* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Networking
Wireless security wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Zero-configuration networking wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Summary - Part 2 - Objectives
The purpose of this basic IP technology training is to explain
video over IP network. This training describes how video can be
used on a network using IP protocol and enables individuals to
understand how the IP network can respond to today’s increasing
need of sharing video any time and anywhere.
“What is it?”
As a first step, three main issues tackled here are IP protocol,
networks, and video over IP. The training consists of nonexhaustive information aimed at demystifying the use of video
over IP network.
“How to run it?”
As a second step, you may refer to the training on Sony IP
monitoring solutions to understand how to run your application
over network.
Basic Training on IP Technology
- Part 2 -
Summary - Part 2
Networks
What is a network ?
Defining the geographical dimension of a network
What network can I access ?
How users access the network
Cabling
Network components
Networks - What is a Network ?
A network is a system that transmits any combination of voice, video
and/or data between users.
A network can be defined by its geographical dimension and by the
method by which the user's PC accesses it.
A network consists of
The network operating system (Windows NT/2000™) on the
user's PC (client) and server;
The cables connecting all network devices (user's PC, server,
peripherals, etc.);
All supporting network components (hubs, routers and switches,
etc.).
Networks - Defining the Geographical
Dimension - LAN (Local Area Network)
A LAN connects network devices
within a limited geographical area
such as office buildings or schools.
The data transfer is managed by a
transport protocol such as TCP/IP.
The transmission of data is
performed by the access method
(Ethernet, Token Ring, etc.).
The actual communications path is
the cable (twisted pair, coaxial,
optical fibre) that interconnects
each network device.
Hub
Hub
Networks - Defining the Geographical
Dimension
WAN (Wide Area Network)
A WAN covers a wide geographic area, carrying data over long
distances, such as a country
WANs can be formed by different LANs
The connection between different LANs may not be permanent.
WANs are sophisticated networks, but transmission speeds
have generally been slower than those commonly achieved on
LANs.
Central
Office
Central
Office
Networks - What Network Can I Access ?
Security decides who can see what.
Internet
(Content for everyone
to see)
Extranet
(Specific Content for
specific users only)
Intranet
(Content for Internal
use only)
Networks - What Network Can I Access?
Internet
The largest public computer network made up of more than 65
million computers in more than 100 countries
There are more than 20 million hosts on the Internet
(a host is a mainframe or medium to high-end server that is always
online via TCP/IP).
Small Internet Service Providers (ISPs) are connected to
regional ISPs, which are connected to the major backbones
covering Metropolitan areas.
Today, the Internet has become commercialized into a world-wide
information highway, providing information on every known
subject.
Networks - What Network Can I Access?
Intranet
An in-house Web site that can be accessed only by the employees
of the enterprise.
Intranets use the same communication protocols and thus provide a
standard way of sharing information internally.
Extranet
A Web site for a dedicated audience (e.g. customers…) rather than
the general public. It can provide access to research, current
inventories and internal databases - virtually any type of
information that is private and not published for everyone.
An extranet uses the public Internet as its transmission system, but
requires passwords to gain entrance.
Networks - How the User's PC Accesses the
Network Cable
The "Access Method" determines how network devices access the
network cable.
Transfers data to and from the connected user's PC on the network.
The access method used is an important factor in determining the
speed at which a LAN can operate.
The most popular access methods are:
Ethernet
Token Ring
Networks - How the User's PC Accesses the
Network Cable: Ethernet
Ethernet is the most popular LAN access method.
Ethernet uses CSMA/CD technology to broadcast each data
packet over the network cable.
All devices connected to the Ethernet are "listening", and the
station with the matching destination address accepts the data
packet.
Each user's PC competes to get its data packets onto the
network.
The transmission speed of today's Ethernet network components
is 10/100Mbps.
Cable types available for Ethernet:
Twisted Pair / Coaxial / Optical Fiber
Twisted Pair Ethernet
Networks - How the User's PC Accesses
the Network Cable - Token Ring
Token Ring is a LAN access method that is still being used, but is no
longer as popular as Ethernet.
It can connect up to 255 devices (or "listening") in a star topology.
All network devices connect to a central wiring hub use twisted pair
cabling.
Token Ring ensures that all users get regular turns at transmitting their
data.
The transmission speed of today's Token Ring network components is
4/16Mbps.
Networks - What Cable to Choose?
Cabling Types
Depending on the access method you can choose several cabling types:
Twisted pair
The wires are twisted around each other to minimize interference
from other twisted pairs in the cable.
Twisted pair cables are available unshielded (UTP) or shielded
(STP). UTP is the most common type and uses a RJ-45 Connector.
Typical cable lengths are up to 100m.
Twisted pair networks use a star
topology.
Coaxial
Coaxial cable uses BNC connectors.
The maximum cable lengths are around 500m.
Coaxial networks use a single bus topology.
RJ-45
BNC
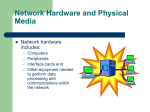
Networks - Network Components
Having defined the geographical dimension and access method of the
network, the network components need to be chosen.
The network components constitute the hardware that is required to
actually build your network.
Network components are:
Network Interface Card
Hubs
Switches
Routers
Networks - Network Components - NIC
A Network Interface Card (NIC) is a circuit board that plugs into both
clients and servers and controls the exchange of data between them.
A specific software ("driver") must be installed (depending on the
make of the NIC).
A physical transmission medium, such as twisted pair or coaxial cable,
interconnects all network interface cards to network hubs or switches.
Ethernet and Token Ring are common network interface cards.
Today's cards support 10BaseT and 100BaseT with automatic
recognition.
Leds
RJ45
Networks - Network Components - Hubs
A Hub is a central connecting device in a star topology LAN
configuration.
Passive hubs are just connecting devices that add nothing to the data
passing through them.
Active hubs, also called "multiport repeaters", regenerate the data
bits in order to maintain a strong signal.
Share the available bandwidth.
Forward all traffic to all hosts and is therefore inefficient.
Networks - Network Components Switches
Switches are intelligent hubs providing dedicated connection and
bandwidth between clients on a LAN.
Switches are also known as "switching hubs".
A switch gives any device on the network the full bandwidth instead of
sharing the available bandwidth.
Intelligence ensures only destination receives the data, at
maximum bandwidth.
Allows a network to be cut into different parts in order to improve
network performance.
Used to implement star network topologies on a LAN basis.
Enables direct connection between multiple hosts.
Networks - Network Components - Routers
A router is a device that forwards data packets from one network to
another.
Routers read the network address in order to route data via the
optimum path.
Routers are also widely used to connect remote offices.
Convert data structure from one media to another, for example
Ethernet <=> ISDN.
Routers can interconnect all networks in the enterprise.
For example two different networks like a LAN and the Internet.
Data packets which are addressed to a device at the same site of
the router will not be let through.