* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 3G and 4G - Web Services Overview
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
Policies promoting wireless broadband in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Wireless security wikipedia , lookup
Asynchronous Transfer Mode wikipedia , lookup
Code-division multiple access wikipedia , lookup
List of wireless community networks by region wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
UniPro protocol stack wikipedia , lookup
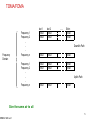
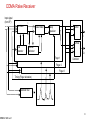
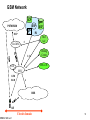
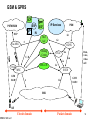
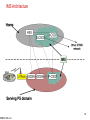
3G and 4G Wireless – Advances and Challenges SRB 041406 ver1 Suresh R. Borkar Adjunct Faculty, Dept of ECE, Ill Instt. of Tech. [email protected] Apr 14, 2006 1 3G and 4G Wireless – Advances and Challenges Where are we? 3G Wireless Summary Where do we Want to go? Evolution to Seamless Networking 4G Wireless Challenges The one who stays still is left behind SRB 041406 ver1 2 Where are We? Classic Wireline MaBell Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) – US Universal coverage achieved early 1980’s “Wireless” First Generation Analog Systems – Speech – AMPS, TACS Second Generation Digital Systems – Enhanced Capacity – CDMA, D-AMPS, TDMA, GSM, DECT, PDC 2.5 Generation Systems – Low Speed Data – GPRS, EDGE Third Generation Systems – “INTERNET” on Wireless – WiFi/HyperLAN <-> WiMAX/HyperWAN <-> CDMA2000/WCDMA – Evolution to All IP Network including VoIP SRB 041406 ver1 3 Representative Wireless Standards GSM/TDMA – Time Division Multiplexing based access CDMA – Code Division Multiplexing based access OFDM – Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing Many toys to play with SRB 041406 ver1 4 TDMA/FDMA Frequency Domain Frequency 1 Frequency 2 . . . Frequency n Frequency 1 Frequency 2 . . . Frequency n slot 1 Circuit Circuit slot 2 Circuit Circuit ... Slot n Circuit Circuit Downlink Path Circuit Circuit Circuit Circuit Circuit Circuit Circuit Circuit Circuit Uplink Path Circuit Circuit Circuit Give the same air to all SRB 041406 ver1 5 CDMA t Freq: Chips user 1 user 2 X usern Separated by PN codes t III Message t Resulting Signal Channelization code: Separate xmissions from a single source from each other Scrambling code: separate different sources from each other Spreading Code = Channelization code x Scrambling code All persons are created equal SRB 041406 ver1 6 Multipath Arrival of Signals Y SRB 041406 ver1 Y Transmitted symbol received signal at each time delay Modified with the channel estimate combined symbol finger #1 finger #2 finger #3 7 CDMA Rake Receiver Input signal (from RF) SRB 041406 ver1 correlator I phase rotator SUM I delay equalizer Q I SUM Q code generator channel estimator Q Finger 1 Combiner Finger 2 Finger 3 Timing (Finger allocation) Matched filter 8 Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) Successor to Frequency Hopping and Direct Sequence CDMA Capability to cancel multipath distortion in a spectrally efficient manner without requiring multiple local oscillators (802.11a and 802.16) Based on use of IFFT and FFT Frequency orthogonality as compared to code orthogonality in CDMA using Walsh Code SRB 041406 ver1 9 3G Services 2MHz video conferencing Internet telemedicine Video on demand radio paging Bandwidth audio conferencing Mobile TV electronic newspaper messaging Mobile radio Fax voice 1KHz bi-directional unidirectional Broadcast/ multicast Who is first? – the customer; who is second? - No one SRB 041406 ver1 10 Key Mobility Services Multimedia Messaging Services (MMS) – Text, sounds, images, and video – Transition from Short Message Service (SMS) – Open Internet standards for messaging Web Applications – Information portals – Wireless Markup Language (WML) with signals using Wireless Application Protocol (WAP) Location Communications Services – Location Awareness Based Personalization of information presentation format – Service capability negotiations (MExE environment) SRB 041406 ver1 11 Customized Application for Mobile Enhanced Logic (CAMEL) CAMEL = IN + Service portability (incl mobility and roaming) Virtual Private Network (VPN) • Mobile user <-> ISP <-> corporate server • Mobility, Security, Capacity and quality Prepaid, Usage Limitations, Advanced Routing Services Virtual Home Environment (VHE) • Subscriber profile, charging information, Service information, numbering information • Integration of array of services, content conversion to heterogeneous services, network user profile, location aware services Take the claims with a grain of salt SRB 041406 ver1 12 GSM Network SCP SSP PSTN/ISDN STP IN ISUP Gw-MSC gsm SCF HLR AuC C Billing Center C, D SMS-GW VLR MSC GSM 04.08 A BSS UE SRB 041406 ver1 Circuit domain 13 GSM & GPRS SCP SSP PSTN/ISDN STP ISUP Gw-MSC gsm SCF IN HLR AuC C PDN IP Services Gi Gc GGSN C, D Billing Center Ga VLR GSM 04.08+ SMS-GW Data, voice, video call Ga CGw Gn Gr MSC SGSN A Gb GSM 04.08+ BSS UE SRB 041406 ver1 Circuit domain Packet domain 14 WCDMA/UMTS SCP gsm SSP SCF STP IN, CAMEL PSTN/ISDN ISUP Gw-MSC HLR+ AuC C PDN IP Services Gi+ Gc+ GGSN C+, D+ Billing Center CGw Ga+ SMS-GW VLR Gn+ Gr+ 3G-MSC GSM 04.08++ Data, voice, video call Ga+ 3G-SGSN Iu-cs Iu-ps GSM 04.08++ UTRAN UE SRB 041406 ver1 Circuit domain Packet domain 15 GSM/UMTS Bit rate, Mobility and Services High (Car / Train) Voice EDGE CS Data Fax Mobility Text Messaging GSM HSCSD GPRS UMTS Low (stationary) SRB 041406 ver1 9.6 14.4 76.0 GPRS HSCSD 384.0 EDGE Bit Rate, Kbps UMTS 2 Mb/s 16 3G Evolution 2.5G GSM HSCSD 15.2 kbps GPRS 170 kbps TDMA CDPD 43.2 kbps PDA/PDC-P 14.4 kbps cdmaOne 76.8 kbps WLAN IEEE 802.11b 11 Mbps 3.5G EDGE 473 kbps EDGE Ph2 GRAN 473 kbps TD-SCDMA Ph 2 2 Mbps TD-SCDMA 284 kbps WCDMA FDD 2 Mbps CDMA2000 1x 307 kps HyperLAN2 54 Mbps IEEE 802.11 a/h 54 Mbps WCDMA TDD 2 Mbps WCDMA HSDPA 10 Mbps 1XEV-DO (HDR) 2.4 Mbps 1XEV-DV (HDR) 5.4 Mbps Harmonized HyperLAN2 And IEEE 802.11a WiMAX/HyperMAN also in the mix Ref: Honkasalo et al, WCDMA and WLAN for 3G and Beyond, IEEE Wireless Communication, Apr 2002 SRB 041406 ver1 17 Some Representative Current Wireless Options 3G Cellular (WCDMA) – Frequency Division Duplex (FDD): Uplink and Downlink are separated in frequency – (“symmetric”) – Time Division Duplex (TDD): Uplink and Downlink are separated in time – allows “asymmetric” traffic (adjust time slots in uplink and downlink) 3G Cellular (CDMA2000) Wi Fi – 802.11a and 802.11b; HyperLAN2 – 2.4 GHz band WiMAX – 802.16d (fixed); 802.16e (“portable”) – 5.8 GHz band; 10 – 20 Mbps symmetrical BW Blue Tooth – RF based LAN technology; 20-30 feet coverage – 2.4 GHz band Darwin’s Theory of Evolution and Survival of the fittest SRB 041406 ver1 18 3G WCDMA Release 99 Release 4 Release 5 Domains, Protocols, and Channels Radio Resource Management Network Dimensioning and Optimization Quality of Service (QoS0 and Location Services The favored twin sister of CDMA2000 SRB 041406 ver1 19 Release 99 Radio Bearer Negotiations Traffic Classes Complex Scrambling Speech Codec – (eight) Adaptive Multi Rate (AMR) Battery Life Transmission “spatial/antenna” diversity Compressed Mode – Measurements in multiple frequency – Use of transmission time reduction techniques # PDP Contexts per IP Address QPSK; coherent detection; Rake receiver Short and Long Spreading Codes Multicall – several simultaneous CS calls with dedicated bearers of independent traffic and performance characteristics Customized Application for Mobile network Enhanced Logic (CAMEL) Phase 3 A lot to gobble SRB 041406 ver1 20 Release 4 Bearer Independent Core Network Tandem Free Operation (TFO), Transcoder