* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Advanced TCP/IP Planning and Design
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
List of wireless community networks by region wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
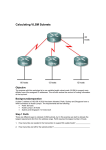
Advanced TCP/IP Planning and Design Variable Length Subnet Mask (VLSM) Supernetting Classless Enter Domain Routing (CIDR) Variable-Length Subnet Mask Variable-length subnet mask (VLSM) provide the capability to use different masks in a network for different segments. Large LANs could use a high bit-mask, while a serial link could use a smaller bit-mask ( /30) for two hosts (routers). Not all routing protocols support VLSM VLSM Case 172.17.0.0/20 How Many IPs will be lost if one of the usable subnets was used in a Point-to-point serial connection??? VLSM Case 172.17.48.0/20 How would VLSM be used to break one of the big subnets into 8 smaller subnets where each subnet would have only 512 hosts?? How would VLSM be used to break one of the 512-host subnet into several smaller subnets that would be used exclusively for serial links??? 172.17.62.0/23 VLSM Case 172.17.48.0/2 3 Subnet bits = ??? Host bits = ??? 172.17.0.0/20 172.17.62.0/3 0 Subnet bits = ??? Host bits = ??? Supernetting Supernetting groups networks into larger supernets How: by borrowing bits from the network portion of the address. Why: Say that you want a LAN network to have more than 254 hosts; a class C network is not sufficient. You can group two Class C networks using supernets. Benefits: Provide more IP addresses to the LAN segment without using secondary IP addresses on the router interface. (How would this effect the Supernetting Case Networks 192.168.4.0/24 and 192.168.5.0/24 are Class C networks with a default mask of 255.255.255.0. These two networks are the same up to 23 bits. They are combined or supernetted, into one network—192.168.4.0/23. The mask for the new network is 255.255.254.0 The first host address is 192.168.4.1. The last host address is 192.168.5.254. Address Aggregation A set of classfull networks can also be summarized in routing entries by creating aggregate addresses at the supernet level. The depicted figure shows how address aggregation summarizes routes in which Router A sends only one route, 208.10.8.0/22, to its Case Assume, for example, that network 172.17.0.0/16 will be used in a medium- to large-sized company with nine areas. Each area could have several sites. How can the network be divided allowing at least 2000 nodes per area? Each area have the following: Two large LANs with around 1000 hosts each Four medium LANs with 200 hosts, Five small LANs with 20 hosts, Reserved addresses for serial links Available room for future medium and small LANs.