* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download COS 420 day 25
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
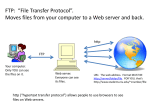
COS 420 DAY 25 Agenda Assignment 5 posted Chap 22-26 Due May 4 Final exam will be take home and handed out May 4 and Due May 10 Latest version of Protocol Definition is better Today we will discuss File Transfer And Access (FTP,TFTP, NFS) Project 2 Grading Meeting Timelines Deliverables Program requirements Protocol Definition Due March 30 15% Due April 13 15% Due May 4 Due May 1 25% 25% Due May 4 10% Better but I hope to see improvement by May1 Working Network Application Final Paper late 10% User Manual Protocol Program requirements Technical Specifications Presentation On-Line File Sharing Always a popular application Two basic paradigms Whole-file copying Piecewise file access Piecewise access mechanism Opaque: application uses special facilities to access remote file Transparent: application uses same facilities to access local and remote files File Transfer Whole file copying Client Contacts server Specifies file Specifies transfer direction Server Maintains set of files on local disk Waits for contact Honors request from client File Transfer Protocol (FTP) Major TCP/IP protocol for whole-file copying Uses TCP for transport Features Interactive access Format specification (ASCII or EBCDIC) Authentication control (login and password) FTP Process Model Separate processes handle Interaction with user Individual transfer requests FTP’s Use of TCP Connections Data transfer connections and the data transfer processes that use them can be created dynamically when needed, but the control connection persists throughout a session. Once the control connection disappears, the session is terminated and the software at both ends terminates all data transfer processes. Control Connection Vs. Data Connection For data transfer, client side becomes server and server side becomes client Client Creates process to handle data transfer Allocates port and sends number to server over control connection Process waits for contact Server Receives request Creates process to handle data transfer Process contacts client-side Question For Discussion What special relationship is required between FTP and NAT? Interactive Use Of FTP Initially a command-line interface User User User User invokes client and specifies remote server logs in and enters password issues series of requests closes connection Currently Most FTP initiated through browser User enters URL or clicks on link Browser uses FTP to contact remote server and obtain list of files User selects file for download Anonymous FTP Login anonymous Password guest Some servers require you to enter an email address Used for ‘‘open’’ FTP site (where all files are publicly available Typically used by browsers Secure File Transfer Protocols Secure Sockets Layer FTP (SSL-FTP) Secure File Transfer Program (sftp) Uses secure sockets layer technology All transfers are confidential Almost nothing in common with FTP Uses ssh tunnel Secure Copy (scp) Derivative of Unix remote copy (rcp) Uses ssh tunnel Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) Alternative to FTP Whole-file copying Not as much functionality as FTP Code is much smaller Intended for use on Local Area Network Runs over UDP Diskless machine can use to obtain image at bootstrap TFTP Packet Types TFTP Retransmission Symmetric (both sides implement timeout and retransmission) Data block is request for ACK ACK is request for next data block Sorcerer’s Apprentice Bug Consequence of symmetric retransmission Duplicate packet is perceived as second request, which generates another transmission Duplicate response triggers duplicate packets from the other end Cycle continues Network File System (NFS) Protocol for file access, not copying Developed by Sun Microsystems, now part of TCP/IP standards Transparent (application cannot tell that file is remote) NFS Implementation Remote Procedure Call (RPC) Also developed by Sun Microsystems, now part of TCP/IP standards Used in implementation of NFS Relies on eXternal Data Representation (XDR) standard for conversion of data items between heterogeneous computers Summary Two paradigms for remote file sharing File Transfer Protocol (FTP) Whole file copying Piecewise file access Standard protocol for file copying Separate TCP connection for each data transfer Client and server roles reversed for data connection Examples of secure alternatives to FTP SSL-FTP, sftp, and scp Summary (continued) Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) Alternative to FTP that uses UDP Symmetric retransmission scheme Packet duplication can result in Sorcerer’s Apprentice problem Network File System (NFS) Standard protocol for piecewise file access Uses RPC and XDR