* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PPT - 清華大學資訊工程學系
TCP congestion control wikipedia , lookup
Wireless security wikipedia , lookup
Net neutrality law wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
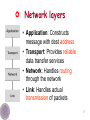
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
List of wireless community networks by region wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
UniPro protocol stack wikipedia , lookup
Zero-configuration networking wikipedia , lookup
Internet protocol suite wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
CS1356 資訊工程導論 Network and the Internet 國立清華大學資訊工程學系 2017/5/25 Network • An intricately connected system of things or people – Webster dictionary • Computer network – A linked computer system 2 Outline • • • • Layered approach for network Link layer Network layer/Transport layer Application layer Application Transport Network Link 3 Layered Approach What and why? Application Transport Network Link 4 A Story 某日,某資工系某家族決定要去竹北某餐廳 家聚。他們決定先在某資電館前集合,再出 發到餐廳。家族共有12人,某學長有一輛車, 可以坐4人,另外還有2個人有摩托車,共可 以載4人,另外4個人決定坐公車。某學長車 上有GPS,可以找出路要怎麼走;有摩托車 的同學上網查出地圖路線;要坐公車的同學 查出要轉一次車,再走一小段路就可以到餐 廳了… 5 Layered Approach • 去竹北某餐廳家聚 Application layer – Decide where to go and what to do • 4人坐車, 4人騎車, 4人搭公車 – Decide the transportation methods • GPS,地圖路線,公車班次 Transport layer Network layer – Decide the routes from the source to the destination Link layer • 汽車,摩托車,公車,司機,馬路,紅綠燈,路標… – Make the real transportation happen 6 Network layers • Application: Constructs message with dest address • Transport: Provides reliable data transfer services • Network: Handles routing through the network • Link: Handles actual transmission of packets 7 Layered Approach: Why? • Each task in different layer can be handled more easily without considering the details of the tasks in other layers. – For example, they can decide a “best” restaurant without considering how to go there • Methods in different layers can be changed easily. – For example, different applications can use the same transport protocol. 8 Protocols • A set of rules used to communicate with each other across a network. – Example 1:先在資電館前集合,再出發到餐廳 – Example 2: bus route and schedule – Example 3: traffic regulations • Protocol is a special algorithm that enables and controls the data communications. 9 (Fig. 4.14) 10 Message Encapsulation • To transmit the data, each layer appends some information to the original message. • The corresponding layer in the receiver side needs to “decapsulate” the message. address 1 address32 address name 1 name address name 342 name 4 11 Link Layer Application Transport Network Link 12 LAN, MAN, WAN • Network can be classified by the scope – Local area network (LAN) – Metropolitan area (MAN) – Wide area network (WAN) • Network for different scopes uses different media and has different protocols. 13 Network Topology • Popular network topologies used in LAN – Bus (Ethernet) – Star (Wireless network with central Access Point, AP) • Different topology uses different protocols. 14 Ethernet and CSMA/CD • CSMA/CD: protocol for Ethernet – Carrier Sense, Multiple Access with Collision Detection – Broadcast messages to all machines on the bus – Resend message if detecting more than one messages sent at the same time (collision) 15 WiFi and CSMA/CA • CSMA/CA: protocol for WiFi – Carrier Sense, Multiple Access with Collision Avoidance • Similar to CSMA/CD – Sensing carriers before sending • WiFi cannot detect collisions – Self signal drowns out others – Hidden terminal problem 16 Collision Avoidance • Before sending data, a node listens to the channel for a period. – If the channel is silent, it sends data. – If the channel is busy, it waits another random period. After waiting, if the channel is silent, it sends data immediately. • Cannot avoid collisions totally. – Before sending data, it sends a request to AP. AP sends an acknowledgement to all machines after receive the data. 17 Network Equipments for LAN • Hub: relays signals it received • Repeater: connects two buses • Bridge: similar to repeater, but only forwards necessary messages • Switch: a bridge that connects multiple buses – All those do not change the protocol 18 Network layer/Transport layer Application IP, TCP, UDP, and the Internet Transport Network Link 19 Terminology • An internet: – a network of networks – It is different from “the Internet”. • The Internet: a global internet that uses TCP/IP protocol suite. – TCP/IP protocol suite: IP+TCP+UDP – TCP and UDP: Transport layer protocols – IP : Network layer protocol 20 Internet Service Provider (ISP) • A company/organization that offers its customers access to the Internet. • The ISP hierarchy 21 How ISPs Work • Connection method to ISPs – – – – Direct connection Dial-up, DSL Cable modem Wireless TANet 台灣學術網路 SeedNet 新世紀資通 Hinet 中華電信 Cable modem 東森有線電視 22 Internet Protocol (IP) • A protocol used for communicating data across an internet. • It is a connectionless protocol. – Telephone network is connection-oriented. – For the same source and destination, different message may be routed differently. 