* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Geometry Content Standards Worksheet
Regular polytope wikipedia , lookup
Tessellation wikipedia , lookup
Technical drawing wikipedia , lookup
Golden ratio wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Reuleaux triangle wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
Area of a circle wikipedia , lookup
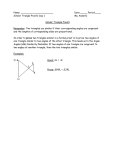
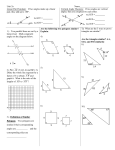
Geometry Mathematics Content Standards Students will: 1.0 Understand undefined terms, axioms, theorems, and inductive and deductive reasoning 2.0 Write geometric proofs, including proofs by contradiction 3.0 Construct and judge the validity of a logical argument; use counterexamples to disprove a statement 4.0 Prove basic theorems involving congruence and similarity 5.0 Prove that triangles are congruent or similar, and utilize the concept of corresponding parts 6.0 Know and be able to use the triangle inequality theorem 7.0 Prove and use theorems involving the properties of parallel lines cut by a transversal, the properties of quadrilaterals, and the properties of circles 8.0 Derive and solve problems involving the perimeter, circumference, area, volume, lateral area, and surface area of common geometric figures 9.0 Compute the volumes and surface areas of prisms, pyramids, cylinders, cones, and spheres; and memorize the formulas for prisms, pyramids, and cylinders 10.0 Compute the areas of polygons, including rectangles, scalene triangles, equilateral triangles, rhombi, parallelograms, and trapezoids 11.0 Determine how changes in dimensions affect perimeter, area, and volume of geometric figures/solids 12.0 Find and use measures of sides and of interior and exterior angles of triangles and polygons to classify figures and solve problems 13.0 Prove relationships between angles in polygons by using properties of complementary, supplementary, vertical, and exterior angles 14.0 Prove the Pythagorean theorem 15.0 Use the Pythagorean theorem to determine distance and find lengths of sides of right triangles 16.0 Perform basic constructions with a straightedge and compass 17.0 Prove theorems by using coordinate geometry 18.0 Know the definitions of the basic trigonometric functions defined by the angles of a right triangle 19.0 Use trigonometric functions to solve for the sides and angles of a triangle 20.0 Know and be able to use angle and side relationships in special 3060-90 and 45-45-90 triangles 21.0 Prove and solve problems regarding relationships among chords, secants, tangents, inscribed angles, and inscribed and circumscribed polygons of circles 22.0 Know the effect of transformations on figures in the coordinate plane and space, including rotations, translations, and reflections NAME_______________________________________ DATE____________________ Geometry Content Standards Worksheet 1.0 Using what you know about parallel lines cut by a transversal, show that the sum of the angles in a triangle is the same as the angle in a straight line, 180 degrees. 2.0 Prove that if two parallel lines are cut by a transversal, then consecutive angles are not complementary. 3.0 True or false: A quadrilateral is a rectangle only if it is a square. 4.0 Prove that if two legs of one right triangle are congruent to two legs of another right triangle, then the triangles are congruent. 5.0 A X , B Y , AB XY prove BC YZ 6.0 Given a triangle with sides 11 and 17, between what two values must the length of the third side be? 7.0 Prove that if the base angles of a trapezoid are congruent, then the trapezoid is isosceles. 8.0 An equilateral triangle is inscribed in a circle of radius 12. Find the difference of the areas of the these two figures. 9.0 Find the total surface area and volume of a prism whose base is a regular hexagon with each side measuring 8 m. and whose height is 10 m. 10.0 A trapezoid with bases of length 12 and 16 is inscribed in a circle of radius 10. The center of the circle lies inside the trapezoid. Find the area of the trapezoid. 11.0 Soap powder is packed in cube-shaped cartons. A carton measures 10 cm on each side. The company decides to increase the length of each edge of the carton by 10 percent. How much does the volume increase? 12.0 A regular polygon has exterior angles, each measuring 10 degrees. How many sides does the polygon have? 13.0 Prove that if the diagonals of a quadrilateral bisect each other, then the quadrilateral is a parallelogram. 14.0 Prove that for any right triangle, the sum of the squares of the length of the legs is equal to the square of the length of the hypotenuse. 15.0 The bottom of a rectangular box is a rectangle with a diagonal whose length is 16.0 Construct a 45 degree angle using a straightedge and compass. Given triangles ABC and XYZ with 4 3 inches. The height of the box is 4 inches. Find the length of a diagonal of the box. 17.0 Use a coordinate proof to show that the median of an isosceles trapezoid has a length equal to one half the sum of its bases. 18.0 Without a calculator, determine which is larger, tan 60 or tan 70 and explain why. 19.0 In a right triangle, one leg measures 5 cm. The angle opposite the leg is 70 degrees. Find the length of the other leg. 20.0 Each side of the regular hexagon ABCDEF is 10 cm long. What is the length of the diagonal AC? 21.0 Two circles, with centers A and B intersect at points P and Q. Circle A has a radius of 7 cm and Circle B has a radius of 10 cm. If the length of the common chord PQ is 8 cm, what is the length of the segment AB that joins the two radii? 22.0 A translation maps A(2,-3) onto A’(-3, -5). Under the same translation, find the coordinates of B’, the image of B(1, 4).