state of ___ ____. 22. In early 1861, the _____ believed that the people of the North would have no stomach for fighting and would not support ________. The ______ believed their huge advantages of industry and resources would mean a swift military victory. Answers/Hints for Study Buddy B 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. North States could determine if a law passed by US Congress was null and void (wrong). North, South colony, Georgia colony South, North Spanish-American War. From Texas all the way to the Pacific Ocean free, Fugitive Slave Law, popular sovereignty Supporters of both abolition and slavery rushed to Kansas to “vote” as a new citizen and in the process, the raids on opposing settlements were so violent, the new state was called “Bleeding Kansas” and the idea of popular sovereignty for deciding upon slavery/abolition in a new state was stopped. Liberia Underground Railroad Uncle Tom’s Cabin running away slavery, economics and states’ rights $1 million, war Ordinance of Secession Confederacy, Confederate States of America Thomas R.R. Cobb rebellion, 3 years South Carolina, Georgia, Alabama, Florida, Mississippi, Louisiana, Texas, Virginia, Arkansas, North Carolina, Tennessee border states wrong, 4 years, 600,000 soldiers died 25 Topic: States' Rights Slavery Standard: Describes views about states' rights and slavery and analyzes reasons for secession. 26 Topic: Civil War Standard: Analyzes Georgia's role in the Civil War and outlines the impact of the war on the state and nation. Study Buddy B 1. The ____________ (North or South) thought that states that voluntarily joined the Union/United States would be behaving unconstitutionally/illegally if they left the Union. 2. Define nullification. 3. In looking at the territories in the West, the _____________ favored developing roads and canals at federal government expense while the _____________ did not want government money spent to develop the West. 4. Every ____________ had allowed slavery, although officially, the practice was banned in the __________ colony until 1749. 5. The __________ wanted territories in the West to become slave states while the ____________ wanted the Western territories to become free states. 6. When the US and Mexico went to war (name the War: ______________________), the US won and Mexico ceded the land from ___________ to the __________ Ocean. 7. In the Compromise of 1850, California came in the Union as a ________ state (for the North) while the South got the _____________ __________ Law passed. Also, it was decided that any new state would decide itself to be a free or slave state by ______________ ______________. 8. The territories of Nebraska and Kansas were to be admitted to the US and decide upon slavery by popular sovereignty. What happened to end the idea of new states deciding upon slavery by popular sovereignty? 9. In 1816, the ________________ ______________ Society created a new colony/later a nation in West Africa for freed people of color called ______________. 10. Abolitionists including Harriet Tubman created a network of people and places to aid escaped slaves in moving to free states. This network was called the ________ _______. 11. Harriet Beecher Stowe wrote a novel about slave life in the South called ________ __________ __________. 12. While some slaves did resist by working slowly, stealing, pretending sickness or revolting, many times the resistance was in the form of the slave ______ _______. 13. In short, what were the 3 fundamental causes of the Civil War? 14. On Nov. 6, 1860, Abraham Lincoln was elected US President. On Nov. 16, 1860, the Georgia General Assembly voted $____ to defend Georgia. GA’s Governor Brown did not think this would lead to _____. 15. Debate went on in GA over whether GA should secede from the Union. After a vote taken on Jan. 19, 1861, GA adopted the ___________ of ___________ by a 208 to 89 margin. 16. GA’s General Assembly had recommended that the seceding states should form a ____________________. (It’s first capital was in Montgomery, Alabama.) 17. ____________________ was an Athens, GA lawyer that modeled the Confederate Constitution after the US Constitution, but gave states many more powers than the federal government. 18. At first, Pres. Lincoln called for 75,000 volunteers to fight for 3 months to put down the Confederate ___________. Within a month, the call was raised for volunteers to serve for ____ years. 19. List the Confederate states. 20. Four slave-holding states of Delaware, Kentucky, Maryland and Missouri were called ___ states. 21. Both sides were ______ because the Civil War lasted ___ years and _________ southern and northern soldiers were killed. Answers/Hints for Study Buddy A 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. South Southerners, mountain Senator John C. Calhoun Because the antebellum President, Andrew Jackson who had “helped” the state by removing the Cherokees from Georgia, was against the idea of nullification. .. So, Georgia supported Pres. Jackson’s view The economy of the North was based on industry and small-scale farming, not plantation farming as in the South. Maine, Missouri, 36 30 California, Compromise of 1850 Popular sovereignty is when the people (of a state) decide for themselves about an issue or law. rose The Liberator Nat Turner zero 1861-1865 (4 years) 1)Abolitionists John Brown’s raid at Harper’s Ferry, VA 2)Abraham Lincoln’s election in 1860 as President 3) secession of Southern states just before the war Georgia was: 1)repealing the ratification of the US Constitution which it had signed in 1788, 2) dissolving it’s membership in the union known as the United States and 3)Georgia would enjoy all rights that belong to any free and independent nation illegal or unconstitutional President Jefferson Davis and Vice-President Alexander Stephens of Georgia military bases, Fort Sumter, South Carolina, Confederate, US/Stars & Stripes, Confederate/Stars & Bars naval blockade of all southern ports, Richmond, Virginia West Virginia South, Abraham Lincoln, North