Free Operation (TrFO), and Out of Band Transcoder Control (OoBTC) Low Chip Rate TDD Operation Network Assisted Cell Change FDD Repeater NodeB Synchronization for TDD IPv6 packet switched network supporting both real time and non-real time traffic – Session Initiated Protocol (SIP) replacing SS7 Home Subscriber Server (HSS) MSC/VLR -> MSC server (mobility management) and MGW (Connection management subtasks) Multimedia Message Service (MMS) environment SRB 041406 ver1 21 Release 5 IP Transport in UTRAN High Speed Downlink Packet Access (HSDPA) (upto 10 Mbps) Intra Domain Connection to Multiple CN Nodes (Iuflex) IP Multimedia CN Subsystem (IMS) “Guaranteed” End to End (E2E) QoS in the PS domain Global Text Telephony Support for Real Time Services in packet domain CAMEL Phase 4 SRB 041406 ver1 22 HSDPA Peak Data rate > 10 Mbps Same spectrum by both voice and data – Up to 12 spreading codes for High Speed DSCH (HS-DSCH) – Fast link Adaptation – Both code and time division for channel sharing Transmission Time interval 2 ms Hybrid Automatic Repeat reQuest (HARQ) – Automatic optimizations to Channel Quality Indicator (CQI) QPSK and 16 QAM modulation at 3.84 Mhz symbol; spreading factor fixed to 16 Incremental Redundancy or chase combining (CH) New DPCCH2 in uplink primarily for HARQ channel state info SRB 041406 ver1 23 WCDMA Domains Home Network Domain [Zu] Cu Uu Iu [Yu] Serving Network Domain USIM Domain Mobile Equipment Domain User Equipment Domain Access Network Domain Transit Network Domain Core Network Domain Infrastructure Domain Standardization of architecture (domains) and standardization of protocols (strata) SRB 041406 ver1 24 WCDMA Protocol Layers Radio Network Layer Control Plane User Plane Application Protocol Data Stream(s) Transport Network Layer Transport Network User Plane SRB 041406 ver1 Transport Network Control Plane Transport Network User Plane ALCAP(s) Signalling Bearer(s) Signalling Bearer(s) Data Bearer(s) Physical Layer 25 WCDMA L1, L2, and RRC Sublayer U-plane information C-plane signalling GC Nt DC Duplication avoidance GC Nt DC UuS boundary L3 control L3/RRC RRC con con trol trol SRB 041406 ver1 PDCP concon trol trol PDCP L2/PDCP RLC RLC BMC L2/BMC RLC L2/RLC RLC RLC RLC RLC RLC Logical Channels MAC L2/MAC Transport Channels PHY L1 26 WCDMA Channels Logical Channels Control BCCH PCCH Mac -b -c/sh Transport Channels Common BCH PCH Physical Channels DCCH CCCH Traffic DTCH SHCCH CTCH -d FACH Mapped to Transport Channels PCCPH SCCPCH RACH PRACH UL CPCH DSCH PCPCH PDSCH Dedicated DCH DPDCH DPCCH Dedicated SCH CPICH AICH PICH CSICH CD/CA-ICH Transport Channels: how information transferred over the radio interface Logical Channels: Type of information transferred over the radio interface Channels made by soft hats SRB 041406 ver1 27 Mapping Between Channels Uplink DCCH DTCH CCCH RACH PRACH Downlink CPCH PCPCH DCH DPDCH DPCCH Logical Channels Transport Channels Mapped Physical Channels Dedicated Physical Channels PCCH BCCH PCH BCH PCCPCH CCCH CTCH FACH SCCPCH DSCH DCCH DTCH DCH PDSCH DPDCH DPCCH SCH CPICH AICH PICH CSICH CD/CA-ICH N to M SRB 041406 ver1 28 WCDMA Channel Usage Examples Uplink/ Downlink Code Usage Dedicated channels DCH Both According to maxm bit rate Fast Power control Soft handover Suited for Yes Yes Medium or large data amounts Suited for bursty data No Common channels FCH RACH Downlink Uplink Shared channels CPCH DSCH USCH Uplink Downlink Uplink, only in TDD Fixed Fixed Fixed Codes Codes codes per codes per codes per shared shared cell cell cell btw users btw users No No Yes Yes No No No No No No Small Small Small or Medium Medium data data medium or large or large amounts amounts data data data amounts amounts amounts Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Flexibility comes with responsibility SRB 041406 ver1 29 Radio Resource Management Power Control Handover