* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Human systems Notes with answers 2010
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
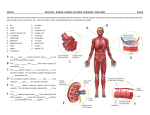
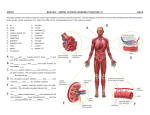
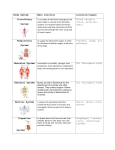
Name________________________________________Date_____________________________ Systems of the Human Body Organization, Support and Movement of the Body A human being is a complex organism made up of many different body systems. Each system carries out a specific life process. Types of cells: Each type is designed to perform a different function. Label the following cells found in the human body: 1. Cheek lining 2. Throat Lining 3. Muscle 4. Red Blood cells 5. Nerve Tissues A group of similar cell acting together forms a tissue. Skin tissue covers the body. Muscle tissue produces body movements. Types of human tissue and their functions: Tissue Function Blood Bone Muscle Transports materials Supports and protects body and organs Helps body to move, circulation, digestion & respiration Nerve Carries messages Skin Covers and protects Organs. A group of tissues working together forms an organ. Heart Kidney Pumps Blood Removes wastes from blood Stomach Brain Breaks down food Controls thinking Exchanges gases with the environment Lung Organ Systems. A group of organs acting together to carry out a specific function makes up an organ system. System Function Ex. of organs/parts Skeletal Muscular Supports body/protects Skull, ribs Moves organs & body parts Muscles in arms/legs Brain, spinal cord Adrenal glands Hypothalamus gland Nervous Controls body activities, carries/interprets messages Endocrine Regulates body temp., metabolism, development & reproduction Digestive Circulatory Respiratory Excretory Reproductive Integumetary Breaks down food to a usable form Stomach, intestines Carries materials to cells and waste materials away from cells Gas exchange Heart, arteries Removes wastes Kidneys, skin Produces offspring Ovaries, testis Protects against injury, infection and fluid Skin, hair, nails loss The Skeletal System Label bones of the human skeletal system: Skull Humerus Radius Ulna Carpals Phallanges Collarbone Sternum Pelvis (hip) Femur Tibia/Fibia Carpals Lungs, bronchi Cartilage, unlike bone, is made of a softer, more flexible tissue. Cartilage acts as a cushion between bones, and provides flexibility at the ends of bones. Where one bone meets another, a Joint is formed. Most joints allow the bones to move. Examples of joints in the human body: Ball & Socket Hinge Immovable Joints Ligaments- At moveable joints, the bones are held together by strips of tissue called ligaments. Ligaments attach bone to bone. Tendons- Bones are moved by muscles, which are attached to bones by tendons. Therefore, tendons attach the muscle to bone. Example: Achilles tendon in the back of the lower leg. The Muscular System Muscles are masses of tissue that contract to move bones or organs. There are 2 types of muscles: 1. Voluntary- Skeletal muscles, which move bones, are examples of this type. These muscles are controlled by our will. The muscles in the face and around the eyes are also voluntary muscles. 2. Involuntary- These muscles are not under our conscious control. Two types are cardiac and smooth. Smooth muscle is found in the respiratory, circulatory, and digestive systems. Smooth muscle aids in breathing , controlling blood flow and movement of food. The Nervous System There are 4 main parts to this system: Match the part to its function B 1. brain A 2. spinal cord D 3. nerves C a. channels nerve impulses to and from the brain, control automatic responses such as pulling your hand a way from a flame b. receives and interprets nerve impulses(messages) and controls thinking, voluntary action, and some involuntary actions such as breathing and digestion c. skin, eyes, ears, nose and tongue; receive info. from the environment 4. sense organs d. provide a means of communication between the sense organs, brain, spinal cord, and muscles and glands. Label the main parts of the Nervous System: Brain Spinal Cord Nerves The Endocrine System The Endocrine system is made up of Glands. A gland is an organ that makes and secretes chemicals called hormones. Example: When you become afraid your adrenal gland secretes adrenaline which makes your heart beat faster, increases your blood pressure and blood flow. Label the major glands of the endocrine system: Pineal Pituitary Thyroid Thymus Adrenal Pancreas Ovaries Testes The Digestive System Label the digestive tract and the accessory organs: Salivary glands Esophagus Stomach Liver Gall Bladder Bile Duct Pancreas Small Intestine Large Intestine Appendix Digestive juices are secreted into the digestive tract to aid in digestion of food: Organ Digestive juice Foods acted on Mouth Stomach Saliva Starches Gastric juices Proteins Small Intestine Pancreas Intestinal Juices Pancreatic juices Sugars, Proteins Protein, Starches, Fats Bile Fats Liver Note: Bile and pancreatic juice are secreted by the liver and pancreas into the small intestine, where digestion occurs. The digestive system breaks down food 2 ways: 1. Physical— chewing & muscle action in the digestive tract 2. Chemical— enzymes found in digestive juices Solid materials( called feces ) that are not digested or absorbed by the small intestines pass on to the large intestines and are expelled from the body. The Circulatory System The Circulatory System transports nutrients to all of the cells in the body. The components of the circulatory system are the blood , heart Blood vessels , lymph, and lymph vessels. Blood= red and white blood cells + platelets. The blood also carries dissolved nutrients, wastes, and hormones. Label the human heart and color the veins blue and the arteries red: Left Atrium Right Atrium Left Ventricle Right Ventricle Label the pathways of the blood through the circulatory system: Color the veins blue and the arteries red. The Respiratory System The Respiratory system provides oxygen to the cells. Cells use this oxygen in the process of cellular respiration. Nutrients from digested food combine with the oxygen to release__Energy____________. The waste materials produced include carbon dioxide__ and water. Respiration is a process that brings _oxygen__ from the air to the blood, and returns carbon dioxide from the blood to the air. This process takes place in all body cells. Label the main parts of the Respiratory System: Trachea Bronchial Tubes Aveoli In the lungs respiratory gases are exchanged- oxygen enters the blood while carbon dioxide leaves the blood and is breathed out, exhaled. The oxygen that enters the blood is carried to the __cells___ of the body, where an exchange of gases takes place again. Oxygen leaves the blood and enters the ___cells____. Carbon Dioxide leaves the cells and goes into the blood. The blood carries the CO2 back to the Lungs_ to be exhaled. The Excretory System This system is responsible for removing ___Wastes_____ from the body. List the organs that make up the excretory system: Organ Function Lung Removes CO2 and water vapor Skin Removes salt when we perspire Liver Produces urea(broken down proteins) Kidneys Removes wastes from blood The Reproductive System- Label the Male and Female Reproductive Organs Function: TO produce offspring Male Gonads: (testes)- Involved in Meiosis Female Gonads: (Ovaries)- Involved in Meiosis Male Gametes: ex: sperm, 23 chromosomes found here(haploid cells) Female Gametes: Egg or ovum, 23 chromosomes found here,(haploid cells)