* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ref_Models
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Power over Ethernet wikipedia , lookup
Passive optical network wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
IEEE 802.1aq wikipedia , lookup
Multiprotocol Label Switching wikipedia , lookup
Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
IEEE 802.11 wikipedia , lookup
Asynchronous Transfer Mode wikipedia , lookup
UniPro protocol stack wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
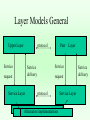
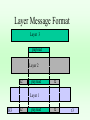
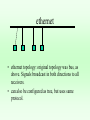
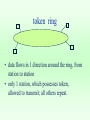
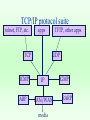
Communication Reference Models • Layer Models • ISO 7 layer Model • IEEE Model • DOD Model • ATM • TCP Protocol Suit Layer Models General Upper Layer protocol Service Service Service delivery request Service Layer Peer Layer request protocol Alternative implementations Service Layer Service delivery Layer Message Format Layer 3 payload Layer 2 H2 payload t2 Layer 1 H3 H2 payload t2 t3 ISO 7-layer model – 1 physical transmit signals – 2 data link reliable point to point – 3 network routing – 4 transport end to end – 5 session logon, security – 6 presentation integers,characters – 7 apps --> ftp, email, telnet,WWW IEEE model • for LANs • compatible with ISO; more detail for specific type of networks -> Application ISO LAYER 7,6,5,3 -> LLC - logical link control 2 -> MAC - medium access control 2 -> physical layer/medium 1 LANs : local area networks • ethernet, or CSMA/CD : IEEE 802.3 – most widely used LAN; more than half of all LANs in the world – broadcast-contention protocol – data rates of 10,100,1000 Mbps – physically configured as bus or a star – can use coax cable (thick or thin), twisted pair, or optical fiber. – utilization of 30-50%, roughly ethernet • ethernet topology: original topology was bus, as above. Signals broadcast in both directions to all receivers. • can also be configured as tree, but uses same protocol. LANs : local area networks • token ring : IEEE 802.5 – – – – 2nd most used in internet; 20-25% of all LANs. physical ring, logical broadcast; no collisions. data rates 4,16,100 (FDDI) throughput 90-95% entirely possible token ring • data flows in 1 direction around the ring, from station to station • only 1 station, which possesses token, allowed to transmit; all others repeat. DOD Model • Internetworking ISO LAYER – applications : email, FTP, telnet, WWW 7,6,5, – host-host --> transport layer: TCP,UDP 4 – internet layer : IP 3 – network interface --> to lower layered networks; eg, ethernet, token ring, FDDI, MILNet, etc. 2 – Physical 1 TCP/IP protocol suite telnet, FTP, etc. apps TCP ICMP ARP TFTP, other apps. UDP IP LAN/WAN media IGMP RARP ATM model • ATM: asynchronous transfer mode • high speed network • layers: physical -- based on optical fiber ATM layer -- switching ATM adoption layer - interface user layers