* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download document 8932812
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
Problem of Apollonius wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Euclidean geometry wikipedia , lookup
Approximations of π wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
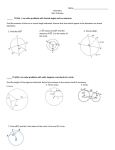
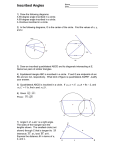
Name: ______________________________________________________________ Date: ______________________ Period: ______ Chapter 13: Circle Arcs & Angles Topic 1: Angle Relationships – Central & Inscribed 1) Central Angle The degree measure of an arc is ________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________ ̂ =___________. If 𝑚 < 𝐴𝑃𝐵 = 60°, then 𝑚𝐴𝐵 According to the provided circle: Major Arc = _______________ Minor Arc = ______________ A circle gets it’s name from the center. Therefore, the diagram above is called Circle P. Examples: 1) ̂ = _______________ 𝑚𝐴𝐵 4) 2) 3) ̂ = _______________ 𝑚𝐴𝐵 𝑚 < 𝐴𝑃𝐵 = ______________ Given: Circle P, 𝑚 < 𝐵𝑃𝐶 = 15° Find: a) 𝑚 < 𝐴𝑃𝐶 = ____________________ ̂ = ___________________ b) 𝑚 𝐴𝐶 ̂ = ___________________ c) 𝑚 𝐵𝐶 ̂ = ___________________ d) 𝑚 𝐴𝐵 ̂ = ___________________ e) 𝑚 𝐴𝐵𝐶 1 2) Inscribed Angle To find the measure of an inscribed angle, we _____________________ __________________________________________________________. Formula: ________________________________________ Examples: ̂ = 140° 1) Find 𝑚 < 𝐴 when 𝑚 𝐵𝐶 ̂ = 60° 2) Find 𝑚 < 𝑁 when 𝑚 𝑀𝑂 ̂ = ________________ 3) Find 𝑚 𝐴𝐶 𝑚 < 𝐴 = ______________ 𝑚 < 𝐶 = ______________ ̂ = _______________ 𝑚 𝐴𝐵 Mixed Examples (Common Core) 4) In the figure below, O is the center of the circle and segment AD is a diameter. a.) Find m<AOB. b.) If m<AOB:m<COD = 3:4, what is m<BOC? 2 5) In the circle shown, BC is a diameter with center A. m<CBE = 26o and m<BDA = 18o. ̂. a.) Find the measure of 𝐶𝐸 b.) Find m<BAE. c.) Find m<DAB. 6) The diagram below is of Circle A. Use the information given to find the measure of the labeled angles. 3 Name: ______________________________________________________________ Date: ______________________ Period: ______ Topic 1: Angle Relationships – Central & Inscribed Complete the following examples. Show all work, including formulas for free-response questions. A correct answer with no work shown will not receive credit on a test or quiz. 1.) In the diagram below of circle O, m<ABC = 24. What is the m<AOC? (1) 12 (2) 24 (3) 48 (4) 60 2.) As shown in the diagram below, quadrilateral DEFG is inscribed in a circle and m<D = 86. ̂. a.) Determine and state 𝐺𝐹𝐸 b.) Determine and state m<F. 3.) Given Circle A, the m<B = 32o. Find m<ACD. 4 ̂ : 𝐶𝐸 ̂ : 𝐸𝐷 ̂ : 𝐷𝐵 ̂ = 1: 2: 3: 4. Find the following measures. 4.) In circle A, 𝐵𝐶 ̂ a.) 𝑚𝐸𝐷 b.) m<BAC c.) m<DAE ̂ d.) 𝑚𝐶𝐸𝐷 ̂ = 𝑚𝐵𝐹 ̂ and <FED = 66o. 5.) Use the diagram below to find the measure of <BCD. Given: 𝑚𝐷𝐵 Review Questions: 6.) What are the coordinates of the midpoint of the line segment with endpoints (2,-5) and (8,3)? (1) (3,-4) (2) (3,-1) (3) (5,-4) (4) (5,-1) 7.) If two sides of a triangle have lengths of 4 and 10, the third side could be (1) 8 (2) 2 (3) 16 (4) 4 8.) Write an equation of a line that is parallel to the line whose equation is 3y = x + 6 and passes through the point (-3,4) 9.) Quadrilateral HYPE has vertices H(2,3), Y(1,7), P(-2,7), and E(-2,4). State and label the coordinates of the vertices H”Y”P”E” after the composition transformations 𝑟𝑥−𝑎𝑥𝑖𝑠 ∘ 𝑇5,−3. 10.) The sum of the interior angles of a regular polygon is 540o. Determine and state the number of degrees in one interior angle of the polygon. 5