* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Postulates – Something you except as true
Dessin d'enfant wikipedia , lookup
Technical drawing wikipedia , lookup
Plane of rotation wikipedia , lookup
Perspective (graphical) wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
Lie sphere geometry wikipedia , lookup
Perceived visual angle wikipedia , lookup
Projective plane wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Duality (projective geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Compass-and-straightedge construction wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
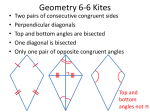
Definitions – Statement that describes a mathematical object and can be written as a true biconditional statement. 1. Congruent – Having the same size shape (measurements are equal) 2. Midpoint – The point that bisects the segment into two congruent segments 3. Bisects – To divide something into two congruent parts. 4. Segment Bisector – Any ray, segment, or line that intersects a segment at its midpoint. 5. Angle Bisector – A ray that divides an angle into two congruent angles. 6. Linear Pair – A pair of angles that are adjacent and whose noncommon sides are opposite rays. 7. Complementary Angles – Two angles whose measures add up to 90°. 8. Supplementary Angles – Two angles whose measures add up to 180°. 9. Vertical Angles – Two nonadjacent angles formed by two intersecting lines. Postulates – Something you accept as true 1. Through any two points there is exactly one line. 2. Through any three noncollinear points there is exactly one plane. 3. If two points lie in a plane, then the line containing those points lies in the plane. 4. If two lines intersect, they intersect in exactly one point. 5. If two planes intersect, they intersect in exactly one line. 6. Segment Addition Postulate: If B is between A and C, then AB + BC = AC 7. Angle Addition Postulate: If S is in the interior of <PQR, then m<PQS + m<SQR = m<PQR. Theorems – Any statement you can prove. 1. Linear Pair Theorem: If two angles form a linear pair, then they are supplementary. 2. Vertical Angles Theorem: Vertical angles are congruent. Definitions – Statement that describes a mathematical object and can be written as a true biconditional statement. 1. Congruent – Having the same size shape (measurements are equal) 2. Midpoint – The point that bisects the segment into two congruent segments 3. Bisects – To divide something into two congruent parts. 4. Segment Bisector – Any ray, segment, or line that intersects a segment at its midpoint. 5. Angle Bisector – A ray that divides an angle into two congruent angles. 6. Linear Pair – A pair of angles that are adjacent and whose noncommon sides are opposite rays. 7. Complementary Angles – Two angles whose measures add up to 90°. 8. Supplementary Angles – Two angles whose measures add up to 180°. 9. Vertical Angles – Two nonadjacent angles formed by two intersecting lines. Postulates – Something you accept as true 1. Through any two points there is exactly one line. 2. Through any three noncollinear points there is exactly one plane. 3. If two points lie in a plane, then the line containing those points lies in the plane. 4. If two lines intersect, they intersect in exactly one point. 5. If two planes intersect, they intersect in exactly one line. 6. Segment Addition Postulate: If B is between A and C, then AB + BC = AC 7. Angle Addition Postulate: If S is in the interior of <PQR, then m<PQS + m<SQR = m<PQR. Theorems – Any statement you can prove. 1. Linear Pair Theorem: If two angles form a linear pair, then they are supplementary. 2. Vertical Angles Theorem: Vertical angles are congruent.