* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PPT Version
National Broadband Plan (United States) wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Net neutrality law wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Zero-configuration networking wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
Policies promoting wireless broadband in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Wireless security wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
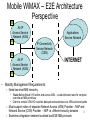
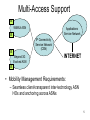
Requirements for NETLMM Protocol: 802.16e Mobile BWA* Perspective Prakash Iyer Perviz Yegani 63rd IETF, Paris NETLMM BOF BWA – Broadband Wireless Access 1 WiMAX/802.16e Mobile BWA • Mobile WiMAX (based on 802.16-2004 amended by 802.16e) is an emerging standard for broadband, wide-area wireless access – Optimized for IP services • Usage will be characterized by – High average/peak data rates to subscriber terminals compared to traditional 3G networks – Mix of audio, video, data and voice applications • Symmetric and asymmetric UL and DL traffic, real-time and non-real-time – Mobility rates exceeding 200 km/hr while satisfying ITU-T and other benchmarks for low handover packet loss, latency, jitter and delay – Need to support low power modes 2 Mobile WiMAX – E2E Architecture Perspective BS All-IP Access Service Network (ASN) BS BS Applications Service Network IP Connectivity Service Network (CSN) All-IP Access Service Network (ASN) BS INTERNET • Mobility Management Requirements: – Need two-level MM hierarchy • ‘Make-Before-Break’ HO within and across ASN – could eliminate need for complex over-the-air MM primitives • Client to remote CSN HO could be delayed and seamless over ASN anchored paths – Must support notion of separate Network Access (ASN) Provider – NAP and Network Service (CSN) Provider - NSP i.e. different security domains 3 – Seamless integration between localized and E2E MM protocols Mobile WiMAX – ASN Variants BS BS To Anchor Router / CSN IP Cloud Gateway ASN BS + Router IP Cloud To CSN BS + Router • Mobility Management Requirements: – Must accommodate Flat and Hierarchical ASN topologies – and variants thereof – Must support multi-hop relay among BSs – Must support multi-path configurations among BSs – Eliminate need for signaling from client to ASN for intra/inter ASN MM • Ideal scenario is network-based MM both within/across ASN and end-to-end – Must work irrespective of client connectivity state – Active, Idle – Client IP reachability in all power states with configurable location anonymity – IPv4 and IPv6 – Eliminate / reduce need to simulcast within ASN for duration of HO – prevent backhaul BW wastage especially for wireless backhaul 4 Multi-Access Support BS WiMAX ASN Applications Service Network BS IP Connectivity Service Network (CSN) BS Beyond 3G Evolved ASN INTERNET BS • Mobility Management Requirements: – Seamless client-transparent inter-technology ASN HOs and anchoring across ASNs 5 Summary • Traditional E2E IP MM protocols (e.g. MIP) are not adequate for needs of MBWA and Next-Gen multi-access wide-area networks • Need for a localized MM protocol – Optimized for handover performance of different application classes, client power-management states and IP reachability – Support • Unbundled provider domains • ASN topology variants • Heterogeneous access networks integrated via common IP core 6