* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download World War II Notes
Operation Bodyguard wikipedia , lookup
New Order (Nazism) wikipedia , lookup
Economy of Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Allied war crimes during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Military history of Greece during World War II wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
Historiography of the Battle of France wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of the attack on Pearl Harbor wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Allied plans for German industry after World War II wikipedia , lookup
Battle of the Mediterranean wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Britain (film) wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Invasion of Normandy wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
German evacuation from Central and Eastern Europe wikipedia , lookup
Causes of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Naval history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Home front during World War II wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
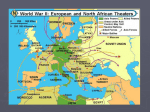
Additional World War II Notes—These will be on the test too!! WWII on the Homefront Mobilizing for War Converting Industry Car factoriestanks & airplanes Shipbuilding Exempt from the Draft Naval ships Liberty ships War Production Board: directs industry Rationing Not enough to go around Everything was rationed Conservation & Recycling Building an Army US had a small army in 1939 (227,000) Selective Service Act (1940) This is the Draft About 1 million by 1941 5 million volunteer after Pearl Harbor 10 million are drafted Segregated military Double V Campaign Tuskegee Airmen Most African Americans are kept in non-combat roles until the end of the war Segregated units with white officers Women in the military Each branch had a women’s auxillary (WAAC/WAC for the Army) Many served as clerks or nurses (all non-combat roles) Racial/Ethnic Tensions Rise in the US Job competition Housing and job discrimination Riots Population Shifts People moved where the war industry jobs were West Coast and the North Great Migration continues and it speeds up during WWII Alabama and WWII Mobile docks & shipbuilding Birmingham steel industry Aliceville POW Camp (near Tuscaloosa) Battle of Midway (June 1942) US has broken Japanese Naval Code US plans to ambush Japanese fleet Japan attacks Midway Island (why?) US carrier aircraft attack Japanese fleet US sinks 4 Japanese carriers (25%) Turning –point in the war in the Pacific Japan is losing territory for the rest of the war Island Hopping Campaign (map on p. 760) Guadalcanal (Aug. 1942) 1st island in campaign Hard fighting Jungle warfare 1st Japanese defeat on land Two-pronged approach Goal: get close enough to Japan to bomb, then invade Battle of Leyte Gulf (Oct. 1944) Naval battle Kamikazes (over 400) used against US ships (16 sunk) Japanese fleet is destroyed 3 battleships 4 carriers 13 cruisers 400 aircraft Battle of Iwo Jima (Mar. 1945) US needed island for an airstrip to bomb Japan Heavily defended (20,700 Japanese) Only 200 Japanese survive Firebombing of Japan Begins FDR dies April 12, 1945 Battle of Okinawa (April-June 1945) Last island before the US reaches the Japanese home islands US needed Okinawa to launch an invasion of Japan from 7,600 Americans died 110,000 Japanese died…few surrender 15:1 kill ratio 1,900 kamikaze attacks Killed 5,000 sailors Sank 30 US ships Damaged 300 US ships Manhattan Project Headed by Robert Oppenheimer Secret project to build an atomic bomb Intended for use against Germany…why wasn’t it? Tested July 16, 1945 in Alamogordo, NM Scientists argue about using it against Japan Truman makes an easy decision Sends Stalin a message US did not want the USSR involved in Japan Stalin already knew about our secret bomb project Hiroshima and Nagasaki August 6, 1945: Hiroshima bombed “Enola Gay” drops “Little Boy” 100,000 died immediately August 9, 1945: Nagasaki bombed “Bock’s Car” drops “Fat Man” 80,000 died immediately August 15, 1945: V-J Day Japan announced it would surrender September 2, 1945: formal surrender ceremony Signed on USS Missouri in Tokyo Bay WWII in the Pacific Leaders in the Pacific Emperor Hirohito Prime Minister Hideki Tojo Admiral Isoroku Yamamoto Gen. Douglas MacArthur Adm. Chester Nimitz Adm. Bull Halsey Pacific Battles Pearl Harbor (Dec. 7, 1941) Philippines (1941-1942) Corregidor Island Bataan Death