* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download mcq2
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
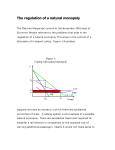
Sample Multiple Choice Questions (the book’s web site contains many more) 1. a) b) c) d) If A and B are complements, an increase in the price of good A would: have no effect on the quantity demanded of B. lead to an increase in demand for B. lead to a decrease in demand for B. none of the above. Answer: C Difficulty: Med 2. a) b) c) d) If a shortage exists in a market, the natural tendency is for: demand to increase. price to increase. quantity supplied to decrease. no change in the market. Answer: B Difficulty: Med 3. If steak is a normal good, what do you suppose would happen to price and quantity during an economic recession? a) price would increase and quantity decrease. b) price and quantity would both increase. c) price and quantity would both decrease. d) price would decrease and quantity increase. Answer: C Difficulty: Med 4. Suppose you produce wooden desks, and government legislation protecting the spotted owl has made it more expensive for you to purchase wood. What do you expect to happen to the equilibrium price and quantity of wooden desks? a) price and quantity will increase. b) price will increase but quantity will decrease. c) price and quantity will decrease. d) price will decrease but quantity will increase. Answer: B Difficulty: Med 5. Suppose that supply increases and demand decreases. What effect will this have on price and quantity? a) price will increase and quantity may rise or fall. b) price will decrease and quantity will increase. c) price will decrease and quantity will decrease. d) none of the above. Answer: D Difficulty: Hard 6. a) b) c) d) Suppose both supply and demand decrease. What effect will this have on price? it will fall. it will rise. it may rise or fall. it will remain the same. Answer: C Difficulty: Hard 7. Suppose that good X is a substitute for good Y. Then an increase in the price of good Y leads to a) an increase in the demand of good X. b) a decrease in the demand of good X. c) a decrease in the supply of good X. d) an increase in the supply of good X. Answer: A Difficulty: Med 8. a) b) c) d) If consumers expect future prices to be higher they substitute current purchases for future purchases of perishable products. stockpiling will happen when products are durable in nature. the position of the demand will not change. the demand for automobiles today will not change. Answer: B Difficulty: Med 9. The demand function a) describes how much of good X will be purchased at the alternative price of good X, given all the other variables being constant. b) recognizes that the quantity of a good consumed depends on its price and demand shifters. c) shows the relationship between the quantity demanded of X and variables other than its price. d) does not include expectations. Answer: B Difficulty: Hard 10. All else held constant, as additional firms enter an industry a) more output is available at each given price. b) less output is available at each given price. c) the same output is available at each given price. d) output could increase or decrease at each given price. Answer: A Difficulty: Med 11. Suppose there is a simultaneous increase in demand and decrease in supply, what effect will this have on the equilibrium price? a) it will rise. b) it will fall. c) it may rise or fall. d) it will remain the same. Answer: A Difficulty: Med 12. The difference between a price decrease and an increase in income is that a) A price decrease does not affect the consumption of other goods while an increase in income does. b) An increase in income does not affect the slope of the budget line while a decrease in price does change the slope. c) A price decrease decreases real income while an increase in income increases real income. d) A price decrease leaves real income unchanged while an increase in income increases real income. e) None of the above. Answer: B Difficulty: Med 13. Joe prefers a three pack of soda to a six-pack. What properties does this preference violate? a) Completeness. b) Transitivity. c) More is better. d) Diminishing MRS. e) All of the above. Answer: C Difficulty: Easy 14. A situation where a consumer says he does not know his preference ordering for bundles X and Y would violate the property of: a) more is be better. b) completeness. c) substitutability. d) complementarity. Answer: B Difficulty: Med 15. Given that income is $200 and the price of good Y is $40. What is the vertical intercept of the budget line? a) 8,000. b) 20. c) 1/5. d) 5. Answer: D Difficulty: