* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 10_Tools_Troubleshooting
TCP congestion control wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
IEEE 802.1aq wikipedia , lookup
Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Remote Desktop Services wikipedia , lookup
List of wireless community networks by region wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Multiprotocol Label Switching wikipedia , lookup
Zero-configuration networking wikipedia , lookup
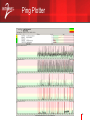
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
Asynchronous Transfer Mode wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Hypertext Transfer Protocol wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
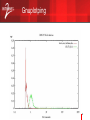
UniPro protocol stack wikipedia , lookup
Videoconferencing: Network Tools & Troubleshooting Dave Devereaux-Weber University of Wisconsin-Madison Internet2 Commons Site Coordinator Training September 27, 2004 Austin, Texas Duplex Mismatch – Detection Show port statistics on the Ethernet switch. When mismatched, the full-duplex end will report a high level of CRC or alignment errors; the half-duplex end will report a high number of late collisions. Port Align FCS Xmit Rcv UnderSize Err Err Err Err 2/11 - 0 0 3077 0 Port Single- Multi- Late- Coll 2/11 3233 0 Excess- CarriSen Coll Coll Coll 2588 0 2489 0 Runts Giants 0 2 Ping Test for availability, loss, and roundtrip time ICMP Echo Request • Plus optional dummy payload – only in the direction of the ping, i.e., source to destination 3 Sample Ping from Windows C:\WINDOWS>ping 10.1.1.1 Pinging 10.1.1.1 with 32 bytes of data: Reply from 10.1.1.1: bytes=32 time=88ms TTL=112 Reply from 10.1.1.1: bytes=32 time=72ms TTL=112 Reply from 10.1.1.1: bytes=32 time=69ms TTL=112 Reply from 10.1.1.1: bytes=32 time=69ms TTL=112 Ping statistics for 10.1.1.1: Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss), Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds: Minimum = 69ms, Maximum = 88ms, Average = 74ms C:\WINDOWS> 4 Sample Ping from Windows C:\WINDOWS>ping -l 40000 10.1.1.1 Pinging 10.1.1.1 with 40000 bytes of data: Reply from 10.1.1.1: bytes=40000 time=2412ms TTL=112 Reply from 10.1.1.1: bytes=40000 time=2721ms TTL=112 Reply from 10.1.1.1: bytes=40000 time=2761ms TTL=112 Reply from 10.1.1.1: bytes=40000 time=2714ms TTL=112 Ping statistics for 10.1.1.1: Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss), Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds: Minimum = 2412ms, Maximum = 2761ms, Average = 2652ms C:\WINDOWS> 5 Ping Big and Fast on Linux ping -c2000 -i.03 -s1470 -q [destination] • Count of 2000 packets • Interval of .03 seconds between packet starts • Packet size of 1470 bytes • (2000)(.03) = 60 second long test • (1/(.03 sec/packet))(1470 bytes/packet)(8 bits/byte) = 392 Kbps 6 Ping Big and Fast on Linux $ ping -c2000 -i.03 -s1470 [hostname] -q PING [hostname] ([hostaddr]) from [hostaddr2] : 1470(1498) bytes of data. --- [hostname] ping statistics -- 2000 packets transmitted, 2000 packets received, 0% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max = 4.8/5.1/13.2 ms 7 Traceroute Used to discover the layer-3 network path (routers) between the two endpoints Doesn’t identify layer-2 devices (switches) Take baselines – know what your path should be in advance of trouble 8 Traceroute Microsoft Windows tracert uses ICMP Unix traceroute uses UDP If Microsoft Windows tracert appears to show continuous timeouts, the router may be filtering ICMP traffic – try a Unix/Linux traceroute. 