* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download World War II
Swedish iron-ore mining during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Italian Empire wikipedia , lookup
Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Economy of Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Propaganda of Fascist Italy wikipedia , lookup
Italian Social Republic wikipedia , lookup
Allied war crimes during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of the attack on Pearl Harbor wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
Fascism in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Allied plans for German industry after World War II wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
Allied Control Council wikipedia , lookup
American Theater (World War II) wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Home front during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Causes of World War II wikipedia , lookup
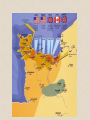
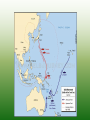
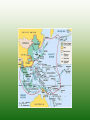
World War II (1942-1945) Mobilizing the Military • Selective Service Act – 5 million volunteers – 10 million drafted – Only 8 weeks of training • Expanding the Military – George Marshall: US Army Chief of Staff – Created WAAC (Women’s Air Corps) – Segregated units for minorities Industrial Changes • War Productions Board: consumer products to military products • New workers: women and minorities (Rosie the Riveter) • Office of Scientific Research and Development – Radar, sonar, DDT, Manhattan Project Opportunity and Adjustment Economic gains (unemployment at 1.2%) Women- 35% of workforce Farmers- able to pay off debts Population shifts (California, Midwest) Families Single parent homes Teenage delinquency Quick marriages GI Bill of Rights: education and training for veterans Discrimination Discrimination • CORE (Congress on Racial Equality) – James Farmer – Detroit Riots (34 dead) • Mexican Americans – Zoot suit riots • Japanese Americans – Internment Camps: 110,000 people – Korematsu v US: gov’t upheld policy US & Great Britain join forces FDR & Churchill’s plans – Decided to focus on Germany first – Would accept only unconditional surrender – Battle of the Atlantic • Germany attacking US ships off east coast • US enhanced ship building program Eastern Front German troops attacking USSR German troops couldn’t continue during winter USSR held onto Stalingrad and Germany retreated Considered a turning point of war http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Qd_Wt4N1Sss North Africa Operation Torch • Led by General Eisenhower • US pushed Germany/Italy north Casablanca Conference: planning of D-Day Italy Allies captured Sicily & headed towards Italy Italians tired of war; forced Mussolini to resign; King of Italy had him arrested German’s took Italy and released Mussolini Allies freed Italy after 1 year of fighting; Italians arrested/killed Mussolini D-Day D-Day (June 6, 1944) – Largest amphibious invasion in history – Allies attacked Normandy, France – Led by Eisenhower and Patton – Sept: Allies freed France from Germany http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=31nt2fsMORU Battle of the Bulge Oct. 1944 Last major battle with Germany Allies won The End (Europe) Liberation of concentration camps FDR died on April 12, 1945 Germany surrendered – April 25, 1945: USSR in Berlin – April 30, 1945: Hitler committed suicide – May 8, 1945: V-E day (Victory in Europe) Pacific Japan advances – Conquered most of Pacific by 1942 – Defeated Gen. MacArthur in the Philippines First Actions Bombed Tokyo Battle of Coral Sea (stopped Japan from attacking Australia) Battle of Midway Stopped Japan from advancing to Hawaii – US Admiral: Chester Nimitz – US victory; the avenging of Pearl Harbor – Considered the turning point in the Pacific Military Strategy Island Hopping – US bypassed Japanese strong islands – Freed the Philippines – Leyte Gulf: use of kamikazes – Last battles: Iwo Jima and Okinawa The End (Pacific) Manhatten project had already begun – Secret creation of the bomb – Led by J. Robert Oppenheimer – 7-16-45: bomb tested in New Mexico – Hiroshima and Nagasaki – August 6, 1945 & August 9, 1945 (200,000 killed) – Sept 2, 1945: Japan surrendered • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ncq_Wye43TM • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gwkyPvlWPM0 Rebuilding (Europe/Japan) Yalta Conference: agreed to establish UN Nuremburg war trials: Nazi leaders on trial Occupation of Japan – Led by MacArthur – Focused on economy, government, education