* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download World War II - Hewlett
British propaganda during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Economy of Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Fascism in Europe wikipedia , lookup
German–Soviet Axis talks wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
New Order (Nazism) wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Nazi views on Catholicism wikipedia , lookup
European theatre of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Appeasement wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
Causes of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of the attack on Pearl Harbor wikipedia , lookup
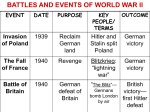
Name ____________________________ UNIT 10 - 1. WORLD WAR II Causes of World War II Although there were many causes of World War II, much of the blame is traced to the failure of the Treaty of Versailles at the end of World War I. During the 1920’s and 1930’s, totalitarian states had established control under: Nazi leader Adolf Hitler in Germany; fascist leader Benito Mussolini in Italy; communist leader Joseph Stalin in the Soviet Union, and Emperor Hirohito in Japan. The inability of the League of Nations to deal with the aggressive acts of these nations, combined with the isolationism of the U.S., and the appeasement of Adolf Hitler eventually led to World War II. In the years following the rise of dictators in Europe, an ethnic cleansing of undesirables was carried out in Hitler’s Final Solution. ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS 1. How did the Versailles Treaty help lead to World War II? VOCABULARY Totalitarian state (gov’t) Fascism 2. What acts of aggression helped lead to WW II? Nazi Party/ Third Reich 3. What role did the following totalitarian leaders play in World War II? a) Benito Mussolini- Master race/Aryans b) Adolf Hitler- Communism c) Joseph Stalin Hitler-Stalin (Nazi-Soviet) Pact 4. What was the Holocaust? Appeasement/ Munich Pact Final Solution Concentration Camps WAR IN EUROPE Beginning with the attack on Poland, the German strategy of blitzkrieg allowed Hitler to quickly overrun much of Europe. The refusal of Britain’s Winston Churchill to surrender and Soviet leader Joseph Stalin’s defeat of the German army at the Battle of Stalingrad thwarted Hitler’s plan to conquer all of Europe. The Allies invasion at Normandy (D-Day), led by Dwight Eisenhower, and the Battle of the Bulge marked the “beginning of the end” for the Germans. ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS VOCABULARY 1. How did the following contribute to the Allied victory in Europe? a-Battle of Britain/ RAF Axis powers Blitzkrieg b-Battle of Stalingrad c-D-Day (Normandy Invasion) Winston Churchill Charles deGaulle General Eisenhower d-Battle of the Bulge HOMEFRONT The war greatly affected our Homefront, as the American government mobilized for war and set up internment camps for Japanese-Americans. We relied on rationing, grew victory gardens, and sold War Bonds. The role of women changed as they entered the work force and joined the armed services. ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS VOCABULARY 1. How did America mobilize its economy for war? Lend Lease Act Japanese-American Internment camps 2. What roles were played by women during WWII? rationing 3. How did rationing, victory gardens, and war bonds help the U.S. war effort? Rosie the Riveter Tuskegee Airmen Harry Truman WAR IN THE PACIFIC The U.S. declared war on Japan after the bombing of Pearl Harbor on December 7, 1941. In order to attack Japan, we embarked on a strategy of island hopping (under the leadership of Douglas MacArthur) to capture Pacific islands such as Iwo Jima and Okinawa. The Manhattan Project was responsible for the development of the atomic bombs dropped on Hiroshima and Nagasaki. ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS 1. What were the results of the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor? 2. Describe our strategy of island hopping used to win the war against Japan? VOCABULARY Douglas MacArthur Kamikaze Bataan Death march 3. What was decided at the Potsdam Conference? Manhattan Project 4. How did the following help contribute to our victory over Japan? a. Battle of Midway Emperor Hirohito b. Iwo Jima/Okinawa Navajo Code Talkers c. Hiroshima/Nagasaki AFTERMATH OF WAR The impact of the war included the physical destruction of countries in Europe and Asia; the loss of millions of civilians; the uncovering of the Nazi Holocaust, leading to the Nuremberg Trials and the creation of Israel, the formation of the United Nations; the change in the role of the United States in foreign affairs; and the beginning of the Cold War between the United States and the Soviet Union. ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS 1. What were the human and economic costs of the war? VOCABULARY Nuremberg Trials Yalta Conference 2. How were the countries of Germany and Japan treated by the Allies as a result of WWII? United Nations