* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 9. telecommunications
Internet protocol suite wikipedia , lookup
Zero-configuration networking wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Net neutrality wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
Net neutrality law wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
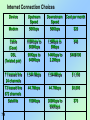
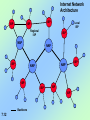
PROTOCOL RULES & PROCEDURES TO GOVERN TRANSMISSION BETWEEN COMPONENTS IN A NETWORK * 7.1 Telecommunications, Networks ANALOG SIGNAL • CONTINUOUS WAVEFORM • PASSES THRU SYSTEM • VOICE COMMUNICATIONS * 7.2 DIGITAL SIGNAL • DISCRETE WAVEFORM • TWO DISCRETE STATES: – 1-BIT & 0-BIT – ON / OFF PULSE • DATA COMMUNICATION • USES MODEM TO TRANSLATE ANALOG TO DIGITAL, DIGITAL TO ANALOG 001011101001110100101010111011110010001000010111101011010 * 7.3 TELECOMMUNICATION SYSTEM COMPONENTS • • • • COMPUTERS TERMINALS (Input / output devices) COMMUNICATIONS CHANNELS PROCESSORS (Modems; multiplexers; front-end processors) • COMMUNICATIONS SOFTWARE * 7.4 COMMUNICATION CHANNELS MEANS BY WHICH DATA ARE TRANSMITTED: • TWISTED WIRES (Copper Wires) – phone lines • COAXIAL CABLE: (Insulated Copper Wires) – Cable television • FIBER-OPTIC CABLE – high speed backbone, thousands of strands of clear glass fiber (hair), • MICROWAVE – Terrestrial or Satellite * 7.5 FIBER OPTICS • SUPER CLEAR GLASS STRANDS • FAST, LIGHT, DURABLE • BILLIONS OF BITS PER SECOND, FULL DUPLEX (10Gbps) • EXPENSIVE, HARDER TO INSTALL • OFTEN USED AS BACKBONE OF NETWORKS PHOTO * SIGNAL LASER CABLE SIGNAL DETECTOR 7.6 COMMUNICATIONS CHANNELS • TRANSMISSION SPEED: Bits per Second (BPS) or Baud • BANDWIDTH: Capacity of Channel; Difference between Highest & Lowest Frequencies BROADBAND – High speed 1.5Mbps connection 1.5MB file 8 seconds to transmit 7.7 BPS: BITS PER SECOND KBPS: KILOBITS PER SECOND MBPS: MEGABITS PER SECOND GBPS: GIGABITS PER SECOND 7.8 Internet Connection Choices Device Upstream Speed Downstream Speed Cost per month Modem 56Kbps 56Kbps $20 Cable (Coax) 100Kbps to 500Kbps 1.5Mbps to 5Mbps $40 DSL (Twisted pair) 90Kbps to 640Kbps 144Kbps to 2.2Mbps $40-$100 T1 leased line 24 channels 1.544 Mbps 1.544Mbps $1,100 T3 leased line 672 channels 44.7Mbps 44.7Mbps $8,000 Satellite 150Kbps 300Kbps to 900Kbps $70 7.9 OTHER SERVICES: • DIGITAL SUBSCRIBER LINE (DSL): enhancing capacity over copper telephone lines • CABLE MODEM: modem for cable TV for high-speed access to Internet • T1 LINE: dedicated telephone connection, 24 channels @ 1.544 megabits per second * 7.10 Internet Infrastructure 7.11 Internet backbone – made up of many large networks (NSP’s) which interconnect Network Service Providers – own internet backbone. Examples are UUNet, CerfNet, SprintNet, IBM, WCOM NAP (Network Access Point) – Where NSP’s connect. ISP’s (Internet Service Providers) – Local and regional delivery subnetworks Internet Network Architecture ISP ISP ISP Local ISP Regional ISP ISP NAP NAP ISP ISP NAP NAP ISP ISP ISP ISP Backbone 7.12 Circuit-Switched Networks • Local and long distance telephone companies were early models in the 1950s • Single paths were created to connect two parties together, called circuit switching 7.13 Packet-Switched Networks • The Internet uses Packet switching – Files and messages are broken down into packets, which are electronically labeled with their origin and destination – The destination computer collects the packets and reassembles the data from the pieces in each packet – Each computer the packet encounters decides the best route towards its destination 7.14 Packet-Switched Network and Message Packets 7.15 The TCP/IP Internet Protocol • Set of protocols developed by Vincent Cerf and Robert Kahn – Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) • Controls the assembly of a message into smaller packets before transmission, and reassembles them once received – Internet Protocol (IP) • Assigns sending and destination IP address to each packet • Rules for routing packets from their source to their destination 7.16 Routers – are packet switches. • A router is connected between networks to route packets between them. • Have updateable maps of the networks on the internet • Determines the path for the packets 7.17 Open Architecture (Internet is based on this design Philosophy) • Independent networks should not require any internal changes in order to be connected to the network • Packets that do not arrive at their destination must be retransmitted • Router computers do not retain information about the packets • No global control exists over the network 7.18 WAN – (Wide Area Network) Telecommunications network covering a large geographic area LAN – (Local Area Network) Connect computers (and devices) within a limited physical area (office, building, etc.) 7.19