23 IP address • How to design a global address –台灣 新竹市 光復路二段 101號 nation-city-roadnumber – 886-3-571-5131 nation-area-phone number • IP address: the global identification for each computer connected to an internet – Pattern of 32 or 128 bits, usually represented in the dotted decimal notation. – For example: 140.114.87.5 is for 楓橋驛站 24 Gateway and Router • Gateway: the “point” linked to an internet • Router: forwards and routes messages – Forwarding: relay messages on an internet – Routing: update and maintain the forwarding table Destination Next hop Cost 140.114.87.5 103.121.1.2 … 140.114.79.3 … … 25 Domain Name • The mnemonic address for human – For example, bbs.cs.nthu.edu.tw is the domain name for 楓橋驛站 – Top level domains (TLD): suffixes in the domain name: .gov, .edu, .com, .net, .org,… – Country-code TLD: .tw, .ca, .jp, .au, … – Subdomains: prefixes of an domain name, bbs., www., … 26 Domain Name System (DNS) Machines like binary addresses DNS Humans prefer domain names • Provides translation between IP addresses and domain names. – Name server – DNS lookup 27 Transport Layer • Two protocols • TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) • UDP (User Datagram Protocol) TCP UDP Handshaking Retransmission Flow control Congestion control 28 Transmission Control • Handshaking: – Make reservation before go to a restaurant • Retransmission: – Ask someone to repeat what he/she said • Flow control: – Ask someone to talk slower • Congestion control: – Lineup of a crowd of people 29 Port Number • TCP/UDP need to know which application should a received message be sent to – This is identified by port numbers – IP address is for the address of computer • Examples Port number Application 53/TCP,UDP Domain Name System (DNS) 80/TCP,UDP Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) 513/TCP Login 30 Application Application Layer Transport Network Link Client/server, peer to peer, distributed system The Internet applications and WWW 31 Client/server Model • Server provides service to clients – One server, many clients • Examples: – Server must execute continuously – Client initiates communication – Printer server, – File server, – Web server, – Email server, – BBS server, –… 32 Peer-to-peer (P2P) Model • Two processes communicating as equals • Examples: – Peer-to-peer file sharing: • FastTrack, BitTorrent, … – VoIP: Skype, … – Streaming media: TVant, … – Instant message, online chat: MSN, google talk, … 33 Distributed System • Consists of software units that execute as processes on different computer. • Examples: – Multitier architecture – Computer cluster – Cloud computing – Grid computing – BOINC system –… 34 The Internet Applications • • • • • • • • Telnet, ssh Email WWW File transfer Peer2peer Internet phone (VoIP), instant message Streaming media … 35 Electronic Mail (email) • Email address • Email server • Email client – Outlook – Thunderbird – Pine • Webmail – Yahoo mail, gmail, hotmail, … 36 World Wide Web (WWW) • A system, invented by Tim Berners-Lee (1989), of interlinked hypertexts via Internet. 37 Web Browser • A software application for retrieving, presenting, and traversing information resources on the World Wide Web. – Internet Explore – Mozilla Firefox – Apple Safari – Google Chrome • Bookmark, RSS, download management 38 HTTP and URL • Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) is an application-level protocol for distributed, collaborative, hypermedia information • Uniform Resource Locator (URL): web address Figure 4.8 A typical URL 39 HTML • Hypertext Markup Language (HTML): encoded as text file • Uses tags to communicate with browsers • XML: eXtensible Markup Language – A language for constructing markup languages (meta-language) 40 Related Courses • Computer network –計算機網路概論、密碼與網路安全概論、 訊號與系統、作業系統 References • Textbook chap 4 sec1,2,3,4 • The Internet 41