* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download No Slide Title - Network Insight Institute
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
National Broadband Plan (United States) wikipedia , lookup
List of wireless community networks by region wikipedia , lookup
Wireless security wikipedia , lookup
IEEE 802.11 wikipedia , lookup
Cellular network wikipedia , lookup
Spectrum reallocation wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
Policies promoting wireless broadband in the United States wikipedia , lookup
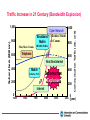
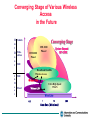
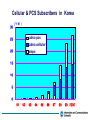
Convergence of Wireless Access and Spectrum Allocations Mar. 19, 2001 a Network Insight seminar, Sydney Seungtaik Yang Preisident, Information and Communications University P.O. Box 77 Yuseong, Daejon, KOREA e-mail: [email protected] Contents Directions to Wireless Multimedia Era Prospects for the Future Mobile Communications Requirement for Future Spectrum Management Korean Perspectives on Spectrum Management Final Remarks Directions to Wireless Multimedia Era Evolution of Mobile Communications Cordless Telephone Satellite GMPCS CT-2 CT-1 PHS DECT Analog Cellular AMPS NMT TACS Digital Cellular PCS GSM DCS1800 ADC(IS-54) IS-54 based PCS 8 kbps ‘80 1st Generation - W-CDMA - cdma2000 Mobile Multimedia PDC Upband IS-95 PCS(CDMA) CDMA IS-95 Data Rate IMT-2000 8 - 114 kbps ‘90 2nd Generation Up to 2 Mbps 2000 3rd Generation Over 2 Mbps 2010 (?) 4th Generation Traffic Increase in 21 Century (Bandwidth Explosion) Broadband Mobile 800 Man-Man Comm. 600 1,000 Cyber Network Machine-Machi ne Comm. IMT-2000, B-WLL Telephone 800 600 Next Gen.Internet 400 Mobile Information Explosion Cellular, PCS 200 400 200 Internet 0 1988 1992 1996 2000 2004 2008 Communication Traffic (arb. unit) Subscribers (Million) 1,000 0 (year) IMT-2000 Service Coverage 9.6 kbps < 144 kbps Zone 4: Global < 384 kbps Zone 3: Suburban < 2 Mbps Satellite Zone 2: Urban Zone 1: In-Building Mega-Cell Macro-Cell remote vehicular stationary/indoor Micro-Cell pedestrian Pico-Cell IMT-2000 Services Services : Voice, Data, Video,& Multimedia as Mobile Internet Video Conference Video Telephony Teleshopping Electronic Newspaper, Data Service(Image,Music) Service Telebanking Data Base Access IPS e-mail Voice Data Rate 10 kbps 100 kbps 1 Mbps 10 Mbps Prospects for the Future Mobile Communications As voice is concerned, “anywhere access” is fully realized with 2-G mobiles, PABX phones, and cordless telephones. As we enter into knowledge-based information society at the turn of the century, main focus on communication is being shifted towards ubiquitous high speed wireless multimedia/internet. “Anywhere access for data” will be the major topics for the next generation mobile systems like IMT2000. But, nobody is sure how much high speed data services will be needed when one is on move. While it is feasible to predict the ever-growing needs for high speed data, wherever one is located stationary. Mobility on fixed network is as important as that on mobile network. Converging Wireless Access as Last Mile Access Public Land Mobile Systems like 2-G and 3-G : Advantage : “wherever service” possible Disadvantage : limited data speed and capacity, and relatively high tariffs No tariffs and high data speed Broadband Wireless LAN *: within campus or large premise, and offices Home R.F.