Access Control Load and Congestion Control Packet Scheduling SRB 041406 ver1 30 WCDMA Power Control (near = far) Keep received power levels P1 and P2 equal Y Y Power control commands to the UEs UE1 NodeB UE2 Uplink and downlink (1500 Hz) Open Loop Power Control Closed Loop Power Control Outer Loop Power Control Equal Opportunity Administration (EOA) SRB 041406 ver1 31 WCDMA Handovers sector 1 The same signal is sent from both sectors to UE Softer Y Y RNC sector 2 Y Y Soft RNC macro diversity combining in uplink NodeB1 The same signal is sent from both NodeB's to UE, except for the power control commands Y Y NodeB2 Hard and Inter-frequency handovers Intersystem cell-reselection “Equivalent PLMN mode” (autonomous cell re-selection (packet) idle mode) SRB 041406 ver1 32 Handover Algorithm T T T Pilot Ec/IO of cell 1 Reporting_range + Hysteresis_event 1B Reporting_range - Hysteresis_event 1A Hysteresis_event 1C Pilot Ec/IO of cell 2 Pilot Ec/IO of cell 3 Connected to cell 1 Event 1A - add cell2 A relay race with multiple batons SRB 041406 ver1 Event 1C = replace cell1 with cell3 Event 1B = remove cell3 33 Network Dimensioning and Optimization Dimensioning Criteria – Coverage, Capacity, Quality of Service Dimensioning – Link budget, capacity (hard and soft) and load factor – Estimation of average interference power – Coverage end Outage probabilities Optimization – Performance Requirements – Antenna adjustments, neighbor lists, scrambling codes Don’t force a round peg in a square hole SRB 041406 ver1 34 WCDMA Quality of Service (Qos) Dynamic Negotiations of properties / Services of radio bearer – Thruput, transfer delay, data error rate – Authentications Traffic class Fundamental characteristics Examples of the application Conversational class Preserve time relation (variation) between information entities of the stream Conversational pattern (stringent and low delay) voice, videotelephony video games Streaming class Preserve time relation (variation) between information entities of the stream Interactive class Request response pattern Preserve data integrity Background Destination is not expecting the data within a certain time Preserve data integrity Streaming multimedia Web browsing, network games Background download of emails One way communications is no communications SRB 041406 ver1 35 Location Services (LCS) UTRAN Node B Uu Iub SRNC SMLC LMU type B HLR Iu Lh UE MSC Um BTS LMU LMU <- alternative -> type B type A Abis A/ (Gb)/ (Iu) Lg Le Gateway MLC External LCS client BSC Ls Lb<- alternative -> Lc (R98 and 99) GERAN SMLC Lp gsmSCF SMLC Cell ID based Observed Time Difference Arrival – Idle Period Downlink (OTDOA-IPDL) Network Assisted GPS You can run but you cannot hide SRB 041406 ver1 36 Why Move Towards 4G? Limitation to meet expectations of applications like multimedia, full motion video, wireless teleconferencing – Wider Bandwidth Difficult to move and interoperate due to different standards hampering global mobility and service portability Primarily Cellular (WAN) with distinct LANs’; need a new integrated network Limitations in applying recent advances in spectrally more efficient modulation schemes Need all all digital network to fully utilize IP and converged video and data Incessant human desire to reach the sky SRB 041406 ver1 37 Where Do We Want to Go? Seamless Roaming Integrated “standard” Networks Mobile Intelligent Internet Onwards to (Ultra) Wideband Wireless IP Networks We are no longer in Kansas, Toto SRB 041406 ver1 38 Upcoming 3.5 G – Evolved radio Interface – IP based core network 4G – New Air Interface – Very high bit rate services – Convergence of Wireline, Wireless, and IP worlds And Now for Something Completely Different SRB 041406 ver1 39 3G All-IP Reference Architecture Legacy mobile signaling Network Applications & Services SCP Alternative Access Network R-SGW Mh Ms Multimedia