* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download World War II Unit Planning Map
Allied war crimes during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Battle of the Mediterranean wikipedia , lookup
Causes of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
British propaganda during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Propaganda in Japan during the Second Sino-Japanese War and World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
American Theater (World War II) wikipedia , lookup
Greater East Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere wikipedia , lookup
World War II and American animation wikipedia , lookup
Naval history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of the attack on Pearl Harbor wikipedia , lookup
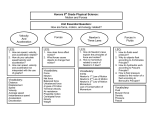
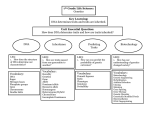
KEY LEARNING OF THIS UNIT The rise of dictatorships in the 1930’s led to World War II. The United States played a major role in the war, fighting in Europe, Africa and Asia. Afterwards, the United States emerged as a global superpower, abandoned isolationism, and began building alliances around the world. UNIT ESSENTIAL QUESTION Was this generation of Americans really the “Greatest Generation” and how did they influence America’s influence globally? CONCEPT In the 1930’s, global economic problems brought dictators to power in Europe and Japan. LEQ What were the significant events, people, vocabulary, maps, and timeline of World War 2 events? 2. How do I create a World War 2 amusement park or gameboard or production interview? 3. Who were the Allies and Axis Powers in World War II? VOCABULARY Allies, Axis Powers, Rome/Berlin/Tokyo Axis 1. 1. 2. 3. LEQ What caused the rise of totalitarian governments in Europe and Asia? What were the types of governments of the Axis Powers and how did it effect life in their country? How did the leaders of the Axis powers rise to power? CONCEPT The shadow of World War I loomed large in the minds of European leaders in the late 1930’s. Although Nazi Germany appeared increasingly aggressive, Britain, France and the United States wanted to avoid another bloody conflict. Efforts to negotiate peaceful agreements with Nazi Germany failed. LEQ 1. How did countries appease Hitler and his actions? 2. Do you think appeasement works when trying to bargain with an enemy? 3. What was the success of the Blitzkrieg early in the war? CONCEPT As World War II began, the United States remained officially neutral but aided Great Britain considerably in its fight against Germany. In the Pacific, Japan’s territorial expansion led to growing tensions with the United States, which peaked when Japan attacked Pearl Harbor. LEQ 1. What were the causes and effects of FDR’s “Quarantine Speech” concerning the Panay Incident, Finnish Interlude, Robin Moor Sinking, aid to Russia, Economic Crackdown on Japan, and Last Ditch Negotiations with Japan? VOCABULARY Treaty of Versailles, Rhineland, Sudetenland, Munich Conference, appeasement, Anschluss, blitzkrieg, Neville Chamberlain, “peace in our time,” German-Soviet Non-Aggression Pact, Molotov, Ribbentrop LEQ 1. What is the importance Dunkirk, the Battle of Britain, and Operation Barbarossa? 2. Should America stay neutral or get involved in World War II? VOCABULARY Quarantine speech, Panay Incident, Robin Moor, Hideki Tojo, Reuben James VOCABULARY Communism, Fascism, Nazism, Capitalism, Militarism, Hirohito, Fransicso Franco, Adolf Hitler, Benito Mussolini, Josef Stalin, Winston Churchill, Franklin Roosevelt, Brown shirts, Black shirts, SS, Big Lie, Purge, USSR, Lenin, collectives, Five Year Plans, “show trials”, Il duce, Der Fuhrer, Manchuria, Rape of Nanking VOCABULARY Maginot Line, Dunkirk, sitzkreig, Operation Dynamo, Luftwaffe, Herman Goering, RAF, “we shall never surrender,” “this is our finest hour,” “never in human history do we our so much to so few,” Winston Churchill, the blitz, “carpet bombimg, Operation Barbarossa, “wolf packs,” Enigma LEQ How did Hitler rise to power? What are the main countries or Europe, Africa, and Asia involved in World War II? LEQ What were the arguments for and against U.S. isolationism and internationalism in the 1930’s? 2. How did America slowly move towards war by providing aid to the Allies? 3. What were FDR’s “Four Freedoms”? Do you agree with these freedoms at any cost? VOCABULARY Nye Report, Neutrality Acts 1935,1936,1937, and 1939, Lend Least Act, Destroyers for Bases Deal, Four Freedoms, FDR, Spanish Civil War, Guernica, League of Nations, America First Committee, Atlantic Charter, Hemispheric Defense zone, 1. 2. VOCABULARY Der Furher, Munich Beer Hall Putsch, Big Lie, propaganda, Goebbels, National Socialist German Workers Party, anti-semitism, “master race,” Aryan, Mein Kampf, Reichstag 1. LEQ What caused tensions between Japan and the United States during the 1930’s? 2. Compare Japanese and American viewpoints towards one another and the harsh propaganda towards each other. 