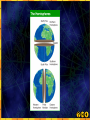
* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
Presentation Plus! Glencoe World Geography Copyright © by The McGraw–Hill Companies, Inc. Developed by FSCreations, Inc., Cincinnati, Ohio 45202 Send all inquiries to: GLENCOE DIVISION Glencoe/McGraw–Hill 8787 Orion Place Columbus, Ohio 43240 Chapter Introduction Section 1 Exploring Geography Section 2 The Geographer’s Craft Chapter Summary & Study Guide Chapter Assessment Click on a hyperlink to view the corresponding slides. Chapter Objectives • Describe the elements of geography and the topics geographers study. • Identify the tools and applications of geography and its relationship to other fields of study. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information. Write a journal entry describing the part of the world in which you live–its physical features, plant and animal life, and people. Think about how your observations are similar to and different from the ways a geographer looks at the world. Exploring Geography Objectives • Describe the physical and human features that geographers study. • Explain how geographers describe the earth’s features and their patterns. • Discuss how geography is used. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information. Exploring Geography Terms to Know • location • formal region • absolute location • functional region • hemisphere • perceptual region • grid system • ecosystem • relative location • movement • place • human-environment interaction • region Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information. Exploring Geography Places to Locate • Equator • North Pole • South Pole • Prime Meridian Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information. Click the Speaker button to listen to the audio again. One of the major goals of ancient geographers was to measure the size and shape of Earth. The appearance of Earth’s shadow on the eclipsing moon proved to most people that Earth was spherical. In the 200s B.C. Greek geographer Eratosthenes used angles of the sun over a specific distance to calculate the circumference of Earth. His estimate was off by only a few hundred miles. The Elements of Geography • Geographers are specialists who describe Earth’s physical and human features and the interactions of people, places, and environments. (pages 19–20) The Elements of Geography (cont.) List some of the tools geographers might use to describe the features of Earth and the relationships between them. Geographers might use maps, atlases, charts, measuring devices, thermometers, and barometers to describe the features of Earth and the relationships between them. (pages 19–20) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer. The World in Spatial Terms Spatial relations means “relations in space”: how places, people, and features of the earth are connected because of their locations. • Absolute location The exact latitude and longitude at which a place is found on the globe is its absolute location. • Relative location Relative location describes a place’s location in relation to another place. (pages 20–21) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information. The World in Spatial Terms (cont.) When is it useful to know the absolute location of a place? When is it useful to know its relative location? Absolute location is useful for a team of explorers trying to find a ship that had sunk, like the Titanic, for example. Relative location is useful for giving directions to travelers. (pages 20–21) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer. Places and Regions • A place is a particular space on Earth with physical and human meaning. • A region, larger than a place, is a group of places that are united by shared characteristics. • A formal region, or uniform region, is an area defined by a common characteristic. (page 21) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information. Places and Regions (cont.) • A functional region is a central place and the outlying areas linked to it by transit systems, for example. • A perceptual region is defined by popular feelings and images rather than by objective data. (page 21) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information. Places and Regions (cont.) Give some examples of a place, a uniform region, a functional region, and a perceptual region. Possible answer: The city of Philadelphia is a place. The Pennsylvania anthracite coal region is a uniform region. The Delaware Valley is a functional region. Pennsylvania–the Keystone State–is a perceptual region. (page 21) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer. Physical Systems • Physical systems–volcanoes, floods, and hurricanes–shape the earth’s surface. (pages 21–22) Physical Systems (cont.) What kinds of physical systems have shaped the earth in the region where you live? Possible answers: Tornadoes, floods, erosion, glaciation, hurricanes, earthquakes, and volcanoes have shaped the region. (pages 21–22) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer. Human Systems • People affect the earth by settling it, forming societies, and migrating. • People also move goods and ideas to new places. (page 22) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information. Human Systems (cont.) What historical movements of people and ideas have changed the United States? Possible answer: Native American societies were greatly changed when Europeans began to settle North and South America. Forced migration of African Americans, waves of European immigrants in the late 1800s, the westward movement across North America, legal and illegal immigrants from Latin America, and Asian immigration following the Vietnam War have also changed the United (page 22) States. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer. Environment and Society • People affect the environment by clearing or planting forests, building industries and cities, and hunting animals. • Features of the environment such as mountain ranges and deserts often pose barriers to human migration. (page 22) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information. Environment and Society (cont.) How can people overcome the physical obstacles of their environment? People can fly planes over mountain ranges. They can build tunnels through mountains for roads or railroads. They can clear paths and build roads through forests. They can build bridges, dams, and canals. (page 22) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer. The Uses of Geography • Geographers provide important information about the planet’s physical features and processes, living things, and human systems. Such information describes the planet and contributes to planning for future needs. (page 22) The Uses of Geography (cont.) What can a geographer tell you about your environment? Possible answers: Geographers can describe a place’s land [flat, mountainous] and water [salt or fresh]. They can also give the distances between all the places in a region, and can describe the temperatures and precipitation levels at different seasons of the year. Geographers can also interpret population patterns and explain cultural relationships. (page 22) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer. Checking for Understanding Define Match each definition in the left column with the appropriate term in the right column. __ M 1. the study of human activities and their relationship to the cultural and physical environments __ F 2. a particular space with physical and human meaning __ B 3. the exact position of a place on the earth’s surface __ K 4. the complex community of interdependent living things in a given environment __ L 5. ongoing movement of people, goods, and ideas Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answers. A. B. C. D. E. F. G. H. I. J. K. L. M. location absolute location hemisphere grid system relative location place region formal region functional region perceptual region ecosystem movement human environment interaction Checking for Understanding Define Match each definition in the left column with the appropriate term in the right column. __ C 6. half of a sphere or globe, as in the earth’s Northern and Southern Hemispheres __ J 7. a region defined by popular feelings and images rather than by objective data __ I 8. a central point and the surrounding territory linked to it __ A 9. a specific place on the earth __ H 10. a region defined by a common characteristic, such as production of a product Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answers. A. B. C. D. E. F. G. H. I. J. K. L. M. location absolute location hemisphere grid system relative location place region formal region functional region perceptual region ecosystem movement human environment interaction Checking for Understanding Define Match each definition in the left column with the appropriate term in the right column. __ D 11. pattern formed as the lines of latitude and longitude cross one another __ G 12. place united by specific characteristics __ E 13. location in relation to other places Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answers. A. B. C. D. E. F. G. H. I. J. K. L. M. location absolute location hemisphere grid system relative location place region formal region functional region perceptual region ecosystem movement human environment interaction Critical Thinking Categorizing Information Consider the physical and human factors that constitute a region. Identify the differences among formal, functional, and perceptual regions. A formal region is defined by a common feature. A functional region is a central place and its surroundings. A perceptual region is defined by an image. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer. Critical Thinking Drawing Conclusions How might geographers’ knowledge of human systems benefit people? Geographers’ knowledge of human systems might lead to developing resources or locating structures. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer. Critical Thinking Making Generalizations Explain how knowing about the geography of a particular city might influence your decision to move there. Knowledge of the climate, landforms, population, or culture might influence your decision to move to a particular city. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer. Analyzing Diagrams Location Study the diagram on the right. In which hemispheres is Africa located? Africa extends into all four hemispheres: Northern, Southern, Eastern, and Western. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer. Applying Geography Relative Location Write a paragraph that describes the relative location of your school in at least five ways. In what instances might relative location be more useful than absolute location? In what instances might absolute location be more useful? Close Write a paragraph to introduce geography to younger students. Reread “A Geographic View” on page 19 of your textbook as a model for descriptive language that sparks interest. The Geographer’s Craft Objectives • Identify the major branches of geography and the topics each branch studies. • Describe the research methods geographers use. • Discuss the relationship of geography to other subject areas. • List the kinds of geographic careers that are available today. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information. The Geographer’s Craft Terms to Know • physical geography • human geography • meteorology • cartography • geographic information systems (GIS) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information. Click the Speaker button to listen to the audio again. Cartography, or mapmaking, began to develop in the Age of Exploration. Explorers such as Christopher Columbus and Ferdinand Magellan drew rough maps of the lands they found across the Atlantic Ocean. By the early 1500s, European maps showed entire unexplored continents between Europe and Asia. Branches of Geography • Physical geography focuses on the study of Earth’s physical features. • Human geography, or cultural geography, studies human activities and their relationship to the environment. (pages 23–24) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information. Branches of Geography (cont.) What kinds of questions would you ask a physical geographer? A cultural geographer? Sample questions: Physical: Where are the world’s tallest mountains? Cultural: Which languages are most commonly spoken worldwide? Record your questions and look for answers as you study various world regions. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer. (pages 23–24) Geographers at Work • Direct Observation Going to a geographic location to see what it is like is direct observation. • Sometimes geographers rely on aerial or satellite photographs. • Mapping Cartographers are people who design and make maps–graphic representations of places and regions and more complicated information about the relationships of people, places, and things. (pages 24–26) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information. Geographers at Work (cont.) (pages 24–26) Click the Speaker button to listen to the audio again. Geographers at Work (cont.) • Interviewing Cultural geographers often interview the people whose activities they study. • Statistics Geographers use statistics to present data, find patterns, and study populations. (pages 24–26) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information. Geographers at Work (cont.) (pages 24–26) Click the Speaker button to listen to the audio again. Geographers at Work (cont.) • Technology Geographers use advanced technology–satellite photos, radar, and geographic information systems (GIS)–to study the environment, the weather, and human settlement patterns. (pages 24–26) Geographers at Work (cont.) Why do geographers often rely on maps rather than on verbal descriptions? Geographers rely on maps because they can show a great deal of information quickly. For example, maps may show relative distances, elevation, crops, population, and resources at a glance. Verbal descriptions take much longer to read. (pages 24–26) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer. Geography and Other Disciplines • History and Government Geographers study history and government to understand changes that have taken place over time. • Culture Human geographers study sociology and anthropology to learn how people have interacted with their environment over time. (pages 26–27) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information. Geography and Other Disciplines (cont.) • Economics Geographers study economics to understand how the location of resources affects the ways people make, transport, and use goods and provide services. (pages 26–27) Geography and Other Disciplines (cont.) What other areas of study might be useful to geographers? Explain. Possible answers: Knowledge of biology would help a physical or cultural geographer interested in the environment. Knowledge of literature, especially travel diaries and journals, would provide eyewitness accounts of how places looked at certain times in history. (pages 26–27) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer. Geography as a Career • Knowledge of geography helps people who work in many other fields. (page 27) Geography as a Career (cont.) Name a job in which it would be helpful to understand geography. Explain. Possible answers: A travel agent needs to inform clients about climates and weather so they can make the best travel plans. A director who wants to shoot a film in the desert needs to know what access he or she will have to necessary supplies and housing and to weather information. (page 27) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer. Checking for Understanding Define Match each definition in the left column with the appropriate term in the right column. __ D 1. the science of mapmaking __ B 2. the study of human activities and their relationship to the cultural and physical environments __ E 3. computer tools for processing and organizing details and satellite images with other pieces of information __ C 4. the study of weather and weather forecasting __ A 5. the study of Earth’s physical features Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answers. A. physical geography B. human geography C. meteorology D. cartography E. geographic information systems (GIS) Critical Thinking Predicting Consequences What might happen if an economic geographer did not interview citizens when preparing a city transportation plan? The plan may not reflect the needs and travel patterns of the citizens and may be unsuccessful. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer. Critical Thinking Making Inferences What kinds of geographers might be employed by a manufacturing company? A manufacturing company might employ economic geographers or environmental specialists. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer. Critical Thinking Making Generalizations How does the study of other disciplines help geographers in their work as countries become increasingly interdependent? Using many disciplines helps geographers contribute effective solutions. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer. Analyzing Maps Place Study the map of the United States in the Reference Atlas on pages RA6–RA7 of your textbook. What kinds of information can you learn from this map? How does the information on this map differ from the map on pages RA8–RA9 of your textbook? Applying Geography Research Methods As a geographer working on a plan for a new community center, what research methods would you use? Explain your choices in a paragraph. Close Write an employment ad describing your dream job in the field of geography. Section 1: Exploring Geography Key Points (pages 19–22) • Geographers study the earth’s physical and human features and their interrelationships. • Geographers use absolute and relative locations as reference points. • Geographers identify three types of regions– formal, functional, and perceptual. • Geography contributes knowledge about the relationships among human activities, the earth’s physical systems, and the environment in order to develop a better future. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information. Section 2: The Geographer’s Craft Key Points (pages 23–27) • Geographers use special research skills, such as direct observation, mapping, interviewing, statistics, and technology. • Studying other social sciences helps geographers analyze the patterns and relationships among these different fields. • Geographers can specialize and may work in government, business, science, planning, or education. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information. Reviewing Key Terms Insert the key term that best completes each of the following sentences. absolute location cartography ecosystem formal region grid system human geography physical geography relative location geographic information systems (GIS) 1. Plants and animals depend on one another in a(n) ___________________. ecosystem grid system 2. Geographers use a(n) ___________________ formed by lines of latitude and longitude to determine ___________________ . absolute location Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answers. Reviewing Key Terms Insert the key term that best completes each of the following sentences. absolute location cartography ecosystem formal region grid system human geography physical geography relative location geographic information systems (GIS) 3. ___________________ is the study of the human Human geography aspects of geography. 4. A(n) ___________________ has boundaries formal region determined by a common characteristic. 5. Another name for mapmaking is _____________. cartography Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answers. Reviewing Key Terms Insert the key term that best completes each of the following sentences. absolute location cartography ecosystem formal region grid system human geography physical geography relative location geographic information systems (GIS) 6. ________________ Relative location is expressed in relation to other places. 7. Computer tools that process data and satellite images with other pieces of geographic information geographic information systems (GIS) are called ________________________________. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answers. Reviewing Key Terms Insert the key term that best completes each of the following sentences. absolute location cartography ecosystem formal region grid system human geography physical geography relative location geographic information systems (GIS) 8. _________________ Physical geography focuses on the study of the earth’s physical features. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer. Reviewing Facts Section 1: Exploring Geography How do geographers determine the locations of places? Geographers determine the location of places by using the latitude/longitude grid or by locating places in relation to other places. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer. Reviewing Facts Section 1: Exploring Geography What are the three types of regions identified by geographers? The three types of regions are formal, functional, and perceptual regions. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer. Reviewing Facts Section 1: Exploring Geography Why do geographers study human systems and human-environment relationships? Geographers study human systems and human-environment relationships to understand how the earth affects and is affected by human activity so that informed decisions can be made. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer. Reviewing Facts Section 1: Exploring Geography What are two ways that every place on the earth can be located? The two ways every place on the earth can be located are by describing its absolute location or its relative location. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer. Reviewing Facts Section 2: The Geographer’s Craft How do physical and human geography differ? Physical geography is the study of the earth’s physical features. Human geography focuses on human activities in relation to the physical world. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer. Reviewing Facts Section 2: The Geographer’s Craft What research methods do geographers use? Geographers use direct observation, mapping, interviewing, statistics, and technology as research methods. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer. Reviewing Facts Section 2: The Geographer’s Craft What other subjects do geographers study? Geographers also study history and government, culture, and economics. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer. Critical Thinking Summarizing the Main Idea How do geographers use the elements of geography to study the earth? The elements of geography help geographers organize information about the earth and learn about geographic events and patterns. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer. Critical Thinking Making Inferences What subjects might you study in order to become an urban planner? Explain. Possible answer: One might study geography, statistics, economics, architecture, and urban design to become an urban planner. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer. Critical Thinking Predicting Consequences Consider the many ways that technology has affected the way people live and work. Then imagine that you have become a geographer of the future. How do you think technology will change the way you work? Locating Places Match the letters on the map with the places and physical features of the earth. __1. North America B __2. South America A __3. Africa D __4. Asia E __5. Europe C __6. Antarctica G __7. Australia F __8. Atlantic Ocean I __9. Indian Ocean H __10. Pacific Ocean J Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answers. Why are international time zones determined from the time at the Royal Naval Observatory at Greenwich, England (Greenwich Mean Time)? Time zones are determined at the Royal Naval Observatory because the Prime Meridian passes through Greenwich. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer. Explore online information about the topics introduced in this chapter. Click on the Connect button to launch your browser and go to the Glencoe World Geography Web site. At this site, you will find interactive activities, current events information, and Web sites correlated with the chapters and units in the textbook. When you finish exploring, exit the browser program to return to this presentation. If you experience difficulty connecting to the Web site, manually launch your Web browser and go to http://geography.glencoe.com Use the circle graph below and your knowledge of geography to answer the following questions. 1. Which ocean covers the smallest area of the earth’s surface? A Atlantic B Indian C Pacific D Arctic Test–Taking Tip Study the information shown on the circle graph for the areas of the earth covered by land and by oceans. Then compare the relative sizes of the different graph segments. By comparing the segments you will be able to determine the correct answers. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer. 2. Which ocean covers about as much of the earth’s surface as land does? F Indian H Arctic G Pacific J Atlantic Test–Taking Tip Study the information shown on the circle graph for the areas of the earth covered by land and by oceans. Then compare the relative sizes of the different graph segments. By comparing the segments you will be able to determine the correct answers. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer. Nighttime photographs taken from space capture population patterns by showing blazes of light where people live. Saving Ecosystems with Maps Scientists show habitat loss and endangered species on color-coded maps that can be used to convince individuals, corporations, and politicians to support conservation and preservation efforts. Global Culture Music, food, and entertainment are crossing traditional boundaries. “World Music” is a growing musical category, and new “fusion” cuisines blend foods from different countries. Understanding Graphs Graphs are visual representations of statistical data. Large amounts of information can be condensed when presented in graphs. Studying graphs allow readers to see relationships clearly. Understanding Graphs Learning the Skill The three main types of graphs present numerical information. Line graphs record changes in data over time. The vertical axis (y–axis) shows units of measurement, and the horizontal axis (x–axis) shows intervals of time. Bar graphs use bars of different lengths to compare different quantities. Circle graphs show the relationship of parts to a whole as percentages. To understand a graph: • Read the graph title to identify the subject. • Study the labels to understand the numerical information presented. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information. Understanding Graphs Learning the Skill The three main types of graphs present numerical information. Line graphs record changes in data over time. The vertical axis (y–axis) shows units of measurement, and the horizontal axis (x–axis) shows intervals of time. Bar graphs use bars of different lengths to compare different quantities. Circle graphs show the relationship of parts to a whole as percentages. To understand a graph: • Study the information presented and the use of colors and patterns. • Compare the lines, bars, or segments, and look for relationships in order to draw conclusions. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information. Understanding Graphs Practicing the Skill Study the graphs to answer these questions. 1. Line graph What is the difference in population between the low and high projections? The difference between low and high projections is three. 2. Bar graph In which decade did migration cause the least change in population. Migration caused the least change in population during the 1930s. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display possible answers. Understanding Graphs Practicing the Skill Study the graphs to answer these questions. 3. Circle graph What percent of immigrants to the United States in the 1990s came from Europe? Thirteen percent of immigrants to the United States in the 1990s came from Europe. 4. What general population trends do the three graphs show? The graphs show an increase in world population, a growing effect of migration on population change, and growing numbers of Asian and Latin American immigrants to the United States. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display possible answers. Charts The Hemispheres The Global Grid Jobs in Geography Click on a hyperlink to view the corresponding slide. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer. End of Custom Shows WARNING! Do Not Remove This slide is intentionally blank and is set to auto–advance to end custom shows and return to the main presentation.