* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Bright Lines
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
IEEE 802.1aq wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
List of wireless community networks by region wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Zero-configuration networking wikipedia , lookup
UniPro protocol stack wikipedia , lookup
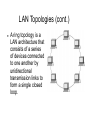
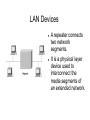
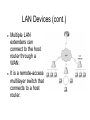
Local Area Network Daniel Shin CS 147, Section 3 November 18, 2008 What Is a LAN? A LAN is a high-speed data network that covers a small geographic area. It typically connects workstations, personal computers, printers, servers, and other devices. Characteristics High data-transfer rates. Small geographic range. Lack of a need for leased telecommunication lines. Advantages LANs offer computer users many advantages. Shared access to devices and applications. File exchange between connected users. Communication between users via electronic mail and other applications. First Commercial LAN The first commercial installation of a LAN was in December 1977 at Chase Manhattan Bank in New York. It was not an Ethernet network, but a network called ARC (Attached Resource Computer or ARCnet). ARCnet It was developed by Datapoint Corporation in 1976 and announced in 1977. ARCnet was the first widely available networking system for microcomputers. It became popular in the 1980s for office automation tasks. It is said to have since gained interest in the embedded systems market, where certain features of the protocol are especially useful. Ethernet Ethernet was developed at Xerox Corp.'s Palo Alto Research Center (PARC) in the early 1970s. The original network speed was just under 3Mbit/sec. Token Ring Token Ring uses a special three-byte frame called a token that travels around the ring. Resides at the data link layer (DLL) of the OSI model. Fiber Distributed Data Interface (FDDI) FDDI provides a standard for data transmission in a LAN that can extend in range up to 124 miles. FDDI uses a dualattached, counterrotating token ring topology. LAN Protocols and the OSI Reference Model LAN Media-Access Methods Ethernet uses carrier sense multiple access collision detect (CSMA/CD). Each network station listens before and after transmitting data. If a collision is detected, both stations wait a random time before trying to resend. LAN Media-Access Methods (cont.) Token Ring passes a special type of packet called a token around the network. If a network device has data to send, it must wait until it has the token to send it. After the data has been sent, the token is released back on the network. LAN Transmission Methods LAN data transmissions fall into three classifications: unicast, multicast, and broadcast. In each type of transmission, a single packet is sent to one or more nodes. LAN Transmission Methods (cont.) In a unicast transmission, a single packet is sent from the source to a destination on a network. A multicast transmission consists of a single data packet that is copied and sent to a specific subset of nodes on the network. A broadcast transmission consists of a single data packet that is copied and sent to all nodes on the network. LAN Topologies LAN topologies define how network devices are organized. Four common LAN topologies are: bus, ring, star, and tree. LAN Topologies (cont.) A bus topology is a linear LAN architecture. Transmissions from network stations create the length of the medium and are received by all other stations. LAN Topologies (cont.) A ring topology is a LAN architecture that consists of a series of devices connected to one another by unidirectional transmission links to form a single closed loop. LAN Topologies (cont.) A tree topology is a LAN architecture that is identical to the bus topology. Except, branches with multiple nodes are possible. LAN Devices A repeater connects two network segments. It is a physical layer device used to interconnect the media segments of an extended network. LAN Devices (cont.) Multiple LAN extenders can connect to the host router through a WAN. It is a remote-access multilayer switch that connects to a host router. LAN Devices (cont.) A hub is a physical layer device that connects multiple user stations, each via a dedicated cable. Hubs are used to create a physical star network while maintaining the logical bus or ring configuration of the LAN.