* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download MT2SPRING2013withAnswers
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
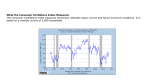
Spring 2013 May 14, 2013 Econ 100 Midterm Examination #2 Name: ______________________________________________ FOR FALL 2014 IGNORE QUESTIONS 41 to 50. Instructions : Please: Absolutely, positively, definitely, NO QUESTIONS during the exam. NO EXCEPTIONS. The exam is 60 minutes. It is a closed-book exam. Please store away all your notes notebooks and books in your bag or under your seat. You cannot leave the classroom for any reason during the exam. Please inspect the exam and make sure you have all 6 pages of questions. Cheating will result in F grade and disciplinary action. Please do not look at or copy from another student’s exam paper, let another student copy from your exam paper. Please do not talk or otherwise communicate with another student in any way during the exam. You can only have your pen, pencil and eraser with you. Put everything else to a place that you cannot reach. Use of any electronic device (including calculators, mobile phones, Google Glasses, etc.,) is prohibited during the exam. Please turn off your phone and put it away during the exam. For each multiple choice question you will receive 2 points if your answer is correct, 0 point if it is wrong, and 1/2 point if you unambigously leave it blank. Good Luck! Total 1 According to TUIK reports, in 2012 in Turkey, the adult population was 55 million, 28 million of which were not in the labor force. The number of unemployed was 2,7 million. The unemployment rate in Turkey in 2012 is about a. 15 percent b. 20 percent c. 5 percent d. X 10 percent 2 If an unemployed person quits looking for work, other things being equal, the unemployment rate a. stays the same, and the participation rate decreases. b. X decreases, and the participation rate decreases. c. and the labor-force participation rate stay the same. d. decreases, and the participation rate increases. 3 Müjde is a full-time housewife, Salih is a full-time student. She is 34, he is 21. They are not looking for a job. According to official statistics, a. both are counted as unemployed b. X both are counted as not in the labor force c. Müjde is employed, Salih is not in the labor force d. Müjde is employed, Salih is unemployed 4 The labor-force participation rate in the Turkish adult population (ages 16 and over) is about a. X 50 percent. b. 75 percent. c. 30 percent. d. 80 percent. 5 The labor force equals the a. X number of people employed plus the number of people unemployed. b. number of people who are employed. c. number of people who are unemployed. d. adult population. 6 Suppose that in some state the adult population is 4 million, the labor-force participation rate is 75%, and that 0.25 million people are unemployed. What is the unemployment rate to the nearest tenth? a. 7.7% b. X 8.3% c. 9.1% d. 6.3% 7 The labor-force participation rate measures the percentage of the a. labor force that is employed. b. total adult population that is employed. c. X total adult population that is in the labor force. d. labor force that is either employed or unemployed. 8 a. b. c. d. X Which of the following definitions is correct? Labor force = population - number of unemployed. Labor force = number of employed. Unemployment Rate=(number of unemployed÷[number of employed + number of unemployed])x100. Unemployment Rate = (number of unemployed ÷ adult population) x 100. 9 Over the last 40 years countries had experienced very different average growth rates in their GDP per capita. The range in the growth rates has been from _________ . a. 0 to 2 percent b. 3 to 6 percent c. 2 to 5 percent d. X 0 to 7 percent 10 The key determinant of a person’s standard of living in a country is a. its growth rate of real GDP. b. the total amount of its physical capital. c. X labor productivity, which is defined the quantity of goods and services produced by one hour of labor time. d. the total amount of goods and services produced within the country. 11 Per capita GDP in poorest countries like Rwanda and Chad a. is 1/5th of that in the richest countries like Singapore and Norway. b. X is 1/50th of that in the richest countries like Singapore and Norway. c. is 1/10th of that in the richest countries like Singapore and Norway d. is 1/20th of that in the richest countries like Singapore and Norway. 12 Which of the following statements is accurate? a. X All of the above are correct. b. In countries that have high GDP per person, people typically live into their late seventies, while in poor countries, people typically live only until their fifties or early sixties. c. In countries that have low GDP per person have higher infant mortality rates, higher maternal mortality, and higher rates of child malnutrition than do rich countries. d. In countries that have high GDP per person, almost all citizens can read, while in poor countries, about half the population is illiterate. 13 Which of the following will increase productivity? a. an increase in the level of technology b. an increase in the workers’ level of skills and knowledge gained by education, training, and work experience c. X All of the above. d. an increase in the physical capital stock per worker 14 Human capital is the a. total number of hours worked in an economy. b. X knowledge and skills that workers acquire through education, training, and experience. c. same thing as technological knowledge. d. stock of equipment and structures that is used to produce goods and services. 