* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download AC Machines 2 - Portal UniMAP
Spark-gap transmitter wikipedia , lookup
Power factor wikipedia , lookup
Power over Ethernet wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Wireless power transfer wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Audio power wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Electric power system wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Commutator (electric) wikipedia , lookup
Amtrak's 25 Hz traction power system wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Brushed DC electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Brushless DC electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Stepper motor wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
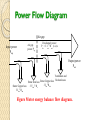
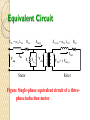
Syafruddin Hasan Motor input in stator Stator copper and iron losses Rotor input Rotor copper losse Mech Power developed or Gross Torque Windage and Friction losses Rotor output or BHP Power Flow Diagram Air gap Input power Psup Air gap power Pag Developed power Pdv = 3 Irot2 Rrot (1-s)/s Output power Pout Ventilation and loss friction losses Stator Iron loss Rotor Copper 3 Irot2 Rrot 3 Vsta2 / Rc Stator Copper loss 3 Ista2 Rsta Figure Motor energy balance flow diagram. Induction Motors Figure shows the energy balance in a motor. The supply power is: Psup Re(S sup ) Re 3 Vsup I * sta The power transferred through the air gap by the magnetic coupling is the input power (Psup) minus the stator copper loss and the magnetizing (stator iron) loss. The electrically developed power (Pdv) is the difference between the air gap power (Pag) and rotor copper loss. Induction Motors The electrically developed power can be computed from the power dissipated in the second term of rotor resistance: Pdv 3 I rot_t 2 1 s Rrot _ t s The subtraction of the mechanical ventilation and friction losses (Pmloss) from the developed power gives the mechanical output power Pout Pdv Pmloss Power and Torque in an IM From Fig.7-12 Input current : I1 = VΦ / Zeq Pcu Stator: Pscl = 3 I12R1 Core Losses : Pcore = 3 E12 Gc Air-gap power : PAG = Pin – Pscl – Pcore = 3I22R2/s Pcu Rotor: PRcl = 3 IR2RR = 3 I22R2 Note PAG : Pconv : PRCL = 1 : (1-s) : S Example 7-3 Induction Motors The motor efficiency: Pout Psup Motor torque (shaft load torque): T Pout m Equivalent Circuit X sta = sy L sta V sup Ista Stator R sta Irot_t X rot_m = rot L rot R rot Irot Rc Xm V sta V rot = s V rot_s Rotor Figure Single-phase equivalent circuit of a threephase induction motor. Induction Motors Xsta Vsup Rsta Ista Stator Rc Irot_t Xm Vsta Xrot Vrot_s Rrot/s Irot Rotor Figure Modified equivalent circuit of a three-phase induction motor. The rotor impedance is transferred to the stator side. This eliminates the transformer Induction Motors Xsta Vsup Rsta Ista Xrot_t Rc Xm Vsta Rrot_t/s Irot_t Stator Rotor Air gap Figure Simplified equivalent circuit of a three-phase induction motor. Induction Motors The last modification of the equivalent circuit is the separation of the rotor resistance into two parts: Rrot _ t s Rrot _ t 1 s R s rot _ t The obtained resistance represents the outgoing mechanical power 1 s R s rot _ t Blocked-Rotor test (cont…) Vblocked_ln Pblocked_A Vblocked 3 Pblocked 3 Vblocked_ln 21.939 V Re P Pblocked_A 2 160 W blocked_A I blocked The stator resistance was measured directly Rrot_t Re Rsta IM Design Classes NEMA & IEC : Class A: normal Tst, normal Ist, normal S Class B: normal Tst, low Ist, low S Class C: high Tst, low Ist, low S Class D: high Tst, low Ist, high S Class E: low Tst, normal Ist, low S Class F: low Tst, low Ist, normal S Starting Induction Motors Problems : - High Starting current - Low starting torque Determining of Istart Read the rated voltage, hp and code letter from name plate. Starting apparent power : Sstart = (rated hp)(code letter factor) Istart = Sstart / √3 VT Example 7-7 Q U I Z 04-10-2005 1. Why the circuit equivalent of an induction motor can be approached by equivalent circuit of a transformer and draw it 2. The output of a 3 phase induction motor is 9 kW. Rotor copper losses is 0.5 kW. Motor runs at 5 % of slip. Stator loss is 0.75 kW a). Calculate the mechanical power that converter by this motor b). Determine the input power c). Calculate the efficiency Speed Control of IM ns = 120 f / p by changing the electrical frequency (f) by changing the number of poles (p) (1) The methode of consequent poles (2) Multiple stator windings by changing the line voltage: n proportional to V2 by changing the rotor resistance Solid-state IM drives Motor Protection Over Current Protection Over Load Protection IM Ratings 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Output power Voltage Current Power Factor Speed Nominal efficiency NEMA design Class Starting Code Service Factor (SF)