Easy 16. How does a decrease in the price of good X affect the market rate of substitution between goods X and Y? a) it increases. b) it decreases. c) remains unchanged. d) indeterminable without more information. Answer: B Difficulty: Med 17. Along the same indifference curve, MRS is a) constant as more of one good is obtained. b) increasing as more of one good is obtained. c) decreasing as more of one good is obtained. d) varying irregularly as more of one good is obtained. Answer: C Difficulty: Med 18. If income increases, then a) the budget line rotates counter-clockwise. b) the budget line rotates clockwise. c) the budget line shifts to the right. d) the opportunity set contracts. Answer: C Difficulty: Easy 19. The substitution effect reflects how a consumer will react to a) a different marginal rate of substitution. b) a different market rate of substitution. c) a different level of real income. d) a different level of nominal income. Answer: B Difficulty: Med 20. If an increase in income causes a decrease in the consumption of good Y we know that good Y is: a) a normal good. b) a substitute. c) a complement. d) an inferior good. Answer: D Difficulty: Easy 21. Which combination of the properties given below rules out indifference curves that intersect one another? a) Completeness and diminishing marginal rate of substitution. b) Transitivity and more-is-better. c) More-is-better and diminishing marginal rate of substitution. d) Completeness and more-is-better. Answer: B Difficulty: Med 22. If a firm's production function is Leontief and the wage rate goes up a) the firm must use more labor in order to minimize the cost of producing a given level of output. b) the firm must use more capital in order to minimize the cost of producing a given level of output. c) the firm must use less labor in order to minimize the cost of producing a given level of output. d) the cost minimizing combination of capital and labor does not change. Answer: D Difficulty: Hard 23. Which of the following statements is incorrect: a) Fixed costs do not vary with output. b) Sunk costs are those costs that are forever lost after they have been paid. c) Fixed costs are always greater than sunk costs. d) Fixed costs could be positive when sunk costs are zero. Answer: C Difficulty: Hard 24. Which of the following conditions is true when a producer minimizes the cost of producing a given level of output? a) The MRTS is equal to the ratio of input prices. b) The marginal product per dollar spent on all inputs are equal. c) The marginal products of all inputs are equal. d) a and b. Answer: D Difficulty: Easy 25. If the last unit of input increases total product we know that the marginal product is: a) positive. b) negative. c) zero. d) indeterminate. Answer: A Difficulty: Med 26. The absolute value of the slope of the isoquant is the: a) Marginal rate of technical substitution. b) Marginal product of capital. c) Marginal rate of substitution. d) Value marginal product of labor. Answer: A Difficulty: Easy 27. Changes in the price of an input cause: a) Isoquants to become steeper. b) Slope changes in the isocost line. c) Parallel shifts of the isocost lines. d) Changes in both the isoquants and isocosts of equal magnitude. Answer: B Difficulty: Easy 28. A production function a) defines the minimum amount of output that can be produced with inputs such as capital and labor. b) defines the average amount of output that can be produced with inputs such as capital and labor. c) represents the technology available for turning inputs into output. d) is determined only by the expenditures on R&D. Answer: C Difficulty: Med 29. The short-run is defined as the time-frame a) in which there are no fixed factors of production. b) in which there are fixed factors of production. c) less than one year. d) less than three years. Answer: B Difficulty: Easy 30. The long-run is defined as a) the horizon in which the manager can adjust all factors of production. b) the horizon in which there are only fixed factors of production. c) the horizon in which there are both fixed and variable factors of production. d) greater than one year. Answer: A Difficulty: Easy 31. The marginal rate of technical substitution a) determines the rate at which a producer can substitute between two inputs in order to increase one additional unit of output. b) is the absolute value of the slope of the isoquant. c) is the absolute value of marginal revenue. d) is constant along the isoquant curve. Answer: B Difficulty: Med 32. The marginal product of an input is defined as a) change in average output attributable to the last unit of an input. b) change