* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 14Wilkins
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
Multiprotocol Label Switching wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Video on demand wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Asynchronous Transfer Mode wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
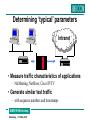
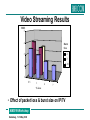
Linking User Acceptance and Network Performance Miles Wilkins (BT) P807 (JUPITER2) AIMS’99 Workshop Heidelberg, 11-12 May 1999 IP-based Services • And many more … • The world has gone IP mad (not ATM) AIMS’99 Workshop Heidelberg, 11-12 May 1999 But…. • • • • • • • ATM can guarantee bandwidth / delay IP services only “Best Effort” QoS support being added by IETF and others Real-time requirements (multimedia) Not enough (reliable) bandwidth/delay on the Internet Early use in corporate intranets How do you support these applications? – and protect other data flows? AIMS’99 Workshop Heidelberg, 11-12 May 1999 What is ‘QoS’? • Quality of Service – variously defined by ITU-T (E.800) and others • Objective – Network measurements • Subjective – User’s perception and expectations • “Constantly meeting customers expectations in a service” AIMS’99 Workshop Heidelberg, 11-12 May 1999 What is the relationship between user perceived QoS and the actual network QoS? I can’t hear him very well. Video IP Network Server How was it for you? Multimedia Collaboration Introduce packet loss & delay What is a realistic range of loss / delay values? AIMS’99 Workshop Heidelberg, 11-12 May 1999 Determining ‘typical’ parameters Intranet • Measure traffic characteristics of applications – NetMeeting, NetShow, Cisco IP/TV • Generate similar test traffic – with sequence numbers and timestamps AIMS’99 Workshop Heidelberg, 11-12 May 1999 Laboratory Subjective Tests User Video Server or Second User Applications - NetMeeting - NetShow - IP/TV Tasks - video clips - editing/ discussion Network Impairment - Packet Loss - Packet Burst Loss - Packet Delay - Packet Jitter (perceived as loss/delay by user) AIMS’99 Workshop Heidelberg, 11-12 May 1999 Data Collection - Questionnaire - Interview - video and screen capture analysis Main Interests & Results • • • • Audio quality Video quality Overall quality Acceptability – (would you use this system again with this quality?) • Quality and acceptability judgements were affected by the amount of loss exhibited by a network and by packet burst size AIMS’99 Workshop Heidelberg, 11-12 May 1999 Video Streaming Results MO S 5 4 Burst Siz e 3 1-2 6-7 9-10 2 1 0.5 1 4 7 % Loss • Effect of packet loss & burst size on IP/TV AIMS’99 Workshop Heidelberg, 11-12 May 1999 Video Streaming Results MOS 5 4 Quality Overall 3 Video Audio 2 1 Loss Burst 0 0 1/2% 1/2% 1-2 6-7 Network Condition 1% 1-2 • Effect of packet loss & burst size on NetShow AIMS’99 Workshop Heidelberg, 11-12 May 1999 Conferencing Results Video Ratings Audio Ratings • Audio quality most important and most disturbing – (for some tasks) • Rating drops between 50mS-120mS jitter – caused by receiver buffer overflow (loss)? AIMS’99 Workshop Heidelberg, 11-12 May 1999 The Next Experiments • Field Trials – video streaming and conferencing applications – network impairment on source • Video Streaming – validate laboratory tests – live video source (BBC News 24) – NetShow & IP/TV • Conferencing – packet loss burst effect? – NetMeeting AIMS’99 Workshop Heidelberg, 11-12 May 1999 Performability • Taking results of user subjective test determine how to use QoS network building blocks to provide required end-end QoS • Looking at: – RSVP (Resource ReSeVation Protocol) – RSVP over ATM – IP Differential Services – Winsock2 (support for native ATM and RSVP) – Queuing technologies (Weighted Fair Queuing, etc) – H.323 Gatekeeper – Multimedia Conference Manager – Sub-net Bandwidth Manager AIMS’99 Workshop Heidelberg, 11-12 May 1999 Performability Approach • Characterise applications traffic / QoS features – two-party and multi-party – multicast & broadcast – include end-system performance • Measure operation of QoS techniques – e.g. RSVP implementation in routers • Match – network performance required for user acceptance – network performance achievable with QoS methods AIMS’99 Workshop Heidelberg, 11-12 May 1999 Example Performability Result • Compare NetMeeting using Best Effort & RSVP Radcom Analyser NetMeeting Host #1 r s NetMeeting Host #2 r s Serial Link Investigate Router - BE (FIFO queue) - Fair Queueing - Reservation - Controlled Load (Video) - Guaranteed Service (Audio) AIMS’99 Workshop Heidelberg, 11-12 May 1999 Router SmartBits Load Generator Experiment & (Early) Results • Examine end-end delay between hosts for audio (G.723.1) & video (H.263) traffic – 1) no background load on serial link – 2) background load , fair-queuing in router – 3) background load , RSVP reservations (1250byte packets) (1250byte packets) • Audio delay – 1) 1.5 ms to 28.4 ms, mean 8.8 ms – 2) 1.5 ms to 39.5 ms, mean 9.0 ms – 3) 90% between 1.2ms and 30ms AIMS’99 Workshop Heidelberg, 11-12 May 1999 Experiment & (Early) Results • Video delay – 1) mean 33.1 ms – 2) 30 ms to 800 ms • Not acceptable to users – 3) 3.7 ms to 30ms • Acceptable to users • RSVP used to meet users’ requirements AIMS’99 Workshop Heidelberg, 11-12 May 1999 Any Questions? AIMS’99 Workshop Heidelberg, 11-12 May 1999