* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Science Medium Term Planning – Spring 1 (year 5)
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Aluminium-conductor steel-reinforced cable wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Fault tolerance wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Crossbar switch wikipedia , lookup
Circuit breaker wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Printed circuit board wikipedia , lookup
Light switch wikipedia , lookup
Electricity market wikipedia , lookup
Earthing system wikipedia , lookup
Transmission tower wikipedia , lookup
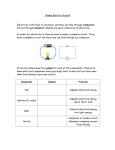
Science Short Term Planning – Spring 1 (Year 4-Circuits and Electricity) 1 Activity Learning objectives Children learn: Core vocab Resources Learning outcomes Children: Tell the chd the new topic that we are going to be looking at this term. Put on the board the words circuits and conductors. Ask the chd to write this in their books for a title page. Then ask them to write it again on the next page but this time write or draw all the things they can think of that are to do with circuits and conductors (mention the word electricity) Circuits Show the children the picture of the drawn circuit with the diagram of the circuit in the centre. Why do we use diagrams instead of drawings? That’s because bulbs, plugs, cells look different from country to country, but the image in the diagram can remain constant. that a circuit needs a power source Battery Bulb Cell Circuit Electricity Lead Component Cells Wires Buzzers Crocodile clips Pictures of circuits explain why devices in some circuits shown in drawings will work but devices in other circuits will not eg the switch is open so there is a break in the circuit and the bulb won't light Have the children use the poster resource to draw and complete three circuit diagrams in their books giving them a time limit to complete. Once finished challenge the children to make a simple circuit that contains a buzzer. Demonstrate what the children might do that could cause their circuit not to work, e.g. connect to plastic not the metal wire, connect the wrong end of the buzzer to the positive side of the cell. that a complete circuit is needed for a device to work that circuits powered by batteries can be used for investigation and experiment, appliances connected to the mains must not identify the purpose of components in a circuit 2 When the children have made a simple buzzer circuit ask them to consider how to make the buzzer quieter. How many options can they list in their books? Discuss some answers, i.e. add more wires; add a cell with less voltage; add another component that will use the power like another buzzer or bulb. Show the images of circuits questions taken from SATs papers and discuss their responses. Insulators and conductors Show the children a plastic covered lead and ask them: What is inside the plastic covering for electricity to pass through? What is the plastic covering for? Explain that an electrical conductor is a material that allows electricity to pass through. A material that does not allow electricity to pass through is called an insulator. Provide children with a range of materials and ask them to carry out an investigation to find out which are insulators and which are conductors. Ask them to predict which objects will allow electricity to pass through (conductor) and which will not let electricity to pass through (insulator). Record their results on the table provided. Discuss results and identify a pattern – all metals are conductors and other materials are not. Provide objects that are made of two materials, e.g. scissors with plastic handles – the answer will depend on where the children clip the wires. that some materials are better conductors of electricity than others how to find out which materials allow electricity to pass through them to use results to draw conclusions about which materials conduct electricity that metals are good conductors of electricity, most other materials are not and that metals are used for cables and wires, plastics Circuit Conductor Insulator 4F PM1 Wires Bulbs Bulb holders Cells/batterie s Crocodile clips Range of materials: Nails Paper clips Coins Lolly stick Scissors Corks Fabric Plastic bag/carton Safety pins Spoons Forks construct a circuit to test which materials let electricity pass through explain that with some materials the bulb did not light because the circuit was not complete make a generalisation about which materials did/did not conduct electricity eg metals let electricity pass, plastics did not, metals are good conductors of electricity and plastics are not explain that metals are used eg for cables and wires because they are good conductors and plastics eg for plugs because they are 3 At the end discuss whether water is a conductor or not. Have the children give you their various opinions. Ask do they have plug sockets in their bathroom? Explain that water is a conductor but not for small amounts of voltage, e.g. in the 9v cells they’re using. But when the voltage is huge, e.g. a plugged in household items. are used to cover wires and as covers for plugs and switches Two tasks this week Quiz board Building on last week’s lesson on conductors and insulators show the chd a quiz board you have made and explain that it works by using conductors taped to the back of the board. Explain that the chd will be making their own quiz board using aluminium foil and masking tape. They punch a set of holes down both sides of an A4 card then write questions on one side of the card and then the correct answers, jumbled up, on the other side always above one of the punched holes. They then connect the correct answer to each question on the back of the board using a strip of foil. They then must insulate the strip with a layer of tape before connecting the next answer. They can then use a simple buzzer circuit to test if they have set up their quiz board correctly, i.e. the buzzer should only sound when they connect the right answer to the question. Switches Demonstrate a range of switches on familiar devices and how they can be used to turn devices on or off. Can chd think of any other appliances which use switches? What does the switch do? Ask chd: that I can apply my knowledge of insulators and conductors to make a simple toy that a switch can be used to make or break a circuit to turn things on or off (using both batteries or mains) insulators Insulator Conductor Switch 4F PM2 Aluminium foil Card Colouring pens and pencils Circuit components Paper clips Split pins Card construct a circuit to test which materials let electricity pass through construct a circuit in which a switch turns a specific device on or off explain how their switch works Why is it useful to use switches in circuits? How do switches work? Show chd a simple aluminium foil ‘fold switch’ and ask them to make one to control a circuit. Ask children: Why is aluminium used in this switch? Could we use cling film instead? Give the chd the sheet showing various designs of switches they can make themselves using pegs, card, paperclips etc…and allow them to make each one at their tables. Can they then make a circuit that incorporates their switch so that it works?