in total output attributable to the last unit of an input. c) change in total input attributable to the last unit of an output. d) change in average output attributable to the last unit of an output. Answer: B Difficulty: Med 33. If the marginal product per dollar spent on capital is less than the marginal product per dollar spent on labor, then in order to minimize costs a) the firm should use less capital and more labor. b) the firm should use less labor and more capital. c) the firm should use less labor and less capital. d) the firm should use more labor and more capital. Answer: A Difficulty: Med 34. In a competitive industry with identical firms, long run equilibrium is characterized by a) P = AC. b) P = MC. c) MR = MC. d) All of the above. Answer: D Difficulty: Easy 35. In the long-run, monopolistically competitive firms: a) charge prices equal to marginal cost. b) have excess capacity. c) produce at the minimum of average total cost. d) b. and c. Answer: B Difficulty: Easy 36. Which of the following market structures would you expect to yield the greatest product variety? a) Monopoly. b) Monopolistic Competition. c) Bertrand Oligopoly. d) Perfect Competition. Answer: B Difficulty: Easy 37. The primary difference between Monopolistic Competition and Perfect Competition is a) the ease of entry and exit into the industry. b) the number of firms in the market. c) all of the above. d) none of the above. Answer: D Difficulty: Easy 38. Which of the following statements concerning monopoly is NOT true? a) A market may be monopolistic because there are some legal barriers. b) A monopoly has market power. c) A monopoly is always undesirable. d) There is some deadweight loss in a monopolistic market. Answer: C Difficulty: Med 39. Suppose that initially the price is $50 in a perfectly competitive market. Firms are making zero economic profits. Then the market demand shrinks permanently and some firms leave the industry and the industry returns back to a long run equilibrium. What will be the new equilibrium price, assuming cost conditions in the industry remain constant? a) $50. b) $45. c) Lower than $50 but exact value cannot be known without more information. d) Larger than $45 but exact value cannot be known without more information. Answer: A Difficulty: Hard 40. Which of the following features is common to both perfectly competitive markets and monopolistically competitive markets? a) Firms produce homogeneous goods. b) There is free entry. c) Long run profits are zero. d) both b and c. Answer: D Difficulty: Med 41. The source(s) of monopoly power for a monopoly may be: a) economies of scale. b) economies of scope. c) patents. d) all of the above. Answer: D Difficulty: Med 42. Economies of scale exist whenever: a) average total costs decline as output increases. b) average total costs increase as output increases. c) average total costs are stationary as output increases. d) both b and c. Answer: A Difficulty: Easy 43. You are a manager for a monopolistically competitive firm. From experience, the profit-maximizing level of output of your firm is 100 units. However, it is expected that prices of other close substitutes will fall in the near future. How should you adjust your level of production in response to this change? a) Produce more than 100 units. b) Produce less than 100 units. c) Produce 100 units. d) Insufficient information to decide. Answer: B Difficulty: Med 44. A linear demand function exhibits: a) constant demand elasticity. b) more elastic demand as output increases. c) less elastic demand as output increases. d) insufficient information to determine. Answer: C Difficulty: Easy 45. Which of the following is not a basic feature of a monopolistically competitive industry? a) There are many buyers and sellers in the industry. b) Each firm in the industry produces a differentiated product. c) There is free entry and exit into the industry. d) Each firm owns a patent on its product. Answer: D Difficulty: Med 46. Which of the following statements is not correct about monopoly? a) A monopolist generally faces a downward sloping demand curve. b) Monopolists always make positive profits in the long-run. c) A monopoly may make negative profits in the short-run. d) There is no close substitute for a monopoly's product. Answer: B Difficulty: Easy 47. Which of the following features is common to both perfectly competitive markets and monopolistically competitive markets? a) Firms produce homogeneous goods. b) Prices are equal to marginal costs in the long-run. c) Long run profits are zero. d) Prices are above marginal costs in the long-run. Answer: C Difficulty: Hard