* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download International Marketing
Marketing plan wikipedia , lookup
Market analysis wikipedia , lookup
Competitive intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Market penetration wikipedia , lookup
Darknet market wikipedia , lookup
Resource-based view wikipedia , lookup
First-mover advantage wikipedia , lookup
Global marketing wikipedia , lookup
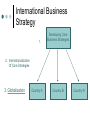
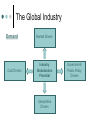
International Business Strategy 1. Developing Core Business Strategies 2. Internationalization Of Core Strategies 3. Globalization Country A Country B Country N International Marketing Dimensions I. II. III. IV. V. Controllable vs. Uncontrollable Standardization vs. Differentiation (Customization) Mode of Involvement (Function of firm’s size, skills, demand, control and risk issues) HQ vs. Subsidiary The Emergence of Trading Blocks The Global Industry Demand Cost Drivers Market Drivers Industry Globalization Potential Competitive Drivers Government/ Public Policy Drivers The Spectrum of International Marketing Involvement •Franchising •Licensing (Licensee Name) Licensing (Licensor Name) Joint Venture Inactive Exporting Proactive Exporting Turnkey Contract Less Involvement Strategic Alliance Management Contract Direct Investment More Involvement Contractual Relations/Arrangements OLI – Dunning Framework and Entry Mode Choice All firms select their entry mode strategies by CONSIDERING 3 VARIABLES: Ownership advantages which are less concerned with control/risk issues as related to inter-firm relationships Location advantages which are concerned with the resources commitment issue, as related to the availability and cost of resources Internalization advantages which are primarily concerned with reducing transaction and coordination costs. OLI – Dunning Framework and Entry Mode Choice Data suggest that the ability to differentiate products is more important to firms in determining entry mode choice than the strength of contractual risk. Also – investment risk is more important than market potential when assessing an entry mode. OLI – Dunning Framework and Entry Mode Choice Recent trend Non equity modes • Modes that are becoming increasingly popular among service firms for organizing overseas ventures/operations. These entry modes are essentially contractual and include leasing, licensing, franchising, and management service contracts. Note: Entry to a large extent is driven by the strategic objectives spelled out in the company’s global mission Licensing A contractual transaction whereby the firm – the licensor – offers some proprietary assets to the foreign company – the licensee – in exchange for royalty fees Assets: trademarks, technology knowhow, production processes, and patents. Royalties: typically between 1-15% Franchising The franchisor gives the franchisee the right to use the franchisor’s trade names, trademarks, business models, and/or knowhow in a given territory for a given time period, normally 10 years. A “package” to the franchisee might include the marketing plan, operating manuals, training and quality monitoring. Entry Decisions: Strategic Parameters Input Processes Output A strategic plan including: Mode of entry (risks control, legal issues) Operational and implementation programs Motivation(s) for entry Inventory of own resource Inventory of competitors’ resources Market intelligence IP protection Decision rules for site(s) selection Market Stage Infancy Developing 1. 2. 3. Customers Product Introduction Distribution Price Competitive Strategies (Types of after market) Mature Decision Criteria for Country Selection Market Size and Growth Risk (Political & Economic; Internal & External) Government Regulations Competitive Environment Local Infrastructure Country Classification Platform – gathering intelligence and establish a network (Singapore, Hong Kong) Emerging Market – Vietnam, Kazakhstan Growth Markets – The Czech Republic, China, Brazil Maturing Markets – Japan, Germany