IP Networks CSCF Mw Mm HSS HLR CAP CSCF Cx Gr Gc Gi Gn R SRB 041406 ver1 UTRAN Uu MGW Iu Mc Gn SGSN MGCF GGSN T-SGW Mc Gi MGW Nb MSC Server Gp Gi MRF GGSN Iu MT Mg Gi SGSN TE Mr Mc GMSC Server Nc PSTN/ Legacy/External T-SGW Signalling Interface Signalling and Data Transfer Interface Other PLMN 40 WCDMA 3G Evolution to All-IP Network SRB 041406 ver1 PSTN/ISDN Wireless Data Server Internet/Intranet/ISP www, email IP GGSN HLR HSS AuC 3G-MSC PCM IP Firewall (G)MSC Server CSCF PSTN/ISDN MGCF SGW MGW IP SS7 MGW SGSN MRF ATM GTP+/IP GGSN RNC RNC Iur Iub Iub N_B N_B UTRAN 41 3.5G Radio Network Evolution High Data rate, low latency, packet optimized radio access Support flexible bandwidth upto 20 MHz, new transmission schemes, advanced multi-antenna technologies, and signaling optimization Instantaneous peak DL 100 Mb/s and UP 50 Mb/S within 20 MHz spectrum Control plane latency of < 100 ms (camped to active) and < 50 ms (dormant to active) > 200 users per cell within 5 MHz spectrum Spectrum flexibility from 1.25 MHz to 20 MHz Eliminate “dedicated” channels; avoid macro diversity in DL Migrate towards OFDM in DL and SC-FDMA in UL Support voice services in the packet domain Adaptive Modulation and Coding using Channel Quality Indicator (CQI) measurements SRB 041406 ver1 42 3.5G WCDMA Evolved System Architecture GERAN Gb Iu GPRS Core PCRF UTRAN Rx+ S7 S3 S4 HSS S6 Evolved RAN S1 MME UPE S5 Inter AS Anchor Evolved Packet Core S2 non 3GPP IP Access Gi Op. IP Serv. (IMS, PSS, etc…) S2 WLAN 3GPP IP Access * Color coding: red indicates new functional element / interface Source: www.3gpp.org SRB 041406 ver1 43 Key 3G and 4G Parameters Attribute 3G Major Characteristic Predominantly voice- data as Converged data and VoIP add-on Wide area Cell based Hybrid – integration of Wireless Lan (WiFi), Blue Tooth, Wide Area 1.6 - 2.5 GHz 2 – 8 GHz Network Architecture Frequency Band Component Design 4G Bandwidth Optimized antenna; multiband adapters 5 – 20 MHz Smart antennas; SW multiband; wideband radios 100+ MHz Data Rate 385 Kbps - 2 Mbps 20 – 100 Mbps Access WCDMA/CDMA2000 MC-CDMA or OFDM Forward Error Correction Concatenated Coding Switching Convolution code 1/2, 1/3; turbo Circuit/Packet Mobile top Speed 200 kmph 200 kmph IP Multiple versions All IP (IPv6.0) Operational ~2003 ~2010 SRB 041406 ver1 Packet 44 Key 4G Mobility Concepts Mobile IP – VoIP – Ability to move around with the same IP address – IP tunnels – Intelligent Internet Presence Awareness Technology – Knowing who is on line and where Radio Router – Bringing IP to the base station Smart Antennas – Unique spatial metric for each transmission Wireless IP <---> IP Wireless SRB 041406 ver1 45 4G Networks Advances Seamless mobility (roaming) – Roam freely from one standard to another – Integrate different modes of wireless communications – indoor networks (e.g., wireless LANs and Bluetooth); cellular signals; radio and TV; satellite communications 100 Mb/se full mobility (wide area); 1 Gbit/s low mobility (local area) IP-based communications systems for integrated voice, data, and video – IP RAN Open unified standards Stream Control Transmission Protocol (SCTP) – Successor to “SS7”; replacement for TCP – Maintain several data streams within a single connection Service Location Protocol (SLP) – Automatic resource discovery – Make all networked resources dynamically configurable through IP-based service and directory agents The demise of SS7 SRB 041406 ver1 46 4G Networks Advances – cont’d Diameter – Successor to “Radius” – Unified authentication, authorization, and accounting (AAA) Integrated LAN card and Subscriber Identity Modules (SIMs) HSS – Unified Subscriber Information Application developers, Service providers, and content creators Expand beyond the circle SRB 041406 ver1 47 Key Challenges Spectral Efficiencies – Challenge Shannon’s fundamental law of data communications (BW, Sig/No) – Hardware Frequency Synthesis techniques esp. for Frequency Hop (FH) systems – Traffic characteristics management (burstiness, directionality) Multi Carrier Modulation (MCM) – Baseband process using parallel equal bandwidth subchannels – MC-CDMA; OFDM – Quadrature Phase-Shift Keying (QPSK); Multilevel Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (M-QAM); Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) – Add cyclic extension or guard band to data – Challenges of Inter Symbol Interference (ISI) and Peak to Average Ratio (PAVR) No pain, no gain SRB 041406 ver1 48 Key Challenges - cont’d - 1 Signal Processing and optimizations – Handling extremely large number of users – Synchronous and asynchronous transmissions – Orthogonality / correlation of large number of codes – Spectrum Pollution – Multi path re-enforcement / interference – Multi User Detection (MUD) and Adaptive Interference suppression techniques (ISI and MAI) SRB 041406 ver1 49 Key Challenges - cont’d - 2 Extremely Fast Arithmetic (esp. multiplication) – N Dimensional vector spaces – IFFT, FFT – Advanced DSP’s for parsing and processing data Smart / Intelligent Antennas – Dynamically adjust beam pattern based on CQI – Switched beam Antennas; adaptive arrays – Coverage limitations due to high frequencies (> 5 GHz) Manage Entropy SRB 041406 ver1 50 Key Challenges - cont’d - 3 More Efficient and Sensitive Transreceiver Designs – Noise figure, gain, group delay, bandwidth, sensitivity, tunable filters, spurious rejection, power consumption – Frequency Reuse; linearity techniques – Tight closed Loop power control – Dynamic Frequency selection and packet assignments – Multi band, wide band, and flexible radios – Error Correction Coding – “Perfect” Synchronization / phase alignment between Xmitter and Receiver • Clock recovery algorithms (e.g., as times-two, zero crossing) – Adaptive digitization of speech and multi media signals SRB 041406 ver1 • A/D and D/A transformations 51 4G RF/IF Architecture Example Source: http://www.mobileinfo.com/3G/4G_CommSystemArticle.htm SRB 041406 ver1 52 4G Transreceiver Processing Example Source: http://www.mobileinfo.com/3G/4G_CommSystemArticle.htm SRB 041406 ver1 53 Key Challenges - cont’d - 4 All IP Network – Tunneling and Firewalls – Fast Handoff control, authentication, realtime location tracking, distributed policy management – Media Gateways for handling packet switched traffic • Trasnscoders, echo cancellations, media conversions Planetary Interoperability Integration across different topologies – Multi Disciplinary Cooperation WPAN WLAN + WWAN WMAN There is packet at the end of the tunnel SRB 041406 ver1 IP 54 Key Challenges - cont’d - 5 Distribute intelligence to the edges – Very Smart User equipment; away from “network Centric” architecture – Access routers – Miniaturization esp User Equipment Security and Levels of Quality of Service (QoS) – Encryption Protocols; Security and “trust of information” – Different rates, error profiles, latencies, burstiness – Dynamic optimization of scarce resources Advanced Used interactions / presentation – Improved User interfaces – advanced Speech recognition and synthesis – Flexible displays SRB 041406 ver1 55 Key Challenges - cont’d - 6 Web AI service / Interactive Intelligent Programs – Smart applications in the web; intelligent agents – Web Adaptiveness – global database schemes, global error corrective feedback, logic layer protocol, learning algorithms – Symbolic manipulation – Derive specifically targeted knowledge from diverse information sources Standardizations and Regulatory – Modulation techniques, switching schemes, roaming – Spectrum – Cooperation/coordination among global Spectrum Regulators SRB 041406 ver1 56 4G Forums Wireless World Research Forum (WWRF) in Europe Next-Generation Internet (NGI) – Led by and focused on US Fed