* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 5
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Net neutrality wikipedia , lookup
Wireless security wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Net neutrality law wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Zero-configuration networking wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
Internet protocol suite wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
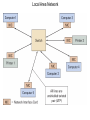
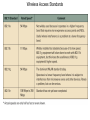
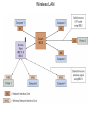
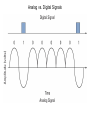
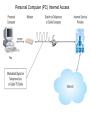
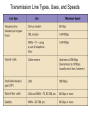
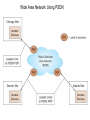
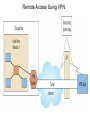
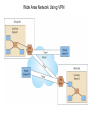
Chapter 5 Data Communication And Internet Technology Purpose • Understand the fundamental networking concepts Agenda • • • • Network Concepts Communication Protocol TCP/IP-OSI Architecture Network Types – – – – • • • • • • LAN WAN Public Switched Data Network Virtual Private Network Network Comparison Internet Domain Name System IP Addressing Schemes Security Discussion and Case Study Network Concepts • A collection of computers that communicate with one another over transmission lines • Types – Local area networks (LANs): connects computers in a single geographic location – Wide area networks (WANs): connects computers at different geographic sites – Internet: a network of networks Communication Protocol • Protocol: a standard means for coordinating an activity between two or more entities • Communications protocol: a means for coordinating activity between two or more communicating computers – The communication protocol is broken into levels of layers – Two machines must agree upon and follow the protocol for exchanging the message TCP/IP-ISO Architecture - I • International Organization for Standardization (ISO): Reference Model for Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) • Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF): Transmission Control Program/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) • TCP/IP-ISO architecture: five layers TCP/IP-ISO Architecture - II • Layer 5 (Application): communication rules between two applications – Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) for email – Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) for processing Web page (sites and users) – File Transfer Protocol (FTP) for copying file between computers TCP/IP-ISO Architecture - III • Layer 4 (Transport): communication rules between two host computers – Transmission Control Program (TCP) – Sending functions: break data into segments, add To and From address, and – Receiving functions: provide reliability by sending acknowledgement, and translate the format, assemble segments into data TCP/IP-ISO Architecture - IV • Layer 3 (Internet): communication rules of routing packets across the Internet – Internet Protocol (IP) – Functions: package each segment into a packet, place IP data in in the packet, add To/From data TCP/IP-ISO Architecture - V • Layer 2 (Data Link): communication rule for transmitting data within a single network – Functions: package packets into frames • Layer 1 (Physical): communication rule between adjacent device connected by a transmission medium Terminology • Architecture: an arrangement of protocol layers with their associated tasks • Protocol: set of rule to accomplish the tasks • Program: software implementing the protocol • Web: sub set of Internet with users and sites to process protocol • Internet: communication structure • Browser: a program implementing the HTTP of the TCP/IP-OSI architecture (Netscape and Microsoft Internet Explorer) TCP/IP-OSI Application Example Network Types • LAN: local area network • WAN: wide area network LAN - I • A group of computers connected together on a single company site and operated by the company • Equipments – Network interface card (NIC) or onboard NIC: an unique identifier named MAC (media access control) address – Unshielded twisted pair (UTP) cable with RJ45 connecter – Optical fiber cable with ST and SC connectors LAN - II • IEEE (Institute for Electrical and Electronics Engineers) • Protocol: IEEE 802.3 or Ethernet – Hardware characteristics (which wire carries which signals) – Package and process message over LAN – Operate on Layer 1 and 2 • 10/100/1000 Ethernet (Mbps) • Bits for communications speeds and bytes for memory sizes Local Area Network NIC Interface Card Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) Cable Optical Fiber Cable LAN - III • Wireless LAN – Wireless NIC (WNIC) – IEEE 802.11g protocol to connect to an access point (AP) and IEEE 802.3 Wireless Access Standards Wireless LAN WAN • Connects computers located at physically separated sites • Internet service provider (ISP) – Provide customer a legitimate Internet address. – Serve as the gateway to the Internet – Communicate between sending computer and Internet • Connecting computer and ISP – Telephone line – DSL (digital subscriber line) – Cable TV line WAN - Equipment • Modem – Convert data between digital and analog – Narrowband with speed less than 56 kbps and Broadband with speed over 256 kbps • Modem types – Dial-Up modem • Narrowband • Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) – DSL modem • Permanent connection and one more