9 Traceroute; Sample Output [dodpears@huck dodpears]$ traceroute www.internet2.edu traceroute to www.internet2.edu (209.211.239.208), 30 hops max, 38 byte packets 1 wcc-sub5-hp1 (129.79.5.253) 11.726 ms 0.627 ms 0.571 ms 2 iub-gw (129.79.8.10) 3.133 ms 0.717 ms 0.651 ms 3 156.56.249.22 (156.56.249.22) 2.544 ms 3.138 ms 2.538 ms 4 abilene-iupui.abilene.ucaid.edu (198.32.11.13) 5.245 ms 3.402 ms 3.493 ms 5 clev-ipls.abilene.ucaid.edu (198.32.8.26) 9.381 ms 9.586 ms 9.244 ms 6 nycm-clev.abilene.ucaid.edu (198.32.8.30) 23.198 ms 21.963 ms 21.775 ms 7 border-abilene-oc3.advanced.org (209.211.237.97) 23.448 ms 23.268 ms 23.052 ms 8 www.internet2.edu (209.211.239.208) 23.559 ms 23.478 ms 23.234 ms 10 Traceroute 8 www.internet2.edu (209.211.239.208) 23.559 ms 23.478 ms 23.234 ms Hop Router/host name Router/host address Round-trip times of each of three probes 11 Traceroute – Example Uses Identify the path, and then perform pings along the path segments to isolate troublesome segments. Insure that Internet2 is being used for a connection, rather than commercial Internet. 12 Looking Glass These network tools work from your vantage point out; what if you want to measure from some other vantage point back in? You want a looking glass: See traceroute.org 13 Ping Plotter Shareware tool; $15 • http://www.pingplotter.com Performs a visual traceroute and ping tests along the entire path Permits identification of bottlenecks along a path 14 Ping Plotter 15 MRTG.ORG Multi Router Traffic Grapher Open Source Collect and graph scalar, time-based data, e.g., router and link performance data. 16 MRTG Example MRTG graph showing traffic from SLAC to a physics lab at University of Wisconsin 17 Iperf Client/server application that • Measures maximum TCP bandwidth • Facilitates tuning of TCP and UDP parameters • Reports bandwidth, jitter, and packet loss http://dast.nlanr.net/Projects/Iperf/ 18 Iperf Example on Intercampus DS3 At server, invoke: iperf -fk -i30 -u -s (f)ormat reports in kbps (i)nterval for reporting = 30 seconds (u)dp (s)erver mode 19 Gnuplotping Pings multiple hosts in parallel with graphical display (gnuplot) of the delay distribution. Runs on Unix/X-Windows 20 Gnuplotping 21 Network Traffic Analyzer Reveals the traffic on a LAN Protocol analysis Reports such as utilization, protocols, conversations, nodes, etc. 22 Network Traffic Analyzer: Software Ethereal http://ethereal.com/ EtherPeek http://wildpackets.com/ 23 Network Traffic Analyzer: Commercial Hardware Fluke Networks NetTool http://www.flukenetworks.com/us/LAN/Handheld+Testers/NetTool/Overview.htm This is a technician-oriented tool to perform diagnostics and testing. Fluke has an excellent white paper on auto-negotiation problems. Highly recommended. Network Associates Sniffer http://nai.com/ This is an engineer-oriented tool to analyze packets and traffic- often needs interpretation. 24 Internet2 Detective I2 Detective is a small application. Very easy to use Detects Internet2 connection. Measures connection bandwidth (using Iperf). Detects multicast connection. • http://detective.internet2.edu/ 25 ANL Web100 based Network Diagnostic Tester (NDT) Highly recommended http://miranda.ctd.anl.gov:7123/ • Located at Argonne National Laboratory; 100 Mbps FastEthernet network connection This java applet was developed to test the reliability and operational status of your desktop computer and network connection. It does this by sending data between your computer and this remote NDT server. These tests will determine: • The slowest link in the end-to-end path (Dial-up modem to 10 Gbps Ethernet/OC-192) • The Ethernet duplex setting (full or half); • If congestion is limiting end-to-end throughput. It can also identify 2 serious error conditions: • Duplex Mismatch • Excessive packet loss due to faulty cables. 26 H.323 Beacon Open Source Software Used to measure, monitor and qualify the performance of an H.323 Videoconference session. Provides H.323-protocol specific evidence and other information necessary to troubleshoot H.323 application performance problems in the network and at the host (end-to-end) • http://www.itecohio.org/beacon/ 27 Other Tools CAIDA Internet Measurement Tool Taxonomy http://www.caida.org/tools/taxonomy/measurement/ 28 ViDe Videoconferencing Cookbook http://videnet.gatech.edu/cookbook/ 29 The Network Information on these slides courtesy of Doug Pearson Indiana University And David Devereaux-Weber University of Wisconsin-Madison 30