March Gen. MacArthur leaves the Philippines “I shall return” Doolittle Raid (April 1942) Pearl Harbor movie shows this US Bombers attack Japan Very little damage done Battle of the Coral Sea (May 1942) Japanese plan to attack Australia US carriers intercept Japanese fleet New type of naval warfare Who won? 1 Red Army (USSR) counterattacks and surrounds the German Army Hitler refuses to allow retreat Hitler refuses to allow surrender 250,000 freezing Germans surrender…only 5,000 survive **This is the turning –point in the war on the Eastern Front** German Army begins a long retreat Battle of Kursk Largest tank battle in WWII The War in Europe and North Africa Leaders in Europe and North Africa Adolf Hitler Benito Mussolini Joseph Stalin Winston Churchill FDR Henri Petain Gen. George Marshall Gen. Dwight Eisenhower Gen. George Patton Gen. Bernard Montgomery Gen. Charles DeGaulle Gen. Georgi Zhukov Gen. Erwin Rommel Men: USSR 1.3 million Germany 1.0 million Tanks: USSR 3,600 Germany 2,700 Planes: USSR 2,400 Germany 2,000 Artillery: USSR 20,000 Germany almost none (Stalingrad) Invasion of Italy German Army escapes N. Africa to Sicily, Italy US & GB follow Italians revolt & drop out of the war Mussolini removed from power German Army controls Italy & does all of the fighting Hitler puts Mussolini back in power Italians actively help the Allies (resistance movements & guerrilla warfare) Bloody fighting in Sicily and at Anzio Long, slow advance for the Allies in Italy Italian geography: rough Germans are dug-in on high ground Rome finally falls in early June 1944…overshadowed by D-Day (June 6) Took 18 months of hard fighting for the Allies to capture Rome Operation Overlord (D-Day) June 6, 1944 Allied invasion of Nazi-occupied France Hitler is tricked by the US & British Hitler believes the invasion will come at Calais, not Normandy 100,000+ troops land on the Normandy beaches on the first day Millions follow them German Army is pushed back by the Allies Gen. Patton rolls through the Germans Paris is liberated (Patton does all of the work) Allies push towards Germany German Army is being squeezed by the Allies US & GB from the west USSR from the east Battle of the Bulge Allies are about to enter Germany German Army mounts a surprise offensive Germans push a bulge in the US/GB lines Allies quickly recover and encircle & cut-off the German advance This is the last major German offensive of the war Allies push deep into Germany V-E Day Soviet Red Army pushes into Germany from the East US & GB push into Germany from the West Eisenhower agrees to allow Red Army to capture Berlin Hitler commits suicide April 30, 1945 rather than be captured German Army surrenders May 8, 1945 (V-E Day) War Crimes Trials Nuremberg for the Germans Tokyo for the Japanese Battles in Europe & North Africa Battle of Britain The air war between the RAF and the Luftwaffe Fought in 1940 over Great Britain Germany was trying to destroy the RAF in order to invade RAF had early warning radar Any time the Luftwaffe attacked, the RAF was waiting on them Luftwaffe fails to gain air superiority Invasion of Great Britain never happens Operation Sea Lion Germany’s plan to invade Great Britain by sea and air Never happened because Germany never gained air superiority Operation Barbarossa Germans invade the USSR in June 1941 Hitler’s biggest mistake in WWII Germany pushes deep into the USSR Soviets follow a scorched-earth policy as they retreat German Army gets within 25 miles of Moscow Leningrad under siege for 900 days Russian winter gets the Germans just like it did Napoleon Coldest Russian winter in 70 years German supply lines stretch 500 miles into USSR Supplies are scarce Operation Torch US invasion of North Africa (1942) Why North Africa? We weren’t ready to attack anywhere else. US attacks from the west and GB attacks from the east GB wanted to protect the Suez Canal in Egypt Battle of El Alamein Montgomery –vs Rommel 1st German defeat in WWII Battle of Kasserine Pass (1st battle for the US) US “wins” the battle Germans are squeezed out of North Africa Battle of the Atlantic German U-Boats try to starve the British out of the war Convoy system works again Long-range aircraft, RADAR, and SONAR help defeat the Germans This battle lasted the entire war Battle of Stalingrad Germans push deep into USSR Stalingrad has war factories Stalingrad is the gateway to Soviet oil reserves Stalingrad is named after Stalin! Germans control 90% of the city (which is in ruins) Movie Enemy at the Gates shows the battle 2