* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Defining Network Protocols
Server Message Block wikipedia , lookup
Parallel port wikipedia , lookup
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
SIP extensions for the IP Multimedia Subsystem wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
Asynchronous Transfer Mode wikipedia , lookup
Multiprotocol Label Switching wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
IEEE 802.1aq wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
TCP congestion control wikipedia , lookup
Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
Communication protocol wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
UniPro protocol stack wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
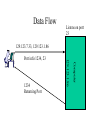
Defining Network Protocols • Application Protocols – Application Layer – Presentation Layer – Session Layer • Transport Protocols – Transport Layer • Network Protocols – Network Layer – Data-Link Layer – Physical Layer Application Protocols • • • • • • • • • • SMTP: Simple Mail Transport Protocol X.400: International Email HTTP: Hyper Text Transport Protocol SNMP: Simple Network Management Protocol FTP: File Transfer Protocol Telnet: Interactive login SSH: Secure Shell telnet Appletalk: Apple’s networking protocol suite NCP: Novell Netware applications DNS: Domain Name Service Transport Protocols • • • • • TCP: Transmission Control Protocol SPX: Sequenced Packet Exchange Nwlink: Microsoft’s IPX/SPX Netbeui: Netbios Extended User Interface ATP: Appletalk Transaction Protocol Network Protocols • IP: Internet Protocol • IPX: Internet Packet Exchange • NWlink: Microsoft’s implementation of IPX • NetBEUI: similar to Transport • DDP: Apple’s Datagram Delivery Protocol Ethernet Packet Ethernet destination Address (first 32 bits) Ethernet Dest (last 16) Ethernet Src (16 bits ) Ethernet source Address (last 32 bits) Type Code or Length of packet IP header, TCP header, then your data Ethernet Checksum TCP/IP Network Communication • Network Layer (IP, Layer 3) (TCP, Layer 4) • Protocols are described in RFCs (Request for Comments) • Available from nis.nsf.net/internet/documents/rfc • TCP/IP Addressing – Class A (1-126).xxx.xxx.xxx – Class B (128-191).(assigned).xxx.xxx – Class C (192-223).(assigned).(assigned).xxx Subnets • Class A 255.0.0.0 • Class B 255.255.0.0 – USU uses 255.255.255.0 for subnetting buildings • Class C 255.255.255.0 Internet Addressing • • • • • • • • Each address is 4, 8 bit, decimal numbers Like Area Code/Exchange/Subscriber 129.123.7.170 129.123 is assigned to USU (domain) 7 is assigned to Computer Science 170 is assigned to PC named java4 Every Internet device must have a number Number to name conversion is done by DNS IP header • Source and Destination IP addresses • Type of Service – Selects delivery speeds vs. accuracy • Protocol (TCP,ICMP, UDP) • Time to Live (Router hops) • Identification and Fragment offset – Reassembly of a fragmented datagram IP Header Version Leng Type of Svc Total Length Identification Flags Frag Offset Time to Live Protocol Header Checksum Source Address Destination Address TCP Header then your data... TCP fields • • • • Ports (service identifiers) Sequence numbers Acknowledgement numbers Windowing – More retries (less acks) smaller packets – Less retries (more good data) larger packets TCP Header Source Port Destination Port Sequence Number Acknowledgement Number Data Offset Reserved Window Flags Checksum Urgent Pointer Your Data… next 500 octets ARP • • • • • • Address Resolution Protocol Associates an ethernet address to an IP address arp -a or multi show/arp only local (router port) addresses shown ARP entries have a finite (timed) lifetime ARP entries are created by routers for non ethernet protocols (token ring, PPP) • tracing an ethernet address – Host system – Router – Switch DHCP • Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol • Assigns IP address, gateway (router) address, name server, netmask, time server, and other configuration information based on a NIC’s MAC address • IP addresses may be fixed or taken from a pool of available addresses • Allows assigning temporary addresses for transient computers. TCP, UDP, ICMP • TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) – – – – Datagrams Connection Oriented End to End error checking Source Port, Destination Port • Sockets, Well Known Ports Data Flow Listens on port 23 129.123.7.33, 129.123.1.86 Computer 1234 Returning Port 129.123.1.86 Port info:1234, 23 Services • /etc/services or multinet:services.master_server • lists service name and port number • Common (well known) ports: – – – – – – FTP 21 TELNET 23 SMTP 25 HTTP 80 SSH 22 Finger 79 UDP (user datagram protocol) • • • • • Connectionless One Way Fast, Simple No guarantee of delivery NFS, DNS, DHCP, NTP, TALK ICMP (Internet control message protocol) • • • • Error Messages Intended for the TCP/IP software itself PING (host unreachable messages) Simple Headers IPX/SPX • • • • • • Internet Packet Exchange Sequenced Packet Exchange Novell Servers Routes on a WAN but not the Internet Generates Service Advertisements (SAP) Address based on a number assigned to the network segment (wire) plus the MAC address. IPX continued • RIP: Routing Information Protocol – Find fastest route to network number • SAP: Service Advertising Protocol – Server name, type, address, node, socket Netbeui • Simple Non routable • NetBIOS name resolution – based on tables in each system • NetBIOS Datagram service – Message sending, no guarantee of arrival • NETBios Session Service – Peer to Peer connection system • For small Microsoft networks • Sends a lot of data on the network wire X.25 • Packet Switching Protocol – Small (128 byte) packets – Uses the PDN (Public Data Network) – Uses store and forward method which requires a lot of buffering – Node to node error checking