* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Operating Systems I Interfaces to Operating Systems MCT260-Operating Systems I
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
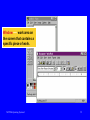
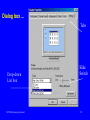
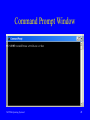
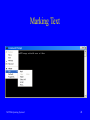
Operating Systems I Interfaces to Operating Systems MCT260-Operating Systems I Primary Learning Objective Understand and Utilize Operating System Interfaces MCT260-Operating Systems I 2 Specific Learning Objectives • Use the Microsoft Windows operating system graphical user interface (GUI) • Understand the differences between the Windows XP and the Windows Classis interface • Recognize and manipulate the components of windows, menus and dialog boxes • Tile and cascade windows • Demonstrate capturing objects from a window and paste them into a document MCT260-Operating Systems I 3 Specific Learning Objectives • • • • • • Use the command line interface (CLI) Understand the purpose of the command prompt and command line Open and close a command prompt window Recognize the elements of the command prompt window Use the command history (DOSKEY) Demonstrate capturing text from a command prompt window and paste it into a document MCT260-Operating Systems I 4 What is the User Interface? The means by which humans and computers communicate is referred to as the user interface. MCT260-Operating Systems I 5 The user interface is a combination of hardware and software. • Software controls the user interface and defines its characteristics • Hardware controls the way you physically manipulate the computer to establish communication MCT260-Operating Systems I 6 The user interface ... • • • • Accepts input and displays output Indicates results of processing Confirms task completion Uses both hardware and software MCT260-Operating Systems I 7 Graphical Objects Graphical user interfaces (GUIs) ... • Use graphical objects, menus, and prompts • Are easier to learn and use than other interfaces • Are based on a metaphor — computer components are represented by real-world objects MCT260-Operating Systems I 8 Graphical objects... • Are small pictures you manipulate with pointing devices • Represent a task, command, or real object • Are used in place of command words or menu options • Include icons, buttons, tools, and windows MCT260-Operating Systems I 9 Graphical Objects Direct manipulation of screen objects Use the mouse to drag the Sports Statistics document to the Recycle Bin. MCT260-Operating Systems I 10 Graphical Objects Window — work area on the screen that contains a specific piece of work. MCT260-Operating Systems I 11 Graphical Objects Icon — small picture that represents an object that you manipulate with a pointing device. Button — helps you make a selection or activate a task; sometimes referred to as tools. MCT260-Operating Systems I 12 Graphical User Interface • • • • • Desktop (Classic vs XP) Start Menu (Classic vs XP) Program Windows Using Menus and Toolbars Dialog boxes MCT260-Operating Systems I 13 Menus and Dialog Boxes Dialog box controls... • Round option buttons allow you to select only one option • Square check boxes allow you to select more than one option MCT260-Operating Systems I 14 Menus and Dialog Boxes Dialog box controls... • Drop-down lists display a list of options when you select the arrow button • Spin boxes let you increase or decrease a number by clicking the arrow buttons or typing a number in the box MCT260-Operating Systems I 15 Dialog box ... Tabs Drop-down List box MCT260-Operating Systems I Slide Switch 16 Commands Command-line user interfaces require... • Typing in commands at screen prompts • Pressing the Enter key after each command • Memorizing command words, parameters, and switches • Using the proper syntax MCT260-Operating Systems I 17 Commands Syntax — specifies the sequence and punctuation for command words, parameters, and switches. MCT260-Operating Systems I 18 Command — an instruction you input to tell the computer to carry out a task. Examples: • • • • • MCT260-Operating Systems I DIR DEL CLS COPY /? 19 Command Prompt Window MCT260-Operating Systems I 20 Capturing a Window • You can capture a window to the clipboard and paste it into a document • You can then resize, edit, and print the document that contains your original window MCT260-Operating Systems I 21 How to Capture • Entire Desktop with all open windows – Press Print Screen Key on the keyboard • This key has various labels depending on the keyboard manufacturer • Highlighted window only – Simultaneously press the ALT key and Print Screen Key • Open a document and paste! MCT260-Operating Systems I 22 Capture Text in a DOS Window • You can capture the entire window but sometimes you may just want to capture (copy) the text that is inside the window • Make sure all text that is desired is visible inside the DOS window • Use the Edit/Mark selection from the program icon menu to mark the text to be captured and then press the Enter key MCT260-Operating Systems I 23 Marking Text MCT260-Operating Systems I 24 Homework Assignment • Reading – Windows XP Textbook – Chap 1 – CLI Textbook - pp. 24-26, 34, 39-42, 52-64 – Handout • Lab Exercise – Online Help – Operating System Interfaces • Homework 2 Basics of Windows XP • Due Date: Next Tuesday MCT260-Operating Systems I 25 References • • • • Windows XP Textbook CLI Textbook Internet Metro Lab MCT260-Operating Systems I 26