* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Resource and Admission Control in NGN Ning Li Co-editor of Y.RACF
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
Wireless security wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
Zero-configuration networking wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
SIP extensions for the IP Multimedia Subsystem wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
List of wireless community networks by region wikipedia , lookup
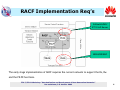
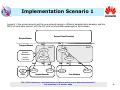
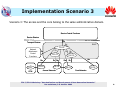
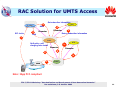
International Telecommunication Union Resource and Admission Control in NGN Ning Li Co-editor of Y.RACF Huawei Technologies ITU-T/ITU-D Workshop "Standardization and Development of Next Generation Networks" Dar es Salaam, 3-5 October 2006 Outline o Works on RACF in ITU-T o Key features of RACF o RACF implementation requirements o RACF implementation scenarios o Example E2E QoS solution o RAC solution for ADSL/LAN access o RAC solution for UMTS access RAC ---- Resource and Admission Control ITU-T/ITU-D Workshop "Standardization and Development of Next Generation Networks" Dar es Salaam, 3-5 October 2006 2 Works on RACF in ITU-T The functional architecture of RACF as defined in ITU RACF document SCF-- Service Control Functions; NACF-- Network Attachment Control Functions; PD-FE -- Policy Decision Functional Entity RACF -- Resource and Admission Control Functions; TRC-FE -- Transport Resource Control Functional Entity; PE-FE -- Policy Enforcement Functional Entity (PE-FE); TRE-FE -- Transport Resource Enforcement Functional Entity ITU-T/ITU-D Workshop "Standardization and Development of Next Generation Networks" Dar es Salaam, 3-5 October 2006 3 Key Features of RACF o Key Features of RAC: • Resource arbitrator • Service-driven QoS control, traffic control, NAPT control and FW inspection mode selection • Incremental implementation • Unified Rs to the service layer • Unified Rw interface going down to network edge devices • Compliance checking of the traffic and QoS against subscribed bandwidth and QoS ITU-T/ITU-D Workshop "Standardization and Development of Next Generation Networks" Dar es Salaam, 3-5 October 2006 4 RACF Implementation Req’s Softswitch/IMS/ IPTV/VoD Server, BRAS/ER/SBC The early stage implementation of RACF requires the current network to support the Rs, Rw and the PE-FE functions. ITU-T/ITU-D Workshop "Standardization and Development of Next Generation Networks" Dar es Salaam, 3-5 October 2006 5 Implementation Scenario 1 Scenario 1: the access network and the core network belong to different administrative domains, and the RACFs at both sides interact with the SCF with no information exchanged in the between. Service Control Functions Service Stratum Rs Rs Transport Stratum Rd RACF PD-FE Network Attachment Control Functions Ru CPE CPN PD-FE Rt Rt TRC-FE Rw Rc PE-FE RACF Rp TRC-FE Rw PE-FE Access Networks Rw Rc Rw PE-FE PE-FE Core Networks ITU-T/ITU-D Workshop "Standardization and Development of Next Generation Networks" Dar es Salaam, 3-5 October 2006 6 Implementation Scenario 2 Scenario 2:The access and the core belong to different administrative domains, and the SCF interacts with either of the RACFs at the two sides. The RACFs in the core and the access exchange information via the Ri reference point. Note: The Ri reference point is to be detailed in R2. Service Control Functions Service Stratum Rs Transport Stratum RACF PD-FE Network Attachment Control Functions Ru CPN Rt Rc PE-FE RACF PD-FE Rt TRC-FE Rw CPE Rd Ri Rp TRC-FE Rw PE-FE Access Networks Rw Rc Rw PE-FE PE-FE Core Networks ITU-T/ITU-D Workshop "Standardization and Development of Next Generation Networks" Dar es Salaam, 3-5 October 2006 7 Implementation Scenario 3 Scenario 3: The access and the core belong to the same administrative domain. Service Control Functions Service Stratum Rs Transport Stratum Rd RACF PD-FE Network Attachment Control Functions Ru CPN Rt TRC-FE Rw CPE Rt PE-FE Rc Rw PE-FE Access Networks Rp TRC-FE Rw Rw Rc PE-FE PE-FE Core Networks ITU-T/ITU-D Workshop "Standardization and Development of Next Generation Networks" Dar es Salaam, 3-5 October 2006 8 Implementation An E2E QoS Solution Scenario 3 180 (SDP2) CSCF CSCF 180 (SDP2) Invite (SDP1) Service Info RACF Invite Service Info RACF Invite (SDP1) (SDP1) RACF RACF DES DES LER GGSN LSR 3G RAN LER LSR BRAS LSR ADSL IP/MPLS Core SIP B SIP A ITU-T/ITU-D Workshop "Standardization and Development of Next Generation Networks" Dar es Salaam, 3-5 October 2006 9 RAC solution for ADSL/LAN access P-CSCF A-RACF&PDF IMS bearer NW Access resource reservation SIP Phone DSLAM VLAN 1 VLAN 2 Modem PC AMS/DHCP Server VLAN 101 2PVC 2VLAN VLAN 102 SBC LAN LAN BAS DHCP Server Radius Server Data NW ITU-T/ITU-D Workshop "Standardization and Development of Next Generation Networks" Dar es Salaam, 3-5 October 2006 10 RAC Solution for UMTS Access P-CSCF SIP: Invite Get subscriber information 2 AAR 4 Diameter Diameter 3 SPR 5 Return subscriber information AAA 1 PCRF QoS policy and charging rules install OCS 7a Diameter Diameter 9 6 7b SGSN 8 GGSN UMTS RAN Note: 3Gpp PCC compliant ITU-T/ITU-D Workshop "Standardization and Development of Next Generation Networks" Dar es Salaam, 3-5 October 2006 11 The End Thank you for your attention! (http://www.huawei.com) ITU-T/ITU-D Workshop "Standardization and Development of Next Generation Networks" Dar es Salaam, 3-5 October 2006 12