* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lec 1
Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
Multiprotocol Label Switching wikipedia , lookup
Asynchronous Transfer Mode wikipedia , lookup
IEEE 802.1aq wikipedia , lookup
List of wireless community networks by region wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Zero-configuration networking wikipedia , lookup
Internet protocol suite wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
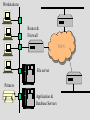
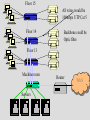
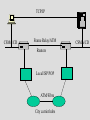
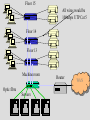
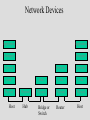
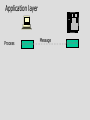
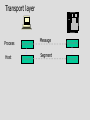
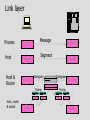
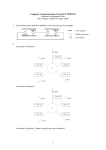
Service Providers & Data Link & Physical layers Week 4 Lecture 1 Internet Architecture Application layer – HTTP, SMTP etc W3C Transport layer – TCP, UDP IETF Network layer - IP Data link & Physical layers – the territory of the Lan & Telcos ITU IEEE Local Area Networks (LAN) • Nearly all organisation have a LAN in each office • All devices are connected to the LAN • LANs are then connected to the WAN via a router and firewall • LANs provide file and print services, and application and database servers Workstations Router & Firewall WAN File server Printers Application & Database Servers Main characteristics • • • • Owned & Operated by the Organisation Single geographic area, usually a building Relatively fast media Most common protocol is Ethernet using CSMA-CD Bus topology using Co-axial cable Hub topology using UTP Floor 15 All wires would be 100mbps UTP Cat 5 Floor 14 Backbone could be Optic fibre Floor 13 Machine room Servers Router WAN LAN Protocols • Most likely to be CSMA/CD at the data link layer • Carrier Sense Multiple Access/Collision Detection • Adaptor listens to see if other devices are transmitting – if not, it sends • Adaptors looks for own packets and accepts • If a collision occurs (propagation delay), the sending adaptors back-off for a random amount of time and then retransmits • CSMA/CD is a connectionless, unreliable service • The IP address is converted to the adaptor address by the Address Resolution Protocol module on each Internet host and Router Ethernet speeds • • • • Ethernet - 10mb Fast Ethernet - 100mb Gigabit Ethernet - 1000mb 10 Gigabit Ethernet - 10000mb TCP/IP CSMA/CD Frame Relay/ATM Routers Local ISP POP ATM/Fibre City carrier hubs CSMA/CD Devices in the network • • • • • • Network Adaptors Hubs Bridges Switches Routers Firewalls Network adaptors • Adaptor, NIC or PCMCIA card – connects the device to the network – Implements the data link layer and physical layer in hardware – Chip set makes adaptors relatively cheap – It is semi-autonomous - accepts and hands over IP packets – full responsibility for transmission & error control – Each adaptor has a unique 6 byte address. IEEE allocates address ranges to manufacturers Hubs • Essentially a repeater – when it receives a bit it sends it down the other links to other adaptors and hubs – thus includes all devices in the one collision zone • Physical layer devices • Carries out some network management functions – if an adaptor malfunctions and floods the Ethernet it can internally disconnect the link – collects some statistics • Extends the length of the LAN as each link has a discrete limit - 200 metres Bridges & Switches • They operate on Ethernet frames and are layer 2 devices – they are store and forward devices but use LAN addresses – LAN devices • Acts as a switch and only sends frames down a link on which the destination address is. Thus it can break a LAN into discrete collision zones – single tree • Uses MAC addresses • It also connects links at different bandwidths i.e. 10mbps and 100mbps • They are plug & play devices and self learn what devices are on what links. • But if there are multiple paths they could generate duplicate packets, so they disable duplicate paths. Floor 15 All wires would be 100mbps UTP Cat 5 Floor 14 Floor 13 Machine room Optic fibre Servers Router WAN Network Devices Application Application Transport Transport Network Link Physical Host Physical Hub Network Network Link Link Link Physical Physical Physical Router Host Bridge or Switch Routers • Routers send packets on best path to the destination. This is necessary for path redundancy • Because they operate at layer 3 they are inherently slower than bridges but more complex technologies are compensating – Route on IP addresses can use different paths • They maintain separate network segments • LAN or WAN devices • Can be used as simple firewalls by filtering out packets within an organisation • Vary between core trunk routers to SOHO routers for less that $1500. Router design • Bus with CPU software switching • Bus with intelligent line cards • Non blocking cross bar switching with up to 5 TBPS switching. Cisco 12000 series is an example. Juniper Networks, Avici and Lucent have similar capacity routers • Switching decisions on 100m packets per second Application layer Process Application Message Application Transport layer Process Host Application Transport Message Segment Application Transport Network layer Process Host Host & Router Application Transport Network Message Application Segment Datagram Network Transport Datagram Network Link layer Process Host Host & Router Message Application Segment Transport Network Datagram Frame Link Host, router & switch Link Application Link Transport Datagram Network Link Network Frame Link Link Link