* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Advanced Math - January 2013
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
Advanced Math - January 2013
Name_________________________________________
Hour________________ Date______________
Preliminary Chapter (Chapter P)
Use
1.
and
to find the indicated intersection or union.
2.
Graph each interval and write the interval in set-builder notation.
3.
4.
5.
Graph each set and write the set in interval notation.
6.
7.
8.
Evaluate or simplify each expression.
9.
11.
when
10.
and
12.
when
, and
Evaluate or simplify each exponential expression.
15.
14.
13.
16.
17.
18.
19.
22.
23.
24.
20.
21.
Evaluate or simplify each exponential
25.
expression.
26.
27.
Simplify each radical expression. Assume variables represent real numbers.
28.
29.
30. b
31.
33.
32.
Perform the indicated operation and express the result in standard form.
35.
34.
37.
36.
Factor the following.
38.
39.
40.
Factor the following.
41.
43.
42.
Simplify each rational expression.
44.
45.
46.
47.
Perform the indicated operation and write the answer in simplest form.
48.
49.
50.
51.
52.
53.
54.
55.
56.
57.
58.
59.
Perform the indicated operation and
60.
write the answer in simplest form.
61.
62. Factor:
Chapter 1
Solve the following equations. Check your solutions.
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7. Is the following a contradiction, a
conditional or an identity?
8. Is the following a contradiction, a
conditional or an identity?
9. Is the following a contradiction, a
conditional or an identity?
Given the graph of a quadratic equation, estimate the solutions (zeros/roots).
10.
11.
12.
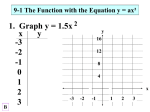
Graph the following quadratic equations and estimate the solutions (zeros/roots).
13.
14.
15.
Solve the following quadratics by factoring.
16.
17.
18.
Solve the following quadratics by
19.
factoring.
20.
21.
Solve the following quadratics using square roots.
22.
23.
24.
Solve the following quadratics by completing the square.
25.
26.
27.
Solve the following quadratics by
28.
completing the square.
29.
Solve the following quadratics using the quadratic formula.
31.
32.
30.
33.
Find the value of the discriminant. Describe the type of roots for the following quadratics.
34.
35.
36.
Solve each equation. Be sure to check your solution(s).
37.
38.
39.
40.
41.
42.
Solve each equation.
43.
Be sure to check your solution(s).
44.
State the excluded value for each equation and then solve.
46.
47.
Excluded Value(s):
Excluded Value(s):
49.
Excluded Value(s):
45.
48.
Excluded Value(s):
50.
Excluded Value(s):
Chapter 2
Section 2.1
Find the distance between the set of points.
1. (6, 4) and (-8, 11)
2. (40, 32) and (36, 20)
1.)_________________
2.)_________________
Find the midpoint between the set of points
3. (6, 4)� and (-8, 11)
3.)________________
4. (40, 32) and (36, 20)
4.)________________
5. (12, −2)� and (7, 2)
6. (5, 3)� and (-6, 9)
5.)________________
6.)________________
Determine the center and radius of the circle with the given equation.
7. (x - 3)2 + (y + 7)2 = 64
8. (x + 8)2 + y2 = 81
Center:________________
Center:________________
Radius:________________
Radius:________________
9. (x - 8)2 + (y - 9)2 = 13
Center:________________
Radius:________________
10. (x - 2)2 + (y - 7)2 = 17
Center:________________
Radius:________________
Find an equation of a circle that satisfies the given conditions. Write your answer in standard form.
11. Center (-5, 2) and radius 7 12. Center (4, -3) and radius 12
11.)______________________
12.)______________________
Find an equation of a circle that satisfies the given conditions. Write your answer in standard form.
13. Center ( 1, 3�), passing through (4, -1). �
13.)______________________
14. Center(-2, 5), passing through (1, 7�)
14.)______________________
Find an equation of a circle that satisfies the given conditions. Write your answer in standard form.
15. The circle has a diameter with endpoints (2, 3) and (-4, 11)
15.)_______________________
16. The circle has a diameter with endpoints (-2, 3) and (4, 3). �
16.)_______________________
Sections 2.2-2.3
State whether the equation defines y as a function of x.
18. y = x2
17. 2x + 4y = 8
17.)_______________
18.)_______________
20. y = x 3
19. y = 3 x�
19.)_______________
20.)_______________
State whether the set of ordered pairs defines y as a function of x.