* or Personal LAN like Bluetooth : at home or on personal move SRD (Short Range Communication Device) Low Tariffs and high data speed, where the fixed system is not conveniently accessible Broadband Fixed Wireless Access* Broadband Satellite Internet Service* Low tariffs and very high data speed SCS (Stratospheric Communication System)* * possible application of microwave and mm-wave technology 4G as the Integration Wireless Digital Convergence Satellite/HAP S Satellite WPAN HAPS SDR IPv6 DVB DAB W-CDMA CDMA2000 GPRS Broadcasting PCS GSM Cellular IS-95 Broadband Wireless1394 W-LAN BWA HIPERLAN Bluetooth LMDS WLAN MMDS Wireless Local Loop W-LAN Indoors Hierarchical Layered Convergence Global •Outdoor • Mobile / still / fixed • Coverage :100Km ~ • Max. Data rate : ~155Mbps • L,S,C,Ku,Ka, mm Wave band Satellite, HAPS / DVB, DAB Global layer Cellular / Macro •Outdoor /Indoor • Mobile / still • Coverage : ~ 3Km • Max. Data rate : ~2Mbps • 800MHz ~ 2GHz handover Macro layer CDMA GSM PCS Wireless LAN / Micro IMT2000 CDMA2000 • Outdoor / Indoor • Still / fixed • Coverage : ~ 300M • Max. Data rate : ~ 54Mbps • 2.4GHz ~ 5.8GHz WCDMA Micro layer WLAN LMDS MMDS •Indoor • Still / fixed • Coverage : ~ 10M • Max. Data rate : ~1Mbps • 2.4GHz Broadband Wireless Access WPAN Bluetooth fixed (wired) layer Wireless PAN / Pico BWA handover Pico layer HIPERLAN Wireless 1394 All-IP Network • Outdoor • Fixed • Coverage : ~ 12.5Km • Max. Data rate : ~155Mbps • 20GHz ~ 60GHz (mm Wave band) Converging Stage of Various Wireless Access in the Future O u t D o o r Vehicle Pedestrian Converging Stage IMT-2000 Phase1 System Beyond IMT-2000 Still LMDS I n D o o r IMT-2000 Phase2 Still Broadband/Satellite Wireless Access Wireless PAN Fixed Ultra High Speed WLAN Wireless WirelessLAN LAN Wired Line 0.1 1 10 Data Rate (Mbits/sec) 100 Requirements for Next Generation(4-G) System High speed data rate : Vehicular : 2 Mbps Pedestrian/ Indoor : 20 Mbps IP based network structure : QoS guaranteed Next generation Internet support : IPv6, Mobile IP High Capacity : 5 ~ 10 times to 3-G Lower system cost Seamless services with fixed, and private networks like Wireless LAN, BWA etc. Frequency band : 3 ~ 8 GHz, possibly higher Frequency Spectrum Requirements : ITU-R recommends additional 180 MHz bands for IMT-2000 services by 2010. For 4-G, conservative estimates is at least 1,000 MHz by 2015 Requirement for Future Spectrum Management Facing More and More Complications Ever Increasing Demands and Values for Frequency Spectrum Convergence of Diverse Services Differentiation among Services or Systems ambiguous Especially for the 4-G Services Appearance of New Unpredicted Services Flexibility of Spectrum Use needed Globalization and De-regularization Trends Need of Long-and–Medium Term Frequency Spectrum Planning Korean Perspectives on Spectrum Management Status of Telecommunications in Korea Population : 46 Millions / 99,300 sq. km Seoul : 11.0 Millions / 605 sq. km Pusan : 4.0 Millions / 436 sq. km Status of Telecommunications - Wireline Operators : KT (Korea Telecom) : Major PTT, IMT-2000 DACOM : PSDN, International & Long Distance Hanaro : Local Loops, WLL Onse Telecom : International & Long Distance - Wireless Operators : SK Telecom : Cellular, IMT-2000 Shinsegi Telecom : Cellular KT Freetel, KTM.com & LG Telecom : PCS 8 Regional Pager Operators : Pager TRS Operators ( 2 national, and 9 regional) : Digital TRS 3 Mobile Data Operators : Wireless Data Regulator : MIC ( Ministry of Information & Communication ) Cellular & PCS Subscribers in Korea 30 ( *1 M ) cdma pcs cdma cellular amps 25 20 15 10 5 0 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 2000 MIC’s Policy on Spectrum Management Provision of Spectrum Resources for Future Demands Technology Development and Incentive to Utilize for Higher Frequency Bands like Millimeter-wave Band Publishing Long-term Frequency Planning Efficiency Spectrum Utilization for Existing Bands of Use Narrower Channel Bandwidth Frequency Spectrum Sharing for Different Services Trunking for