* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download network jeopardy
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Zero-configuration networking wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
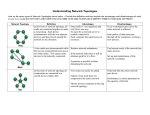
Networks JEOPARDY Unit 3 & 4 IP&M Acknowledgements: • VITTA for the jeopardy pro-forma • Mark Kelly’s Network slideshow Reasons For Networks Network Hardware Network Types Lucky Dip Network Topologies 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500 500 Reasons For Networks 100 At its simplest, a network is two or more computers that are connected so they can exchange information and share resources. A: What is a network? Reasons For Networks 200 Email, videoconferencing and chat are examples of how a network improves this. A: How does a network improve communications? Reasons For Networks 300 a They allow you to share information, save money on expensive equipment and communicate better with customers and employees. A: Why network? Reasons For Networks 400 Faster communication, cost savings (compare email costs with phone calls and physical travel) A: What are the efficiency indicators of a network? Reasons For Networks 500 Collaborative work is easier, access to resources broader. A: How does a network make an organisation more effective? Network Hardware 100 This allows a stand-alone computer to connect to a network. There are cabled and wireless cards. A: What is a NIC (network interface card)? Network Hardware 200 This is a robust central computer at the heart of the network A: What is a server? Network Hardware 300 These are connection points where cables can join up a split. Typically, a single incoming cable is split into multiple outgoing cables. A: What is a switch? Network Hardware 400 These are security devices that guard the connection between a LAN and the outside world (another LAN or WAN). They can be programmed to allow only authorised incoming and outgoing traffic as well as block one part of the network from another part. A: What is a router? Network Hardware 500 These boost fading network signals on long cables. A: What is a repeater? Network Types 100 It is typically restricted to one building or one site. Can be cabled - UTP, coaxial or wireless. Longer distance between buildings may need fibre optic cable. A: What is a LAN? Network Types 200 It is spread over wide distances. Connections use landline data cables (eg ISDN, ADSL), satellite. A: What is a WAN? Network Types 300 It is usually within a limited geographical region eg. A city. Connections usually with landline data cables (ISDN, ADSL), microwave, fibre optic cable. A: What is a MAN? Network Types 400 This is made up of inter-networked WANS. May run on UTP, coaxial, fibre optic, satellite, microwave, wireless, mobile phones, modems over phone lines. High speed digital data lines, submarine cables and even mains power lines. A:What is the Internet? Network Types 500 The universal protocol for Internet use the backbone of the Internet. A: What is TCP/IP? (transfer communication protocol/ internet protocol) Lucky Dip 100 A: What does a star topology look like? Lucky Dip 200 This is made of glass and is optical not electrical meaning little signal fade. Can transmit multiple signals on a single fibre. It is very fast, flexible, has high bandwidth, can travel long distance without repeaters and is very secure. A: What is fibre optic cable? Lucky Dip 300 This allows only one node to transmit at one time. A node can only transmit if it holds a special network packet called a token. A: What is a token ring network? Lucky Dip 400 This defines both how packets are handled and cabling options. When a node wants to communicate to another node, it transmits its addressed packet. The packet travels to every node on the segment. Each node inspects the packet however only accepts it if it is addressed to them. A: What is Ethernet? Lucky Dip 500 Two examples of this are: • Quality of the connection needs to be higher where there are many users as more people connected can slow down transmission. (think of our Internet connection • Users sometimes have to wait for resources (eg. Print queues) A: What are two problems for the average network user? Network Topologies 100 In this type of topology every device has exactly two neighbours for communication purposes. All messages travel in the same direction. A failure in any cable or device will take down the entire segment. They are more expensive and slower. A: What is a ring topology.? Network Topologies 200 This topology has a central connection point- usually a hub or switch with cables branching to many nodes. While it takes more cable, the benefit is that is a cable fails; only one node will be brought down. A: What is a star topology? Network Topologies 300 Also known as the ‘hierarchical topology’, this topology is a combination of bus and star topologies and is very common in larger networks. The node in the highest point in the hierarchy – usually the server – controls the network. A. Why is a tree topology? Network Topologies 400 This topology uses lots of cables to connect every node with every other node. It is very expensive to wire up but if one cable fails there are alternative ways to communicate. A: What is mesh topology? Network Topologies 500 Many devices connect to a single cable ‘backbone’. If the backbone is broken the entire segment fails. They are relatively easy to install and don’t require much cabling compared to the alternatives, however they get congested with too many nodes. They are best for small networks. A: What is a bus topology?