* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download the geography of religion
Survey
Document related concepts
Islam and violence wikipedia , lookup
Islam and modernity wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of Islamism wikipedia , lookup
Soviet Orientalist studies in Islam wikipedia , lookup
War against Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Bangladesh wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Indonesia wikipedia , lookup
Islamic culture wikipedia , lookup
Morality in Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islamic schools and branches wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Mormonism wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Sikhism wikipedia , lookup
Schools of Islamic theology wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
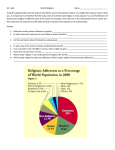
THE GEOGRAPHY OF RELIGION Geography 105, Week 10 Wednesday: The Walkabout Geography is deeply intertwined with our everyday lives. Geography is truly everywhere. “Taken-for-granted landscapes of our daily lives are full of meaning. Much of the most interesting geography lies in decoding them.” Cosgrove (1989:133) How are different cultures embedded in our landscape near PCC? Groups of 2-3 40-50 minute ‘Walkabout’ Photos to describe our landscape Residual Cultures—historic cultures that have disappeared or are in the process of fading away Emergent Culture—cultures that are just now appearing Excluded Cultures—those that are actively or passively excluded by the dominant culture Religion and Population What is religion? The structures set of beliefs and practices through which people seek mental and physical harmony with the powers of the universe Rituals provide milestones Birth Puberty Marriage Death Religion vs. Cult Cult—an unconventional belief system Often used perjoratively Rajneesh, Heaven’s Gate While not true, cults often considered religion outside of the mainstream Types of Relgion Proselytic religions Religions that actively seek to recruit new members and convert all of humankind—often grow out of ethnic religions Christianity and Islam Universalizing religions Also proselytic, seek to expand through active of new members Ethnic religions A religion identified with a particular ethnic/tribal group—do not seek converts Judaism Monotheism The worship of only one god Islam, Christianity, Judaism Types of religions, cont. Polytheism Syncretic religions Strand within most major religions that emphasizes plurity of faith and is not open to blending with others Literally right (ortho) teaching (doxy) Fundamentalism Religions that combine elements of two or more belief systems Brazilian Umbanda Orthodox religions Worship of many gods Haitian Vodun, pre-colonial American religions Movement which focuses on the return to founding principles, which often includes literal interpretation of religious texts or prophet Animism Retaining indigenous religions or traditions What kinds of areas are dominantly Animist? How does this relate to patterns of language and the distribution of indigenous peoples? Religions of the world geographically Religions of the world by population Christianity and Islam By the numbers Christianity—1.9 billion Islam—1.1 billion Hinduism—781 million Buddhism—324 million Sikhism—19 million Judaism—14 million Southwest Asia—A Cultural Hearth The three major world religions have similar origins Judaism—2000 BCE Christianity—26-36 CE Islam—610 CE Abrahamic religions Judaism, Christianity, Islam Venerate patriarch Abraham Cultural hearth: southeast Asia Judaism as parent of Christianity—Judeo-Christian Torah (Old Testament), prayer, clergy Judaism Monotheism One all knowing and all powerful god; created humans for bestowing kindness Torah Holy Book which comprises the first five books of the Hebrew Bible Covenant with Abraham—considered to be the father of the Jewish people Judaism, cont. Diaspora Refers to the forced dispersal of Jews from Palestine in Roman times Dispersal and spread as minority group to Europe, North Africa, Arabia Ashkenazim—Germany and France migrants Sephardim—Spain and Portugal migrants; expelled in 1492 Holocaust—systematic murder of Jewish people Killed 1/3 of world’s Jewish Population Migration: 6 million in N. America, 5 million in Israel Symbol: The Star of David Hexagram used since the 17th century Originally used as architectural element to symbolize synagogue Used in WWII to identify Jews Why does the snake figure in so many religious traditions? Christianity Heavily influenced by Judaism Monotheism—one all knowing and all powerful god Belief that Jesus Christ died for sins Salvation comes from the faith in God Book: Old Testament and New Testament of the Bible First four books of new testament written by Jesus followers Christianity, cont. God is a Trinity, consisting of Father, the Son, and the Holy Spirit Jesus as the incarnate son of God Branches Roman Catholics, Protestants, Eastern Christians Christians represent about 1/3 of the global population; Roman Catholics 1/6 What does this pattern tell us about the U.S.? Does the pattern in the Midwest and Great plains relate to the presence of ethnic islands? Islam Proselytic faith Extent: desert belt of Asia, N. Africa; tropics of Indonesia to Philippines Muslim—adherent of Islam Literal: “those who submit to the will of god” Allah—Muslim God Mecca—Muslim city where Muhammad was born Islam, cont. Founded by Muhammad, the last and most important in a line of prophets Angel Gabriel revealed name Allah to Muhammad in 610 CE. Qur’an, Islam’s holy book is text of revelations Serves as basis of Islamic Law, or Sharia 5 Pillars of Islam Belief in Allah, the one God whose prophet was Muhammad Pray 5 times daily at established times Give alms, or zakat, to the poor Fast from dawn until sunset during Ramadan Make at least one pilgrimage to Mecca Islam Bifurcation Shiite Muslims 16 percent of Muslims Majority in Iran and Iraq Belief that Ali, son-in-law of Muhammad to have succeeded Muhammad Sunni Muslims Islamic Orthodoxy Accept Abu Bakr as the first Caliph Majority worldwide How would gatherings like this help to spread ideas, as well as diseases?