Similar Services from Different Entities/Organizations Clean Electromagnetic Environment Maximization of Spectrum Resource Utilization Improvement of Spectrum Allocation Method Adoption of Global Standards or Trends in Spectrum Allotment Spectrum Reassignment through Actual Frequency Usage Statistics Spectrum Allocation by Market-based Mechanism Public Access to Current Frequency Database Electronic Filing System for Procedure of Radio Station Licensing Current Spectrum Allocations Policy 1. Appraisal of Proposals with Pre-fixed Pricing (hybrid form) Based on Economic Values and Technical Effectiveness Existing Competitions in the Market Needs for Accelerating Commercial Services Price Range Pre-fixed, and Fund Contributed for Telecommunication Development Exclusive Right to Use for Specific Services, and Renewable with Additional Prices after Licensing Period of less than 20 yrs 2. Allocation by Conventional Review Process with No Price Based on Effectiveness of Intended Spectrum Use Fairness and Conformity to Public Interest Needs of Applicants Technical and Financial Capabilities of Applicants 3. Spectrum Auction (X) Once considered, but discarded due to negative reactions of general public, and many other adverse effects Status of Hot Service Licensing's IMT-2000 Services ( Method 1) Will license 3 Operators, each with 2*20 MHz Duplex Bands 1 for cdma2000 system, 1 for W-CDMA system, and 1 with option to take either Telecom. Development Fund ranged between 1 billon ~ 1.1 billion US$ Commercial Services due by May, 2,002, but possibilities of delay Result among 4 Applicants: ( Dec., 2,000) - 2 W-CDMA Licenses to SK Telecom and KT, with fund of 1.1 billion US$, each - a cdma2000 applicant disqualified, and procedure postponed Digital Terrestrial Broadcasting Services (method 2) ATSC standard adopted in 1997 Test Transmitting during 1999 ~ 2000, and at present, Trial Services in Seoul Full Commercial on-air in late this year beginning from Seoul Incumbent TV Broadcasters provided with Digital Channels on condition that after 2,006, returning existing analog channels Satellite Broadcasting Service (method 1) 1 license on Platform of KoreaSat II and III Broadcasting Development Fund fixed at 17 million US$ Administered by Independent Broadcasting Commission Result among 2 Applicants : (Dec., 2,000) KT/KBS Consortium to be licensed with 17 million $ fund Frequency Allocation in Korea 894M-960 M Cellular 1.71G -1.885G CT GMPCS 824M-894M 1.53G-1.66G 2.17G-2.2G IMT2000 (MSS Downlink) PCS 2.4G-2.48G 2.7G-2.9G 3G IMT2000 IMT2000 WLL (802.11bGMPCS (New) (New) Bluetooth) 2.5G-2.69G 10G IMT2000 IMT2000 (MSS (TDD) (TDD) (Uplink) uplink) 1.90G -1.92G - 1.98G WLAN 2.16G-2.2G 2.3G-2.4G 1.98G-2.02G-2.025G TV (Korea) 11.7G-12.2G HIPER WLAN WLAN (HIPER (HIPER LAN/1) LAN/2) LINK 4G ? WLAN (802.11a) 24.25G-26.7G WLAN (reserved) (reserved) 17.1G - 17.3G 2.11G - 2.17G 5.725G-5.875G 5.15G-5.35G WLAN (Downlink) 5.47G-5.725G 17.7G-17.735G Sat. IMT2000 19.2G-19.3G BWLL WATM (project) 40G-60G Final Remarks Each country has its own regulation and customs for frequency allocation, but globalization and roaming requirements ask for more conformance to global standards. As demands for frequency use accelerated, harmful interference may occur between neighboring countries unless close frequency planning coordination worked out. As more diverse services merged vertically or horizontally, spectrum management becomes more complicated. The worldwide study is required to resolve. Perhaps, economic values of spectrum use may be deemed differently from country to country. Trend is to levy some price tags. Spectrum cap or specific use of certain bands will be removed for improving flexibility of spectrum utilization.