Agencies (DoD, DoE, NASA, NIH etc.) – High Performance networks: vBNS (NSF), NREN (NASA), DREN (DoD), ESnet (DoE), Internet2 – US Universities Initiated – Focus on Gigabit/sec Points of Presence (gigaPoPs) SRB 041406 ver1 57 Summary Mobile Intelligent Internet and multi media applications Seamless Roaming, substantially high and selectable user bandwidth, customized QoS, Intelligent and responsive user interface Mobile IP, Radio Routers, smart Antennas Continued advances and challenges from 1G -> 4G – Modulation techniques, transreceiver advances, fast manipulations, user interfaces, IP tunelling and firewalls – Spectrum usage, regulatory decisions, “one” standard, authentication and security, multi disciplinary co-operation Packing so much intelligence in smaller and smaller physical space, esp. User Equipment (UE) IP + WPAN + WLAN + WMAN + WWAN + any other stragglers = 4G IP in the sky with diamonds SRB 041406 ver1 58 SRB 041406 ver1 Back-up 59 1st Generation Analog Cellular Systems Standard Region AMPS USA TACS Europe ETACS UK NMT 450 Europe NMT 900 Europe C-450 Germany Portugal Italy RTMS Radiocom 2000 NTT JTACS / NTACS SRB 041406 ver1 France Japan Japan Frequency (MHz) 824-849 869-894 890-915 935-980 872-915 917-950 453-457.5 463-467.5 890-915 935-960 450-455.74 460-465.74 450-455 460-465 414.8-418 424.8-428 870-885 860-870 915-925 Channel Spacing (kHz) 30 No. of Modulation Channels Data Rate (kbps) 832 FM 10 25 1000 FM 8 25 1240 FM 8 25 180 FM 1.2 12.5 1999 FM 1.2 10 573 FM 5.28 25 200 FM - 12.5 250 FM - 25 25 600 400 FM FM 0.3 8.0 60 2nd Generation Cellular and Cordless Systems SRB 041406 ver1 System Country IS-54 USA GSM Europe IS-95 USA Access Technology TDMA / FDMA TDMA / FDMA CDMA / FDMA (DS) 869-894 824-849 FDD 935-960 890-915 FDD Frequency Band BS(MHz) MS(MHz) Duplexing RF Channel Spacing (kHz) Modulation 30 Pi/4 DQPSK Fixed Frequency Assignment Power Control MS Y BS Y Speech VSELP Coding Speech rate (kbps) 7.95 Channel Bit 48.6 Rate (kbps) Channel 1/2 rate Coding convolution GMSK CT-2 Europe, Asia FDMA CT-3 DCT-90 Sweden TDMA / FDMA DECT Europe TDMA / FDMA 869-894 864-868 862-866 1800-1900 824-849 FDD TDD TDD TDD 200 1250 100 1000 1728 GFSK GFSK GFSK Fixed BPSK / QPSK Fixed Dynamic Dynamic Dynamic Y Y RPE-LTP Y Y QCELP N N ADPCM N N ADPCM N N ADPCM 8 (variable 13 rate) 270.833 1228.8 1/2 rate 1/2 rate None convolution forward, 1/3 rate reverse, CRC 32 32 72 32 640 CRC 1152 CRC 61 3G WCDMA and CDMA2000 Standards UMTS-WCDMA CDMA2000 "No' Backward Compatibility Cell Sites not synchronized Each cell site with different scrambling code for spreading Complex soft Hand Over Scrambling code 38,400 chips; frame of 10 ms Backward compatibility with CDMAOne Cell sites synchronized thru' GPS timing Adjacent cell sites use diffferent time offset of same scrambling code for spreading Simple Soft Hand Over Preudo Random (PN) sequence of length 215 - 1 chips; period of 26.67 ms; different site offset of 64 chips Walsh Codes OVSF Codes SRB 041406 ver1 62 Cdma2000 Layered Structure Packet Data Application Upper Layers (OSI 3-7) Signaling Services TCP Packet Data Application UDP IP PPP LAC Link Layer (OSI 2) LAC Protocol MAC Control State Packet Data Application High Speed Circuit Network Layer Services Null LAC Best Effort Delivery RLP MAC Multiplexing Physical layer (OSI 1) SRB 041406 ver1 QoS Control Physical Layer 63 Unique to cdma2000 UMTS Spectrum Allocation IMT-2000 TDD IMT-2000 TDD GSM 1800 DL DECT IMT-2000 UL IMT-2000 DL MSS UL MSS DL Europe PHS IMT-2000 DL IMT-2000 UL Japan IS-95 DL IMT-2000 DL IMT-2000 UL Korea PCS/DL PCS/UL USA 1800 SRB 041406 ver1 1850 1900 1950 2000 2050 2100 2150 2200 64 WCDMA Circuit Switched Protocols CM CM MM MM RRC RRC CODEC RLC RLC MAC MAC Phy-up Phy-up RANAP RANAP Q.2630.1 ALCAP NBAP FP SSCF-UNI SSCF-UNI PHY SRB 041406 ver1 ALCAP SSCF-UNI SSCF-UNI FP SSCOP SSCOP SSCOP SSCOP