line for telephone conversation • Asymmetric digital subscriber line (ADSL) for home and small business with slow upload speed with 256 kbps and faster download speed ranging from 256 to 768 kbps • Symmetric digital subscriber line (SDSL) for advanced users and larger business with 1.544 Mbps performance level guarantees – Cable modem • Permanent connection and one more line for TV • 10 Mbps download speed and 256 kbps upload speed Analog vs. Digital Signals Personal Computer (PC) Internet Access WAN - Equipment • Access devices – Switch (Layer 2) – Router (Layer 3) • Lease lines from telecommunication company – T1 line with 1.544 Mbps speed – T3 line with 44.763 Mbps speed – Optical fiber cable-768 with 40 Gbps – Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) Transmission Line Types, Uses, and Speeds WAN – Public Switched Data Network • Public switched data network (PSDN) • Developed and maintained by a vendor for selling time to other company • Shown as a cloud in the map or diagram • User must have a leased line connecting to PSDN as point of presence (POP) • PSDN types – Frame Relay with 56 kbps to 40 Mbps: slower and cost less but simple and easy to support – Asynchronous transfer mode (ATM) with 1 to 156 Mbps: faster and cost more but transmitting data and voice – Ethernet with 10 to 40 Gpbs Wide Area Network Using PSDN WAN – Virtual Private Network • Virtual private network (VPN): a private internet as a private point-to-point connection • Tunnel: a virtual, private pathway over a public or shared network from the VPN client to the VPN server • Encrypted message • Remote access Remote Access Using VPN Wide Area Network Using VPN Network Comparison • Setup costs – – • Operational costs – – – – • Lease fees for line and equipment ISP charges Training Maintenance: problem diagnosis, repair, and updating Performance – – – – – – • • • • • Equipment: lines, switches, routers, and access devices Labor Speed: line and equipment Latency: transmission delay due to congestion Availability: service outages Loss rate: transmission problem Transparency Performance guarantee: availability, error rate, speed, etc. Growth potential Contract commitment period Management time Financial risk Technical risk Summary of LAN and WAN Networks Internet • Network address – Physical or MAC address in Layer 2 program: permanent and unique – Logical or IP address in Layers 3, 4, and 5: not permanent, such as 192.168.2.28 – Public IP address used on the Internet to major institutions in blocks assigned by Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN) – Private IP address used within private networks and internets • DHCP server has Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) to assign a temporary IP address for accessing the Internet • Network Address Translation (NAT): The process of changing public IP addresses into private IP addresses, and the reverse Domain Name System • Convert user-friendly name into their IP address • domain name: any registered, valid name with ICANN • resolving the domain name: the process of changing a name into its IP address – ICANN has 13 computer as root servers for maintaining a list of IP addresses of servers to resolve each type of TLD in the world • Top-level domain (TLD) – Non-U.S. is the two letter abbreviation for the country – U.S. is the type of organization • Uniform resource locator (URL): document’s address on the Web • Domain name resolvers store the correspondence of domain names and IP address IP Addressing Schemes • IPv4 and • IPv4 – 32 bits divided into four groups of 8 bits, and a decimal number represents each group – 63.224.57.59 – The largest decimal number between the period is 255 (0 – 255) • IPv6 – 128 bits due to the growth of the Internet – Currently both IPv4 and IPv6 are used on the Internet Security • Encryption algorithms: DES, 3DES, AES • Key – Symmetric encryption – Asymmetric encryption: public key and private key • HTTPS – Secure Socket Layer (SSL) and Transport Layer Security (TLS) – Public key, private key and symmetric encryption Summary • TCP/IP-OSI five layers – – – – – Application layer Transport layer Internet layer Data link layer Physical layer • Public switched data network (PSDN) • Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) to assign a temporary IP address for accessing the Internet • Domain name Discussion • Problem solving (121a-b) – What are the new opportunities for the business generated by the Internet? – What are the new threats for the business generated by the Internet? • Opposing forces (129a-b) – State your opinions related to the negative impact on the society when everyone is connect through the Internet. • Security (133a-b) – State the impacts on the society and business from the government having an decryption method to decode everything over the Internet. • Ethics (141a-b) – State the impacts from the employee’s private usage of company’s computer facility. • Reflections (143a-b) – How should you react properly from not getting lost from this Internet age? Case Study • Case 5-1 (148-149) Network Services: questions 1, 3, 4, 5, 6, 9, and 10 Points to Remember • • • • Network Concepts Communication Protocol TCP/IP-OSI Architecture Network Types – – – – • • • • • • LAN WAN Public Switched Data Network Virtual Private Network Network Comparison Internet Domain Name System IP Addressing Schemes Security Discussion and Case Study