3. What were the different interpretations concerning who was more responsible for the Pearl Harbor attacks? What can we learn from these interpretations? VOCABULARY Hirohito, Pearl Harbor, U.S.S. Arizona, Henry Stimson, Walter C. Short, Husband Kimmel, George C. Marshall, tora tora tora, “a day which will live in infamy,” December 7, 1941, “awakened a sleeping giant,” battleship row, Hideki Tojo, Operation Magic, General Douglas MacArthur, Doolittle’s Raid, Bataan Death March LEQ 1. What was the historical significance and consequences of the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor? 2. How does the attack on Pearl Harbor relate to the 9/11 terrorist attacks? 1. VOCABULARY Hirohito, Pearl Harbor, U.S.S. Arizona, Henry Stimson, Walter C. Short, Husband Kimmel, George C. Marshall, tora tora tora, “a day which will live in infamy,” December 7, 1941, “awakened a sleeping giant,” battleship row, Hideki Tojo, Operation Magic CONCEPT The early battles of the war on both fronts required changes in strategy from all sides. After the British and American troops won victories in North Africa and Italy, Allies leaders made plans for the invasion and ultimate destruction of Germany with goals to create a peaceful post war world. LEQ 1. What was the Second Front Controversy and who should the United States focus more of their efforts? CONCEPT Fierce fighting in the Pacific theater by the United States through island hopping eventually gained the unconditional surrender of the Japanese through the use of atomic bombs. VOCABULARY Review of previous vocabulary terms VOCABULARY Chester Nimitz, Douglas MacArthur, Admiral Halsey, “I shall return,” Battle of the Coral Sea, Battle of Midway, Admiral Yamamoto, U.S.S. Yorktown, U.S.S. Lexington, Battle of Tarawa, Okinawa, Iwo Jima, kamikaze, island hopping, Battle of Guadalcanal, Mt. Suribachi LEQ 1. Should the United States have dropped the atomic bomb on Japan? Were there any other options? 2. What were the major consequences as a result of the atomic bomb? 3. How did the battles of Iwo Jima and Okinawa influence the decision to drop the atomic bomb? VOCABULARY “Little Boy,” “Fat Man,” “Enola Gay,” Bock’s Car,” Hiroshima, Nagasaki, August 6, 1914, August 9, 1945, Manhattan Project, Enrico Fermi, Albert Einstein, Oppenheimer, V-J Day, napalm, General Curtis LeMay, Harry S. Truman, Operation Olympic LEQ 1. Which significant person involved in World War II should be inducted into the World War II Hall of Fame? 1. 2. LEQ How were the battles of El Alamein and Stalingrad turning point battles in 1942? What are the experiences and preparations of the typical American G.I. VOCABULARY El Alamein, Bernard Montgomery, Erwin Rommel, Desert Fox, Afrika Corps, Kasserine Pass, Operation Husky, Operation Torch, George Patton, Dwight D. Eisenhower, Battle of Stalingrad, Molotov cocktails, convoy system LEQ 1. How did the Allies prepare for the invasion of Fortress Europe? Were they successful? 2. Why do you think this day is considered one of the most important days in World/American history? VOCABULARY Strategic bombing, carpet bombing, D-Day, hedgerow, Casablanca Conference, Fortress Europe, June 6, 1944, Operation Overlord, Double Cross, Operation Fortitude, French Resistance LEQ 1. What were the factors leading up to the Battle of the Bulge and the major results? 2. What was the importance of the “Big Three” conferences (Teheran, Yalta, Potsdam, and U.N.)? 1. 2. LEQ Why was the Battle of Midway a major turning point in the Pacific theater? How do you evaluate the U.S. strategy of island hopping? VOCABULARY See names on Hall of Fame assignment sheet or all of the names on the unit planning map VOCABULARY Bastogne, Battle of Britain, Omar Bradley, Teheran Conference, Yalta Conference, Potsdam Conference, United Nations, V-E Day CONCEPT Although women and African Americans gained new work opportunities, Latinos and Japanese Americans faced violence in American cities. To assist with the war effort, the government controlled wages and prices, rationed goods, encouraged recycling, and sold bonds. LEQ 1. How did Americans treat Japanese Americans during World War II? 2. Was the Japanese American treatment a necessary evil in America during World War II? 3. What were the Zoot Suit Riots? VOCABULARY Zoot suit, victory suit, Executive Order 9066, War Relocation Authority, Korematsu vs. the United States, Nisei 1. 2. 3. LEQ How did the role of women change during World War II and how did they help win World War II? What was the social change regarding women being mass employed? How successful do you feel the Double V campaign was carried out? VOCABULARY “Rosie the Riveter,” disenfranchised, Double V Campaign, Tuskegee Airmen, Buffalo Soldiers, WAAC, WAC, WASPS, Oveta Culp Hobby, A Philip Randolph, Executive Order 8802, March on Washington, LEQ What was the sacrifice that civilians made during World War II? 2. What was the role of the government in mobilizing Americans for war? 3. How did American propaganda help win the war? VOCABULARY “arsenal of democracy,” Henry Stimson, Frank Knox, George C. Marshall, ration, liberty ships, War Production Board, Office of War Mobilization, “GI,” Office of Price Administration, victory gardens 1. CONCEPT CONCEPT CONCEPT LEQ LEQ LEQ VOCABULARY VOCABULARY VOCABULARY LEQ LEQ LEQ VOCABULARY VOCABULARY VOCABULARY LEQ (2 days) LEQ LEQ VOCABULARY VOCABULARY VOCABULARY