AAL5 AAL5 AAL5 AAL5 Q.2150.1 SCCP SCCP Q.2150.1 MTP3b MTP3B MTP3B MTP3b SSCF-NNI SSCF-NNI Iu UP SSCF-NNI SSCF-NNI SSCOP SSCOP SSCOP SSCOP AAL5 AAL5 AAL5 AAL5 PHY AAL2 UE NBAP Iu UP Q.2630.1 AAL2 AAL2 ATM ATM ATM ATM PHY PHY PHY PHY Node B RNC AAL2 Core 65 WCDMA PACKET CONTROL PLANE PROTOCOLS Uu Iub SM GMM RRC RLC MAC-cd PHY-up PHY PHY CDMA CDMA UE/MTE SRB 041406 ver1 FP ALCAP NBAP SSSAR SAAL SAAL AAL2 AAL5 AAL5 ATM PHY NODE B Iu-ps RRC RLC MAC-cd PHY-up NBAP ALCAP FP SAAL SAAL SSSAR AAL5 AAL5 AAL2 ATM PHY RNC SGSN 66 WCDMA PACKET USER PLANE PROTOCOLS Uu Iub Iu-ps IP PDCP RLC MAC PHY-up PDCP RLC MAC PHY-up PHY PHY CDMA CDMA FP ALCAP ALCAP FP AAL2 SAAL SAAL AAL2 ATM PHY UE/MTE SRB 041406 ver1 NODE B ATM PHY RNC SGSN 67 HSDPA Protocol Architecture RLC RLC MAC MAC-D MAC-c/sh MAChs PHY SRB 041406 ver1 PHY Uu HSDSCH FP HSDSCH FP HSDSCH FP HSDSCH FP L2 L2 L2 L2 L1 L1 L1 L1 Iub Iur 68 IMS Architecture SRB 041406 ver1 69 Standards IEEE 802.11a and b: Wireless LAN (WiFi) IEEE 802.15: Wireless PAN (Bluetooth) IEEE 802.16d and e: Wireless MAN (WiMAX) IS-41: Inter-systems operation (TIA/EIA-41) IS-54: 1st Gen (US) TDMA; 6 users per 30 KHz channel IS-88: CDMA IS-91: Analog Callular air interface IS-93: Wireless to PSTN Interface IS-95: TIA for CDMA (US) (Cdmaone) IS-124: Call detail and billing record IS-136: 2nd Genr TDMA (TDMA control channel) IS-637: CDMA Short Message Service (SMS) IS-756: TIA for Wireless Network Portability (WNP) IS-2000: cdma2000 air interface (follow on to TIA/EIA 95-B) SRB 041406 ver1 70 Glossary 3GPP:3G Partnership Project AAA:Authentication, Authorization, Accounting AMR:Adaptive Multi Rate (Speech Codec) ANSI:American National Standards Institute ARIB:Association of Radio Industries and Businesses (Japan) BRAN:Broadband Radio Access Network (HYPERLAN 2) 2.5 Mbps CAMEL:Customized Application for Mobile Enhanced Logic CDMA:Code Division Multiple Access CWTS: China Wireless Telecommunications Standards group (China) ECMA:European Computer Manufacturers Association EDGE:Enhanced Data for GSM Evolution ETSI:European Telecommunications Standards Institute FDD:Frequency Division Duplex FDMA:Frequency Division Multiple Access GGSN:Gateway GPRS Support Node GMSC:Gateway MSC GPRS:General Packet Radio Service GSM:Global System for Mobile communication GTP:GPRS Tunneling Protocol HIPERLAN:High Performance Radio Local Area Network HLR:Home Location Register HSCSD: High Speed Circuit Switched Data HYPERLAN: High Performance Radio Access network IMSI:International Mobile Subscriber Identity SRB 041406 ver1 IMT:International Mobile Telecommunications ITU:International Telecommunications Union OVSF:Orthogonal Variable Spreading Factor PDN:Public Data Network PLMN:Public Land Mobile Network PSTN:Public Switched Telephone Network QoS:Quality of Service RAB:Radio Access Bearer RNC:Radio Network Controller RRC:Radio Resource Control SGSN:Servicing GPRS Support Node SIM:Subscriber Identity Module TDD:Time Division Duplex TDMA:Time Division Multiple Access TTA:Telecommunications Technology Association (Korea) TTC:Telecommunications Technology Commission (Japan) UMTS:Universal Mobile Telecommunications System UTRAN:UMTS Terrestrial Radio Access Network VoIP:Voice over Internet Protocol WCDMA:Wideband Code Division Multiple Access WLAN: Wireless Local Area Network WPAN: Wireless Personal Area Network WWAN: Wireless Wide Area Network 71 References 1. www.3gpp.org 2. WCDMA for UMTS, Ed.: H. Holma and A. Toskala, John Wiley, 2001 3. UMTS - Mobile Communications for the Future, Ed. F.Muratore, John Wiley, 2001 4. WCDMA: Towards IP Mobility and Mobile Internet, Eds E.Djanpera and R.Prasad, Artech House, 2001 5. IS-95 CDMA and CDMA2000, V.K.Garg, Publishing House of Electronics Industry, Beijing, 2002 6. IP Telephony, O. Hersent, D. Gurle Et, and J-P Petit, Addison-Wesley, 2000 7. www.mobileinfo.com SRB 041406 ver1 72