* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 23-wrapup
Multiprotocol Label Switching wikipedia , lookup
Policies promoting wireless broadband in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Wireless security wikipedia , lookup
Asynchronous Transfer Mode wikipedia , lookup
Net neutrality law wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Internet protocol suite wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
Zero-configuration networking wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
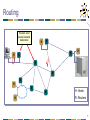
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Routing in delay-tolerant networking wikipedia , lookup
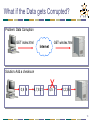
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
CS 268: Computer Networking L-23 Course Wrap-up Goals and Objectives • Understand state-of-the-art in network protocols, architectures, and applications • Process of networking research • Constraints and thought processes for networking research • Problem Formulation—Approach—Analysis— Results • Different from undergraduate networking (EECS 122) • i.e., training network programmers vs. training network researchers 2 Class Topic Coverage • Little on physical and data link layer • Little on undergraduate material • Supposedly you already know this, though some revisiting/overlap is unavoidable • Focus on the why, not the what • Focus on network-to-application layer • We dealt with: • Protocol rules and algorithms, tradeoffs, rationale • Routing, transport, DNS resolution, … • Network extensions and next generation architecture • Wireless, mobile, sensor, … 3 Lecture Topics • • • • • • Traditional Layering Internet architecture Routing (IP) Transport (TCP) Queue management (FQ, RED) Naming (DNS) • • • • • • • • Recent Topics Multicast Mobility/wireless Active networks QoS Network measurement Overlay networks P2P applications Datacenter networking Italics topics on Quiz #2 4 What is the Objective of Networking? • Communication between applications on different computers • Must understand application needs/demands • Traffic data rate, pattern (bursty or constant bit rate), target (multipoint or single destination, mobile or fixed) • Delay and loss sensitivity • Other application-support services • Overlays, Active Networks, Data-oriented, … 5 Back in the Old Days… 6 Packet Switching (Internet) Packets 7 Packet Switching • Interleave packets from different sources • Statistical multiplexing to use resources on demand • Supports multiple applications types • Accommodates bursty traffic via queues • Store and forward • Packets are self contained units • Can use alternate paths – reordering • Effects of contention: congestion and delay • Semester readings on Fair Queuing, Router Design, Network Topology and Network Measurement 8 Internet[work] • A collection of interconnected networks • Host: network endpoints (computer, PDA, light switch, …) • Router: node that connects networks • Internet vs. internet Internet[work] 9 Challenge • Many differences between networks • • • • • Address formats Performance – bandwidth/latency Packet size Loss rate/pattern/handling Routing • How to translate between various network technologies? • Gateways 10 Extensions to the Network • New kinds of networks within the Internet • • • • • Mobile Wireless Sensor Delay Tolerant Content Distribution/Data Oriented Networks • Semester readings on Roofnet, Ad hoc and sensor net routing, DTNs, CDNs, DOT, etc. 11 How To Find Nodes? Internet Computer 1 Computer 2 Need naming and routing 12 Naming What’s the IP address for www.cmu.edu? It is 128.2.11.43 Computer 1 Local DNS Server Translates human readable names to logical endpoints 13 Extensions to the Network Architecture • Naming • • • • DNS as an Overlay Network Problems with Host-to-IP Address bindings Problems with Service-to-Host bindings Solutions based on the idea of an extra level of indirection: flat identifiers plus resolution based on DHT lookup • Semester readings on DNS and on flat names and DHTs in the context of i3, DOA, etc. 14 Routing Routers send packet towards destination H R R R H H R R R H R R H H: Hosts R: Routers 15 Extensions to the Network Architecture • Forwarding • Problems with Internet routing • Beyond point-to-point routing: multicast, mobility, alternative schemes and metrics for wireless/sensor nets, delay tolerant nets, etc. • Indirection schemes and intermediaries (“performance enhancing proxies”) to implement new forms of forwarding • Semester readings on Internet topology, multicast, wireless, i3, DTN, DOA, policyaware switching, network measurement 16 Meeting Application Demands • Reliability • Corruption • Lost packets • • • • Flow and congestion control Fragmentation In-order delivery Etc. … 17 What if the Data gets Corrupted? Problem: Data Corruption GET index.html Internet GET windex.html Solution: Add a checksum 0,9 9 6,7,8 21 X 4,5 7 1,2,3 6 18 What if Network is Overloaded? Problem: Network Overload Solution: Buffering and Congestion Control • Short bursts: buffer • What if buffer overflows? • Packets dropped • Sender adjusts rate until load = resources “congestion control” 19 What if the Data gets Lost? Problem: Lost Data GET index.html Internet Solution: Timeout and Retransmit GET index.html Internet GET index.html GET index.html 20 What if the Data Doesn’t Fit? Problem: Packet size • On Ethernet, max IP packet is 1.5kbytes • Typical web page is 10kbytes Solution: Fragment data across packets ml x.ht inde GET GET index.html 21 What if the Data is Out of Order? Problem: Out of Order ml inde x.ht GET GET x.htindeml Solution: Add Sequence Numbers ml 4 inde 2 x.ht 3 GET 1 GET index.html 22 Lots of Functions Needed • • • • • • • • Link Multiplexing Routing Addressing/naming (locating peers) Reliability Flow control Fragmentation Etc. … 23 What is Layering? • Modular approach to network functionality • Example: Application Application-to-application channels Host-to-host connectivity Link hardware 24 Protocols • Module in layered structure • Set of rules governing communication between network elements (applications, hosts, routers) • Protocols define: • Interface to higher layers (API) • Interface to peer • Format and order of messages • Actions taken on receipt of a message 25 Layering Characteristics • Each layer relies on services from layer below and exports services to layer above • Interface defines interaction • Hides implementation - layers can change without disturbing other layers (black box) 26 Application-Oriented Networking • All kinds of new application-specific routing and transport layers • • • • • Sensor network dissemination protocols Content distribution/data oriented networks Overlay networks Active networks Middleboxes/”Performance Enhancing Proxies” • Layering and E2E assumptions questioned and revised 27 Quo Vadis Networking? • GENI: new architecture for Next Generation • New naming and forwarding as foundation • Security and authenticity from first principles • Experimentation in upper layers, e.g., DTN • Refocus from wide-area to local-area • • • • Unified telephony and data, wired/wireless Datacenters for web and batch parallel apps O(10,000) node DC and enterprise networks New addressing, transport opportunities 28 What Next? • Thursday, 4 December: Quiz #2 • Friday, 12 December: Research Project Poster Session -- 12-2 PM in Soda 6th Floor • Poster more or less equivalent to 9 slide research talk • Remember the Heilmeyer Questions! • Monday, 15 December: 5 PM Project Reports • Specification on the web, 10-20 pages 29