22. {(6, 3), (-7, 3), (8, 3), (9, 3)}
21. {(5, 2), (3, 7), (4, -3), (5, 6)}
21.)______________
22.)________________
Evaluate the function.
23. Given f (x)
x2 5 .
a. f(-2)
23a.)_______________
b. f(0)
c. f(3)
23b.)_______________
23c.)_______________
Evaluate the function.
24. Given f(x) = 3x2 +1
a. f(-2)
24a.)_____________
b. f(0)
c. f(3)
24b.)_____________
24c.)_____________
Determine the domain of the function represented by the given equation.
25.)______________
26. f(x) = x2 – 5x
25. f(x) = 2x + 5
26.)______________
Determine the domain of the function represented by the given equation.
27. f (x) 6 x
28. f (x)
x 3
27.)______________
28.)______________
29. f (x)
4
x 6
30. f (x)
7
�
x 8
29.)______________
30.)______________
Find the real value or values of 𝒂 in the domain of 𝒇 for which f(a) equals the given number.
31. f(x) = 3x – 2; f(a) = 8
32. f(x) = 2 - 5x; f(a) = 7
31.)______________
32.)______________
33. 𝑓 𝑥� = 𝑥�2� − 3; 𝑓 𝑎� = −4
34. 𝑓 𝑥� = 𝑥�33. f(x) = x2 + 2x - 2; f(a) = 1
2|; f(a) = 6
33.)______________
34. f(x) = |x +
34.)______________
Find the zeros, or x-intercepts, of f(x).
35. f(x) = 3x + 2
36. f(x) = 6 + 2x
35.)______________
36.)______________
37. f(x) = x2 – 5x – 24
38. f(x) = x2 + 4x - 21
37.)______________
38.)______________
Find the slope of the line through the given points.
39. (8, -2), (-4, 10)
40. (-2, -7), (4, -9)
39.)______________
40.)______________
Graph 𝒚 as a function of 𝒙 by finding the slope and y-intercept of each line.
41. 𝑦 = −3𝑥 +
42. 𝑦 =
41.) slope=________
41.) y-int.=_________
42.) slope=________
42.) y-int.=_________
43. 2𝑥 − 3𝑦 = 12
44. −3𝑥 + 5𝑦 = −15
43.) slope=________
43.) y-int.=_________
44.) slope=________
44.) y-int.=_________
Find the equation of the indicated line in slope-intercept form.
45. y-intercept = (0, -5), slope = -17
46. y-intercept = (0, 2), slope = 6
45.)______________
46.)______________
47. Through (4, -6), slope = 12
48. Through (-5, -1), slope = -3
47.)______________
48.) _____________
47. Through (4, -6), slope = 1�
Find the equation of the indicated line in slope-intercept form.
49. Through (5, -6) and (2, -8)
50. Through (-5, 6) and (-3, -4)
49.)______________
50.)______________
Find the equation of the line, in slope-intercept form, that satisfies the given conditions.
51. The graph is parallel to the graph of 𝑦 = − 𝑥 + and passes through the point
whose coordinates are (-4, 2).
52. The graph is parallel to the graph of
51.)______________
3�𝑥 − 1 and passes through the point
whose coordinates are (-3, -5).
52.)______________
53. The graph is perpendicular to the graph of 3𝑥 − 2𝑦 = 5 and passes through
the point whose coordinates are (-3, 4).
53.)______________
54. The graph is perpendicular to the graph of 𝑦 = −𝑥 + 3 and passes through
the point whose coordinates are (-5, 2).
55. Use the Vertical Line Test to determine which of the following graphs are functions.
Write the letters of the graphs that ARE functions in the blank.
54.)______________
55.)______________
A.
B.
C.
D.
Use the indicated graph to identify the intervals over which the function is increasing, decreasing or constant.
56.
57.
Use the indicated graph to identify the intervals over which the function is increasing, decreasing or constant.
58.
59.
Section 2.4 & Quadratic Transformations
Use the equation of the quadratic function to determine (a) the vertex, (b) the max or min value of the vertex, (c) if the
vertex is a max or min (circle either max or min), and (d) the equation for the axis of symmetry.
60. y 3 x 7 12
61. y ( x 4) 2 6
a.)____________________
a.)____________________
2
[vertex]
[vertex]
b.)____________________
2b.)____________________
[max or min value]
c.) max / min
[max or min value]
c.) max / min
[circle one]
d.)___________________
[circle one]
d.)___________________
[axis of symmetry]
[axis of symmetry]
Use the method of completing the square to find the standard form of the quadratic function.
62. y x 2 14 x 12
63. y x 2 8 x 12
63.)_____________________
64.)_____________________
Use the method of completing the square to find the standard form of the quadratic function.
66. y 2 x 2 8 x 17
65. y 5x 2 20 x 7
65.)_____________________
66.)_____________________
67. y 3x 2 12 x 8
68. y 4 x 2 32 x 10
67.)_____________________
68.)_____________________
Use the vertex formula 𝒙 =
to determine the vertex.
79. 𝑓 𝑥� = 𝑥�69. f(x) = –x2 + 4x +1
Vertex:_________________
70. f(x) = x2 -10x
69.
80. 𝑓 𝑥� = − 𝑥�
Vertex:_________________
70.
Find the maximum or minimum value of the function. State whether it is a maximum or a minimum. Find the range
of the function.
71. f(x) = -x2+ 6x + 2
71.
Max/Min Value:_________________
Max. / Min.
(circle one)
Range:_______________________
72. f(x) = x2+ 10x - 3
72.
Max/Min Value:_________________
Max. / Min.
(circle one)
Range:_______________________
Use the parent function f(x) = x2 to graph the quadratic function 𝒈(𝒙). Identify the vertex of g(x).
73.)
g(x) = -(x + 2)2 - 4
74.)
g(x) = (x -5 )2 + 4
Vertex: g (x ) :_____________
Vertex: g (x ) :_____________
75.)
g(x) = 2(x - 1)2 - 3
Vertex: g (x ) :_____________
76.)
g(x) =
(x + 3)2 - 5
Vertex: g (x ) :_____________
Section 2.6
77. Let f(x) = 3x3 – 4x2 +3 and g(x) = 2x2 – 6. Find the following:
a) (f – g)(x)
b) (f + g)(x)
c) (f + g)(7)
77a. _______________
77b. _______________
77c. _______________
78. Let f(x) = 3x +2 and g(x) = 2x – 4. Find the following:
a) (f+ g)(x)
b) (f g)(x)
c) (f –g)(-4)
78a.________________
78b. _______________
78c. _______________
2
79. Let f(x) = 4x -3 and g(x) = x +7. Find the following:
a) (f(g(x))
b) g(f(x))
c) f(g(3))
80. Let f(x) = 3x2 and g(x) = 6x -10. Find the following:
a) (f(g(x))
b) g(f(x))
c) g(f(4))
Chapter 3
Use Synthetic Division to divide the first polynomial by the second.
1.
2.
3.
4.
Use Synthetic Division and the Remainder Theorem to find
.
5.
6.
Synthetic Division:
Synthetic Division:
Remainder Theorem:
Remainder Theorem:
Use Synthetic Division and the Factor Theorem to determine whether the given binomial is a factor of
7.
.
8.
Use Synthetic Division to show that is a zero of .
9.
10.
Examine the leading term and the degree of the polynomial to determine the far-left and far-right behavior (end
behavior) of the graph of the polynomial function.
11.
12.
13.
14.
Use the graph below to identify the relative maximum and/or relative minimum values of
.
15.
16.
Relative Maximum:_________________________
Relative Maximum:_________________________
Relative Minimum:_________________________
Relative Minimum:_________________________
Find the real zeros of the polynomial function by factoring. Identify the multiplicity of each zero.
17.
18.
Find the real zeros of the polynomial function by factoring. Identify the multiplicity of each zero.
19.
20.
Use the Intermediate Value Theorem to verify that
has a zero between
.
21.
22.
Determine the x-intercepts of the graph of
Theorem to determine whether the graph of
. For each x-intercept, use the Even and Odd Powers of
crosses the x-axis (passes through) or intersects but does not cross
the x-axis (hits and bounces).
23.
24.
Sketch the graph of #23 and #24. Do not use a graphing calculator.
25.
26.
Use the Rational Zero Theorem to list the possible rational zeros for each polynomial function. Then find ALL the zeros
(real and/or imaginary). Don’t forget to check for multiplicities!
27.
28.
29.
30.
Find a polynomial function of lowest degree with integer coefficients that has the given zeros.
31.
32.
33.
34.
Chapter 4
Use composition of functions to determine whether
and
1.
2.
3.
4.
are inverses of each other.
Find the inverse of the function. If the function does not have an inverse function, write “no inverse function.”
5.
Find
7.
6.
. State any restrictions on the domain of
.
8.
9.
10.