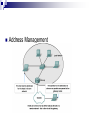
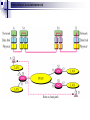
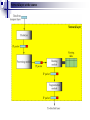
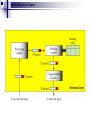
* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Network Layer
Multiprotocol Label Switching wikipedia , lookup
IEEE 802.1aq wikipedia , lookup
Asynchronous Transfer Mode wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Internet protocol suite wikipedia , lookup
List of wireless community networks by region wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
UniPro protocol stack wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup