* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 3/11
Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
Internet protocol suite wikipedia , lookup
Multiprotocol Label Switching wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
Asynchronous Transfer Mode wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
TCP congestion control wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
Wireless security wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Cross-site scripting wikipedia , lookup
Nonblocking minimal spanning switch wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
Zero-configuration networking wikipedia , lookup
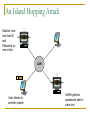
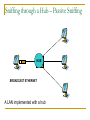
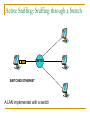
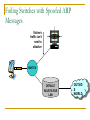
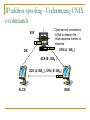
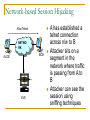
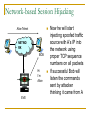
Network Attacks Bharatha Yajaman ISQS 6342 Outline Sniffing IP Address Spoofing Passive Sniffing Active Sniffing Changing the IP address Undermining UNIX r – commands With source routing Session Hijacking NetCat Sniffing Sniffers are most common tools used by attackers Data link layer of the protocol stack is targeted Sniffer is a program that gathers traffic from local network & is useful for attackers for attackers to get all information as well as network administrators trying to trouble shoot problems An attacker can read data passing by a given machine in real time or can even store the data in a file Type of Data Sniffer can capture? User IDs and Passwords DNS queries and responses email messages FTP passwords Files shared using Network File System or Windows Shares An Island Hopping Attack Attacker now has UserID and Password on new victim LAN User telnets to another system Sniffer gathers passwords sent in clear text Various Sniffing tools tcpdump, freeware for UNIX platform, www.tcpdump.org windump, freeware of tcpdump for Windows 9x, NT and 2000 Snort, freeware sniffer and network-based intrusion detection system, www.snort.org Ethereal, freeware for UNIX and WinNT with nice User Interface, www.ethereal.com/ Sniffit, widely used in attacker community, reptile.rug.ac.be/ ~coder/sniffit/sniffit.html Sniffing through a Hub – Passive Sniffing Transmitting data across a Hub based LAN just like shouting in a crowded room A hub implements a broadcast medium shared by all systems on the LAN Any data sent across the LAN is actually sent to each and every machine connected to the LAN Sniffing through a Hub – Passive Sniffing HUB BROADCAST ETHERNET A LAN implemented with a hub Sniffing through a Hub – Passive Sniffing If an attacker runs a Sniffer on one system on LAN, he can gather data sent to and from any other system on the LAN Majority of the Sniffer tools are well suited to sniff data in a hub environment These tools are called passive sniffers as they passively wait for the data to be sent to them, silently gathering the data from the LAN Active Sniffing: Sniffing through a Switch Switched Ethernet does not broadcast all information to all systems on the LAN A switch which is more intelligent than the hub looks at the MAC address associated with each frame passing through it and sends the data to the required connection on the switch Active Sniffing: Sniffing through a Switch SWITCH SWITCHED ETHERNET A LAN implemented with a switch Active Sniffing: Sniffing through a Switch The switch limits the data that a passive Sniffer can gather If there is a passive Sniffer activated on a switched LAN the sniffer will only be able to see data going to and from one machine – the system with sniffer installed Active Sniffing: Sniffing through a Switch So how do attacker over come this difficulty of sniffing a switched LAN? Attackers have created a variety of tools that support sniffing a switched environment These tools actively inject traffic into LAN to sniff a switched LAN Dsniff is an active sniffing tool, www.monkey.org/~dugsong/dsniff Foiling Switches with Floods ( MAC flooding ) MAC address are physical hardware addresses unique to every Ethernet Card LAN switches hold the MAC addresses in the switch memory What happens if the traffic is flooded with random MAC address on LAN ? As number of different MAC addresses in use increases the switch dutifully stores the MAC addresses used by each link on the switch Foiling Switches with Floods ( MAC flooding ) What happens if the traffic is flooded with random MAC address on LAN ? Eventually, the switches memory is exhausted with bogus MAC addresses Some switch implementations start forwarding data to all links connected to all the links if their memory links are exhausted The attacker can take advantage of this flaw and use any passive switching tool to sniff the switched LAN Foiling Switches with Spoofed ARP Messages Some switches are immune to MAC flooding These switches stops storing new MAC addresses once their memory reaches a given limit To sniff in a switched environment where MAC flooding doesn't work Attacker can use DSniff’s tool called arpspoof arpspoof allows an attacker to manipulate ARP traffic on LAN Foiling Switches with Spoofed ARP Messages Victim’s traffic isn’t sent to attacker SWITCH DEFAULT ROUTER FOR LAN OUTSID E WORLD Foiling Switches with Spoofed ARP Messages To use arpspoof the attacker First consults a map of the network likely generated during the scanning phase of the attack Looking at the network topology the attacker observes the IP address of the default router for the LAN Sets up the attack by configuring the IP layer of the attacker’s machine to forward any packet it receives from the LAN to the IP address of the default router (IP forwarding) Foiling Switches with Spoofed ARP Messages To use arpspoof the attacker Sends the fake ARP replies to the victims machine This ARP changes the victims ARP table by remapping the default router’s IP (layer 3) to attacker own MAC address (layer2) The victims sends the data, forwarding it to what it thinks is the default router (but using the attackers MAC address) Foiling Switches with Spoofed ARP Messages To use arpspoof the attacker The attacker sniffs the information using any kind of sniffing tool The attacker’s machine will promptly forward the victim’s traffic to default router on the LAN Upon reaching the default router the traffic is transmitted to the outside world The attacker is now sniffing in a switched environment Foiling Switches with Spoofed ARP Messages 2. Send fake ARP response to re-map default router IP to attacker’s MAC SWITCH 3. Victim sends traffic destined for outside world based on poisoned ARP table entry 1. Configure IP Forwarding 4. Sniff the traffic from the link 5. Packets are forwarded from attacker’s machine to the actual default router for delivery to the outside world DEFAULT ROUTER FOR LAN OUTSID E WORLD Sniffing and Spoofing DNS The attacker fires up the dnsspoof program which sniffs the LAN for DNS queries for specific hosts ( www.bank.com ) - using Dsniff At sometime later victim tries to resolve the name www.bank.com using DNS by trying to surf the website Now the attacker sniffs the DNS query and immediately sends a fake DNS response Sniffing and Spoofing DNS This response will have a lie claiming that www.bank.com should resolve to IP address of the attackers machine (say 10.1.1.56) The victim machine will cache this incorrect DNS entry The victims machine will ignore the real response from the real DNS server as it has the mapping for www.bank.com Finally the victims browser makes a connection with the attackers machine Sniffing and Spoofing DNS 1. Attacker activates dnsspoof program 4. Attacker quickly sends fake DNS response with any IP attacker wants the victim to use 3. Sniff the DNS request from the line Desired destination www.bank.com SWITCH 2. Victim tries to resolve a name using DNS 5. Victim now surfs the attackers site instead of desired location DEFAULT ROUTER FOR LAN OUTSID E WORLD Attacker’s machine at 10.10.1.56 Sniffing HTTPS and SSH Even though the S’s in HTTPS, SSL and SSH stand for secure, it is built on a trust model of underlying public keys When an HTTPS connection is established the server sends a certificate which the browser verifies If the certificate was signed by a trusted Certificate Authority, an SSL connection will be established Sniffing HTTPS and SSH SSL connection uses a session key to encrypt all data sent by server and client SSH does not support digital certificates but is based on same public key encryption idea SSL and SSH protocols are sound from a security perspective but the problem is exploited in the trust certificates and public keys Sniffing HTTPS and SSH For SSL if a web server sends a browser a certificate and if the browser does not recognize the browser will ask the user whether to accept this untrusted certificate or not For SSH the user will be warned that server’s public key has changed but will still be permitted to establish connection Sniffing HTTPS and SSH How Dsniff exploits the problem ? Dsniff uses webmitm and sshmitm tools for attacking HTTPS or SSH mitm stands for “monkey in the middle” a reference to a classic person-in-the-middle attack Attackers position themselves between two systems and actively participate in the connection to gather data Sniffing HTTPS and SSH Person–in–the–middle attack NETWORK NETWORK ATTACKER Sniffing HTTPS and SSH Person–in–the–middle attack To conduct a person in the middle attack The attacker runs the dnsspoof program configured to send false DNS information so that a DNS query for a given website will resolve to the attacker’s IP address The attacker will also activate webmitm program that will transparently proxy all HTTP and HTTPS traffic it receives The DNS spoof program detects DNS request for www.bank.com and redirects the client to attacker’s machine Sniffing HTTPS and SSH Person–in–the–middle attack To conduct a person in the middle attack Victim’s browser starts to establish a secure connection All messages for establishing SSL connection are sent to webmitm on attacker’s machine webmitm acts as a SSL proxy, establishing 2 SSL connections one from victim to the attacker's machine and the other from attacker’s machine to the actual web server Sniffing HTTPS and SSH Person–in–the–middle attack To conduct a person in the middle attack webmitm when establishing the SSL session between victim machine to the attacker will send the attacker’s own certificate Victim’s browser will notice that the certificate is not signed by a trusted Certificate Authority and show a message to the user asking the user whether to accept this un-trusted certificate or not Sniffing HTTPS and SSH (Modify) 10.1.2.3 1. Attacker activates dnsspoof and webmitm program 2. Dnsspoof sends fake DNS response with IP address of the machine running webmitm (10.1.2.3) 4. Webmitm proxies the https connection establishing an https connection to server and sending attacker’s own certificate SWITCH 3. Victim establishes SSL connection not knowing attacker is proxying the connection 5. Victim now accesses the desired server, but all the traffic is viewable by attacker using webmitm as proxy DEFAULT ROUTER FOR LAN OUTSID E WORLD Desired destination 10.22.12.41 IP address spoofing Simply changing the IP address Simplest way of spoofing another system’s IP address can be achieved by simply changing the IP of system to the other’s system address This can be done by using ifcommand in UNIX, or the Windows NT network control panel This method is remarcable in achieving limited goals if the attacker wants To send packets that look like they look like they come from some where else Obscure the source of packet flood or other Denial-ofservice attack IP address spoofing (3 way handshake diagram) SYN (A , ISNA ) ACK (A, ISN A ), SYN ( B, ISNB ) A B RESET TCP three way handshake inhibits simple spoofing IP address spoofing - Undermining UNIX r-commands EVE ALICE BOB IP address spoofing - Undermining UNIX r-commands Eve interacts with Bob by sending TCP SYN packets to one or more of his open ports again without spoofing This connection initiation allows Eve to approximate rate at which the initial TCP sequence numbers in Bob’s SYN-ACK response are changing with time Eve launches a denial-of-service against Alice (SYN flood or smurf attack) IP address spoofing - Undermining UNIX r-commands Alice is dead for a period of time. This prevents Alice from sending RESET packet and dropping our spoofed TCP connection Eve initiates a connection to Bob using Alice’s IP address The first part of the 3 way handshake is complete Bob responds to 2nd part of 3 way handshake to Alice but Alice is dead and cannot respond with a RESET IP address spoofing - Undermining UNIX r-commands Using the information gathered, Eve sends a ACK to Bob including a guess at sequence number, ISBB, spoofing Alice’s IP. If the sequence number is incorrect a connection will not be established but if the sequence number is correct, Eve will open a TCP connection with Bob, pretending to be Alice IP address spoofing - Undermining UNIX r-commands EVE DIE Open several connections to Bob to observe the initial sequence number in response SYN (A , ISNA ) ACK (B , ISNB ) ACK (A, ISN A ), SYN ( B, ISNB ) ALICE BOB IP address spoofing - Spoofing with Source Routing A far easier method for IP address spoofing is based on source routing This technique will let the attacker get responses in interactive sessions and even avoid to conduct Denial-of-service attack Source routing is an option in IP that allows the source machine sending packets to specify path it will take on the network IP address spoofing - Spoofing with Source Routing EVE ALICE PACKET Route 1. Bob 2. Eve 3. Alice Packet Contents PACKET Route 1. Alice 2. Eve 3. Bob Packet Contents BOB Eve generates packets with fake source route Packets claim to come from Alice Source route includes Eves address making Eve look like a router Packets include destination Bob IP address spoofing - Spoofing with Source Routing EVE ALICE PACKET Route 1. Bob 2. Eve 3. Alice Packet Contents PACKET Route 1. Alice 2. Eve 3. Bob Packet Contents BOB Eve injects these spoofed packets on the network Bob will take action on packets and responds When Bob responds packets will be transmitted to Eve who is a part of the source route Eve will intercept the packet but will not forward packet to Alice IP Spoofing Defense The initial set of sequence numbers generated by TCP stacks must be difficult to predict For UNIX machines in particular, using of weak r-commands must be avoided Implementation of anti-spoof packet filters at border routers and firewalls connecting organization to the Internet and business partners IP Spoofing Defense NETWORK A FILTERIN G DEVICE NETWORK B Dropped Packet with IP source address on Network A The filtering devise drops all packets coming in on one interface that have a source address of network on another interface These packets indicate a possible spoofing attack IP Spoofing Defense Source routed packets through the network gateways must not be allowed This can be done by configuring routers using no ip sourceroute (this woks for Cisco routers) to drop all source routed packets at gateways Careful with trust relationships throughout the environment Avoid extending UNIX and Win NT trust relationship to systems across an unprotected network Session Hijacking Marriage of sniffing and spoofing is called session hijacking An attacker can hijack a session even if strong authentication is used assuming the conversation following the initial authentication is not cryptographically protected As the session is sent in clear text after initial authentication and a attacker can hijack the it at any point after authentication Network-based Session Hijacking Alice Telnet NETWO RK BOB ALICE EVE A has established a telnet connection across n/w to B Attacker sits on a segment in the network where traffic is passing from A to B Attacker can see the session using sniffing techniques Network-based Session Hijacking Alice Telnet NETWO RK BOB EVE Attacker can also monitor TCP sequence numbers of these packets while observing the session At some point the attacker will decide to hijack the connection Network-based Session Hijacking Alice Telnet NETWO RK BOB Hi I’m Alice EVE Now he will start injecting spoofed traffic source with A’s IP into the network using proper TCP sequence numbers on all packets If successful Bob will listen the commands sent by attacker thinking it came from A Session Hijacking – ACK storm When a system receives a packet with TCP connection that is out of order it resends its last ACK packet Retransmission of ACK is supposed to help the systems resynchronize their sequence numbers Session Hijacking – ACK storm ACK ACK ACK ACK ACK NETWO RK BOB What happens if the attacker is injecting traffic in the TCP connection ? Packets with increasing sequence number EVE The sequence number between attacker and B will go on increasing As traffic gets routed back to A it will see sequence numbers increasing even though A has not sent any packets Session Hijacking – ACK storm ACK ACK ACK ACK ACK NETWO RK BOB Packets with increasing sequence number EVE TCP stacks of A and B get confused as attacker sends the traffic in increasing sequence number To resynchronize connection A will resend ACK messages again and again consuming a good amount of bandwidth in what is know an ACK storm Session Hijacking – ACK storm ACK ACK ACK ACK ACK NETWO RK BOB Packets with increasing sequence number EVE During an ACK storm the performance quickly starts to suffer the attacker will be able to get one or two commands executed on B before the ACK storm causes the connection to be dropped Session Hijacking Defenses Utilizing all defense techniques used for spoof attacks Using encryption tools like SSH or VPN for securing sessions Encrypted sessions will prevent session hijacking as attackers will not have keys to encrypt or decrypt Netcat : General purpose network tool Netcat is one of the most useful tools available for interacting with systems across network Netcat is often referred as “Swiss Army knife of network tools” The idea behind Netcat is it allows a user to move data across a network while functioning much like the UNIX cat command Instead of dumping data on the local system Netcat moves arbitrary data over any TCP or UDP port Netcat : General purpose network tool Netcat executable operates in one of two modes Client mode Listen mode In client mode Netcat can be used to initiate connection to any TCP or UDP port on another machine In listen mode Netcat opens any TCP or UDP port on the local system Netcat supports source routing Netcat : General purpose network tool Using these basic building blocks people have devices many different scenarios based on Netcat File Transfer Port Scanning Making connections to open ports Vulnerability scanning To create a passive backdoor command shell To actively push a backdoor command shell Relaying traffic Netcat : Defence Preventing Netcat file transfers Securing against port scanning Blocking arbitrary connections to a port Protecting against vulnerability scanning Stopping backdoors Preventing relay attacks References Counter Hack Hacking Exposed http://www.cert.org/advisories/CA-1995-01.html http://ciac.llnl.gov/ciac/bulletins/f-08.shtml http://www.iss.net/security_center/advice/Undergrou nd/Hacking/Methods/Technical/default.htm http://www.althes.fr/ressources/avis/smartspoofen.pdf Thank You