15 In a closed economy, national saving equals a. private saving plus public saving. b. income minus the sum of consumption and government purchases. c. X All of the above are correct. d. investment. 16 Institutions and markets in the economy that help to match one person's saving with another person's investment are called the a. banking system. b. loanable funds market. c. X financial system. d. monetary system. 17 In a closed economy, private saving is a. the amount of tax revenue that the government has left after paying for its spending. b. the amount of income that businesses have left after paying for the factors of production. c. always equal to investment. d. X the amount of income that households have left after paying for their taxes and consumption. 18 Which of the following would a macroeconomist consider as investment? a. X Zeynep buys a newly constructed building for her new restaurant. b. All of the above are correct. c. Veli buys Arçelik shares at the IMKB, Istanbul Stock Exchange. d. Ali puts some of his monthly income into a bank. 19 Suppose that in a closed economy GDP is equal to 11,000, Taxes are equal to 1,500, Consumption equals 7,500, and Government purchases equal 2,000. What is national saving? a. None of the above is correct. b. –500 c. X 1500 d. 0 20 A government has a budget deficit when government expenditure G is larger than taxes T. An increase in the size of the budget deficit a. makes investment spending rise. b. X makes investment spending fall. c. may increase, decrease, or not affect investment spending. d. does not affect investment spending. 21 In the language of macroeconomics, investment refers to a. the purchase of stocks, bonds, or mutual funds. b. saving. c. X the purchase of new capital, which is machinery, tools and equipment etc. d. All of the above are correct. 22 GDP does not include a. X All of the above are correct. b. the value of leisure (=free time). c. the quality/cleanliness of the environment. d. the value of goods and services we produce at home. 23 For the purpose of calculating GDP, investment is spending on a. real estate, housing, gold, and financial assets. b. gold, silver, stocks, bonds, and other financial assets. c. capital equipment, inventories, and structures, excluding household purchases of new housing. d. X new capital equipment, inventories, and structures, including household purchases of new housing. 24 25 years ago a country had nominal GDP of $1,000, a GDP deflator of 200, and a population of 100. Today it has nominal GDP of $3,000, a GDP deflator of 400, and population of 150. What happened to the real GDP per person? a. It decreased. b. It increased, but it less than doubled. c. X It was unchanged. d. It more than doubled. 25 If nominal GDP rises from one year to the next, then we can say that a. the market prices of goods and services must be higher. b. employment or productivity must be rising. c. the economy must be producing more goods and services. d. X either the economy must be producing more goods and services, or the prices are higher, or both. 26 Gross domestic product GDP is defined as a. the market value of all goods and services sold by the domestic firms in a given period of time. b. the market value of all final goods and services produced in a country minus the country’s debt to foreigners. c. the total quantity of all manufactured goods consumed in a country in a given period of time. d. X the market value of all final goods and services produced in a country in a given period of time. 27 In GDP, household spending on education is included in a. Household spending on education is not included in any component of GDP. b. investment. c. X consumption, although we can say that it fits better in investment. d. government spending, because most students go to publicly-supported schools and universities. 28 In 2011, Turkey’s GDP was 1,300 billion TL; investment was 260 billion TL; government purchases were 190 billion TL; and net exports were –115 billion TL (negative 115 billion TL). It follows that consumption was a. 60 percent of GDP. b. 1,195 billion TL. c. X 965 billion TL. d. 1,415 billion TL. 29 In the equation Y = C + I + G + NX, a. X All of the above are correct. b. C represents household consumption expenditures on goods and services. c. I represents investment expenditures. d. Y represents the economy’s GDP, which also equals the total income of everyone in the economy. 30 In 2012, U.S. GDP was about _____, while the Turkish GDP was about ________ a. X $14 trillion, $750 billion (≈ 1400 billion TL). b. $44 trillion, $7,5 trillion (≈ 14 trillion TL). c. $4 trillion, $75 billion (≈ 140 billion TL). d. $4 trillion, $750 billion (≈ 1400 billion TL). 31 Line A shows ______, line B shows ________ . a. Turkey’s nominal GDP, Turkey’s real GDP with base year 1998 b. Turkey’s real GDP with base year 2002, Turkey’s real GDP with base year 1994. c. X Turkey’s real GDP with base year 1998, Turkey’s nominal GDP d. Turkey’s nominal GDP, Turkey’s real GDP with base year 2002 32 Over the last 75 years the average growth rate of Turkish real GDP per person has been approximately 2,7%. This means that real GDP per capita in Turkey doubled about every a. 35 years. b. 100 years on average. c. 70 years. d. X 25 years. 33 In the calculation of the CPI (Tüketici Fiyat Endeksi; TÜFE), tea is given greater weight than coffee if a. coffee is imported and tea is produced domestically. b. the price of coffee is higher than the price of tea. c. most coffee is of good quality, and tea is of low quality. d. X consumers buy more tea than coffee. 34 What basket of goods is used to calculate the CPI (Tüketici Fiyat Endeksi; TÜFE)? a. the least expensive goods and services in each product category b. X the goods and services that are typically bought by consumers as determined by government surveys c. only food, clothing, transportation, entertainment, and education d. a random sample of all goods and services produced in the economy 35 The Turkish CPI (base year 2003) was 140 in 2007, 155 in 2008, 164 in 2009, 178 in 2010, 190 in 2011, and 207 in 2012. We can say that the rate of inflation in Turkey during the last five years has been between ____%, which is _____ most other Eurozone countries in the same period. a. 2 and 5%, higher than b. X 5 and 10%, higher than. c. 2 and 5%, close to. d. 10 and 20%, higher than 36 If the consumer price index was 90 in year 1, 100 in year 2, and 95 in year 3, then the economy experienced a. 10 percent inflation between years 1 and 2, and 5 percent deflation between years 2 and 3. b. 11.1 percent inflation between years 1 and 2, and 5 percent inflation between years 2 and 3. c. X 11.1 percent inflation between years 1 and 2, and 5 percent deflation between years 2 and 3. d. 10 percent inflation between years 1 and 2, and 5 percent inflation between years 2 and 3. 37 In an imaginary economy, the average typical consumer buys 6 shirts and 4 pairs of pants. A shirt cost $20 in 2006 and $25 in 2007. A pair of pants cost $30 in 2006 and $40 in 2007. Using 2006 as the base year, which of the following statements is correct? a. The consumer price index is 134 in 2007. b. All of the above are correct. c. For the typical consumer, the number of dollars spent on shirts is equal to the number of dollars spent on pants in each of the two years. d. X The rate of inflation is 29.17% in 2007. 38 The Consumer Price Index – CPI (Tüketici Fiyat Endeksi- TÜFE) is a measure of the average prices of a. stocks traded on the Istanbul Menkul Kıymetler Borsası (İstanbul Stock Exchange). b. inputs purchased by a firms. c. X goods and services bought by a typical consumer. d. goods and services produced in the economy. 39 a. b. c. d. X The term inflation is used to describe a situation in which the economy is growing rapidly. incomes in the economy are increasing. stock-market prices are rising. the overall level of prices in the economy is increasing. 40 Suppose the CPI for Turkey was 900 in 1998, and currently the CPI is 19,000 (Yes. Nineteen thousand!!!). According to the CPI, 10TL in 1998 purchased approximately the same quantity of goods and services as a. X 211TL purchases today. b. 111 TL purchases today. c. 0.05 TL purchases today. d. 2111 TL purchases today. 41 Over the last 30 years, the Turkish economy has become, a. X a more open economy. b. more self-sufficient. c. less trade-oriented. d. a more closed economy. 42 Canada (the largest trading partner of the US) experiences an economic slowdown (recession, falling incomes, rising unemployment, etc.) Other things being equal a. US net exports will not change b. Canadian net exports will decrease c. US net exports will increase d. X US net exports will decrease 43 In the last 20 years, both Turkey and the United States had a. X almost every year a trade deficit. b. almost every year a trade surplus. c. balanced trade. d. trade deficits in some years and trade surpluses in some other years. 44 Korean car manufacturer Hyundai expands its production facilities in Izmit. This transaction will _________ Turkey’s net capital outflow, and is considered a foreign ______ investment. a. increase, direct b. decrease, portfolio c. X decrease, direct d. increase, portfolio 45 A country imports $250 billion of goods and services and exports $160 billion of goods and services. What is the value of net exports? a. $160 billion b. X –$90 billion c. $410 billion d. $90 billion 46 A country (such as Turkey) that has large trade deficits (NX < 0) also has ___ saving, relative to its investment, and is a net _____ of loanable funds in international financial markets. a. X low, borrower. b. low, lender. c. high lender. d. high, borrower 47 The U.S. is the domestic country. The nominal exchange rate is 2 Thai bhat for one U.S. dollar. A sandwich in the U.S. costs $6 dollars in the U.S. and 8 bhat in Thailand. The real exchange rate is a. X 2/3 b. 2/3 c. 8/3 d. 3/8 48 The nominal exchange rates are 120 yen per dollar, 0.8 euro per dollar, and 10 pesos per dollar. A bottle of beer in New York costs 6 dollars, 1,200 yen in Tokyo, 7.2 euro in Munich, and 50 pesos in Cancun. Where is the most expensive and the cheapest beer in that order? a. X Tokyo, Cancun b. Munich, New York c. Cancun, New York d. New York, Tokyo 49 France saves €1,000 billion and French net capital outflow is ‒€200 billion. French domestic investment (I) must be a. €1,000 billion. b. €200 billion. c. X €1,200 billion. d. ‒€200 billion. 50 A trade deficit means that the country as a whole is spending _______ its current income, AND is ____________ enough savings to finance its investment. a. less than, not generating b. X beyond, not generating c. beyond, generating d. less than, generating